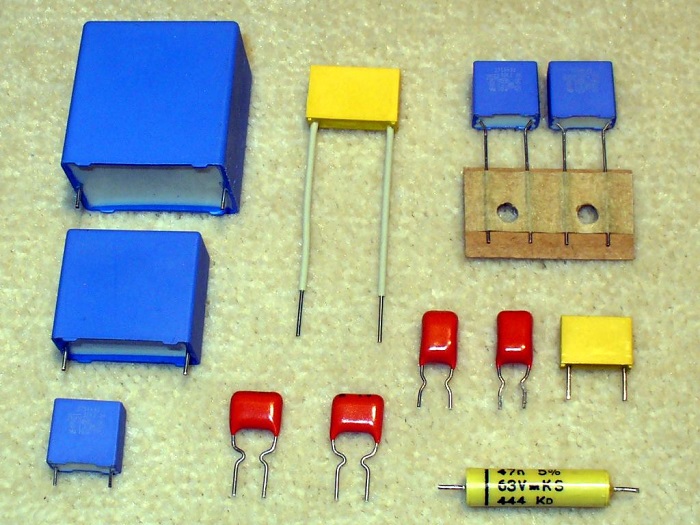
A film capacitor falls within the category of non-polarized capacitors that is widely used due to its flexibility and inexpensive cost. As a result, this type of capacitor is favored in power applications and AC signals. Continue reading the new blog post in Linquip to learn more about the film capacitor, including what it is, how it works, what its characteristics are, and where it is used.
Brief History of Film Capacitors
Paper capacitors were employed in decoupling circuits before the introduction of the film capacitor. They were made from impregnated paper that was wrapped around metal strips and curled into cylindrical forms. However, because these capacitors used paper as a dielectric, they were not only susceptible to environmental flaws but also rather large in size.
As a result, scientists began looking for a remedy that would mitigate these issues. It was a time when the plastics industry was thriving, and scientists found how the use of certain plastic films as dielectrics provided long-term stability in terms of electrical characteristics. It also helped to reduce the size by replacing multilayers of paper with only a few sheets of plastic. As technology improved, the size of these capacitors shrank as thinner polymers with great durability became available.
What is a film capacitor?
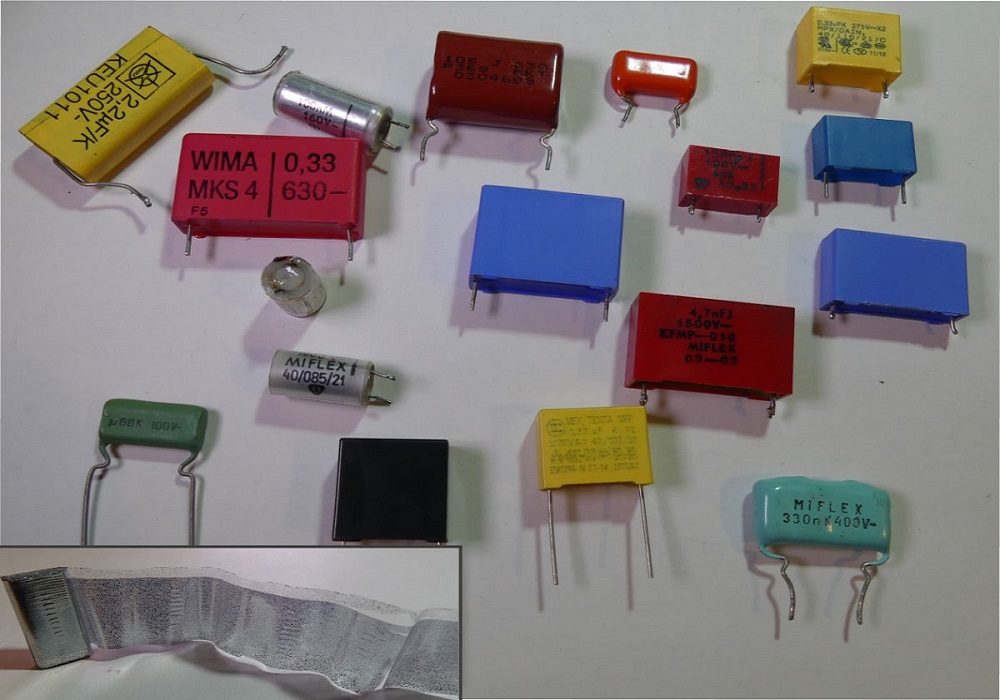
One of the most common and extensively used capacitors is the film capacitor. A film capacitor is defined as a capacitor that employs a thin plastic film as a dielectric. It is used in electrical and electronic equipment. This type of capacitor has some other names including, plastic film capacitor, polymer film capacitor, or film dielectric capacitor. It is also known as a film cap and power film capacitor.
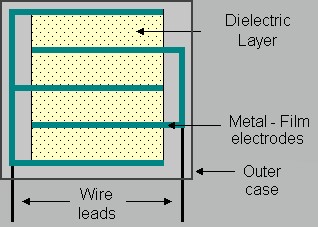
The dielectric characteristics of the film capacitor are different. The dielectric used in this sort of capacitor can be any form of film. There is a ‘direct electrical connection’ establishment with the electrodes that are present on both windings in the modern form of film capacitor. This reduces the current’s route to the electrode to a minimum.
Film capacitor is relatively simple to analyze and build. It is well-known for its dependability. This sort of capacitor is inexpensive to produce. The use of this capacitor reduces losses even on transmissions with high frequencies. Its structure is made of “Plastic Films.” These films are made to be very thin. Once the “Film drawing procedure” is done, the created film can be coated with a metal or left as is, depending on the use.
This capacitor offers numerous advantages, including nearly infinite shelf life, the ability to withstand power surges without damage, and a low self-inductance. The capacitor also has the advantage of a very low ESR (ohmic resistance) and ESL (Parasitic Inductance). This is preferable in a variety of AC applications. It is also utilized even in applications requiring high frequencies.
Characteristics
A film capacitor is extensively used in different applications due to its superior characteristics:
- Because this capacitor is not polarized, it is appropriate for AC signal and power applications.
- This capacitor can be designed with extremely high accuracy capacitance values to maintain the value longer than other types of capacitors. As a result, the aging process is typically slower than in other capacitor types. So, a film capacitor has a long shelf life and service life, as well as a very low average failure rate.
- Film capacitor may be manufactured with very high precision capacitance values and keeps that value for a longer period than other capacitor kinds.
- It can tolerate voltages in the kilovolt range and provide extremely strong surge current bursts.
How a Film Capacitor is Constructed? And What are the Properties?
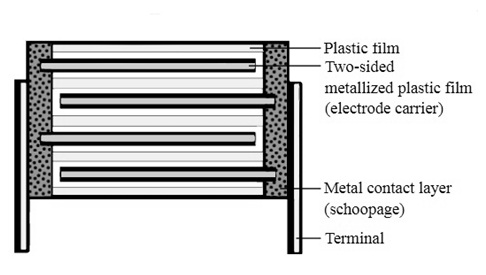
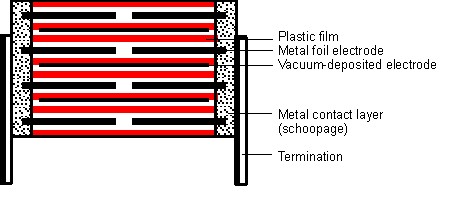
Using a sophisticated film drawing technique, this film is created incredibly thin. The film is sliced into ribbons once it has been pulled to the required thickness. The width of the ribbons is determined by the capacity of the capacitor being manufactured. Two film ribbons are wrapped together to form a roll, which is frequently flattened into an oval shape to fit inside a rectangular casing.
This is significant because rectangular components conserve valuable printed circuit board areas. Depending on the required characteristics of the capacitor, the film may be metalized or left untreated after fabrication. After that, electrodes are attached, and the assembly is placed in a casing to protect it from environmental influences. Using the self-healing characteristic of film capacitors, a voltage is provided to burn away any flaws. After that, the casing is sealed with silicon oil to preserve the film roll from moisture and dipped in plastic to hermetically seal the inside.
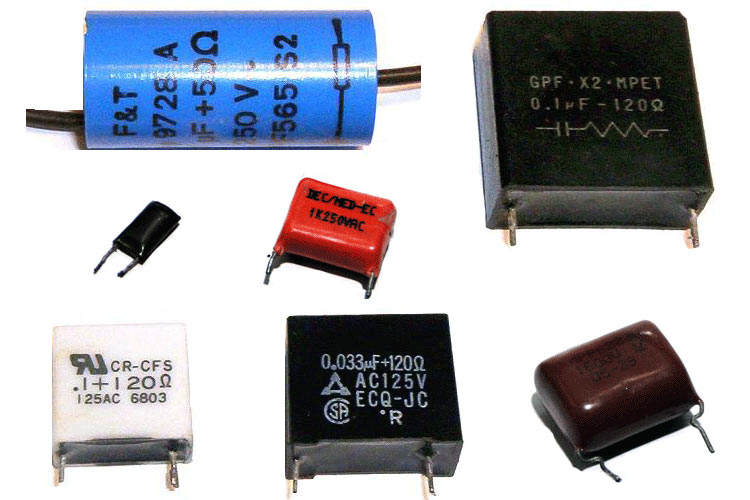
Film capacitor comes in a variety of materials, including polyester film, metalized film, polypropylene film, PTFE film, and polystyrene film.
Capacitances of the film capacitor range from less than 1nF to 30F. It is available in voltage ranges ranging from 50V to more than 2kV. It can be designed to be used in high-vibration automobile settings, high-temperature situations, and high-power applications. Film capacitor has low losses and high efficiency.
How does a Film Capacitor Work?
The film Capacitor operates on the same concept as a “General Purpose Capacitor”:
It holds the electric charge as well as the electric energy on the electrode. It is typically used in conjunction with an inductor to produce the LC oscillating circuit. The capacitor’s operating principle is that the electric charge will travel under the electric field when the conductor has a medium between them. Having a medium between them inhibits the flow of charge and causes the charge to collect on the conductor, resulting in charge accumulation.
Applications for a Film Capacitor
Because of the features like stability, cheap cost, and low inductance, film capacitor is utilized in a variety of applications, including:
Film capacitor is widely employed in circuits for high-frequency filtering, high-frequency bypass, and first or second-order filtering. Electronics, household appliances, telecommunications, electric power, electrified trains, hybrid cars, wind power, solar power, and many more sectors make extensive use of it.
As previously stated, the film capacitor has lower ESR and ESL values and a lower distortion factor. In addition, in terms of the aging time, the film capacitor tends to resist the wearing-out stage for the longest period. As a result, it is a superior option for high-voltage and high-frequency applications.
Film capacitors can also be employed in more traditional applications such as voltage smoothing capacitors, filters, and audio crossovers. It can be used to store energy and then release it in the form of a high-current pulse when required.
Summary
This article aimed at comprehending the definition, construction, working process, and applications of one of the most popular types of capacitors known as the film capacitor. Please keep in mind that the film capacitor is known by several different names, as mentioned in the article. Need to find out more? Register in Linquip and then comment your questions. Our experts will enthusiastically answer you.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- What is a Non-Polarized Capacitor? Types & Function
- Difference between Capacitor and Inductor- Capacitor vs. Inductor
- What is a Paper Capacitor?
- What is Paper Capacitor Used for?
- What is Mica Capacitor Used for?
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor? Usage & Application
- What is Capacitor and How Does it Work?
- 7 Types of Capacitors and Their Uses
- What is Ceramic Capacitor Used for?
- What are Mica Capacitors? Comprehensive Overview
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor?
- What is Film Capacitor? Different Types & Working
- What is Ceramic Capacitor? A Basic Description
- Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a nutshell 2022
- Types of Capacitors: All You Need to Know