If you’re an industrial businessman or if you have encountered industrial equipment in any way, you have probably heard of condensers and evaporators before. These devices are near you, and you use them and touch them every day without even realizing it! But what are they? How do they function? Which devices can they be found in? And most importantly, what are the differences between condenser and evaporator?
To understand these useful devices and their differences, we’ll have to explore further into their universe and dig up their mysteries. Having this knowledge can be extremely vital to those who work in the industrial business, as they are common components of industrial equipment. So keep on reading and don’t miss out on anything, as we discover the difference between Condenser and Evaporator with Linquip.
Is there any Difference Between Condenser and Evaporator?
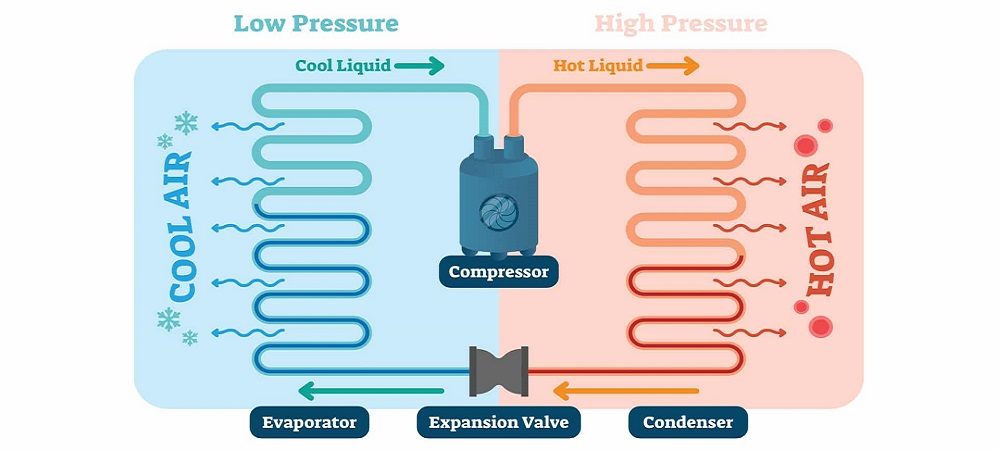
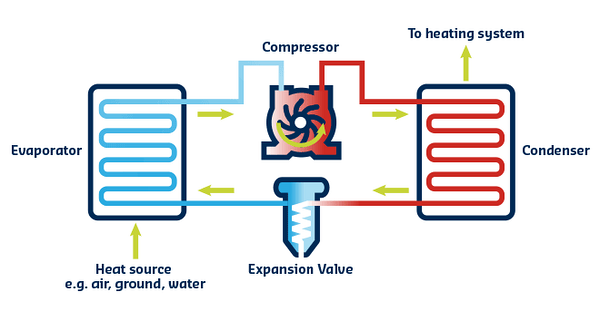
The difference between Condenser and Evaporator can be studied in many aspects. For starters, even though evaporators and condensers both have the characteristics to be considered heat exchange equipment, the evaporator absorbs heat, while the condenser releases heat. With that said, they are both essential parts of the refrigeration system. But it doesn’t end here!
Evaporators and condensers have different working mechanisms. While evaporators are the vaporization and heat absorption of the medium, condensers liquefy it and remove the heat and release it into the surrounding environment. Evaporators, on the other hand, absorb the external heat and change the refrigerant’s state from gas to fluid. During the exothermic process of condensation, usually, the interior pressure is quite high. Meanwhile, the change of substance state from liquid to gas in evaporators is the endothermic process of evaporation, and the interior pressure is commonly low.
The Condenser in a nutshell
One of the components of the refrigeration system is the condenser. Condensers are considered to be a kind of heat exchanger. Their purpose is to convert the substance from a gas state into a liquid state and by doing so, they surrender the heat in the pipe to the surrounding air around it swiftly and rapidly.
The Working mechanism of condensers is an exothermic process, so you can expect a high temperature of condensers while they’re working. An excellent example of condensers in the industry is power plants. Power plants have multiple condensers and assign the task of condensing the vapors from the turbines to them. Refrigeration systems are also a go-to example while studying condensers. Condensers in the freezer have the job of condensing refrigeration vapors like Freon and Ammonia.
Condensers can also be found in the petrochemical industry. Here they’re employed to condense various chemical vapors such as hydrocarbons during the distillation process. Another situation in which the term “condenser” is used is while referring to the means for converting the vapor substance into a liquid state. In general, all condensers fulfill the process of absorbing the heat of vapor or gas.
Understanding Condensers
One of the basic heat exchange devices in the refrigeration system is the condenser. It functions as a cooling apparatus and does so by taking the superheated steam disposed of the chiller and condensing it into a refrigerant liquid while emitting heat to the cooling system. Air and water are generally the used cooling media. Condensers are components that release heat.
Their main process is taking the high-pressure and high-temperature gas refrigerant that is compressed by the compressor and transforming it into a high-pressure and low-temperature fluid. During this process, heat conversion is attained as heat bursts out to the external surroundings and gets sucked and disposed of by the evaporator. Based on their structure they can be categorized into the following groups:
- shell-and-tube type
- casing type
- plate type
- watering type
The Evaporator in a nutshell
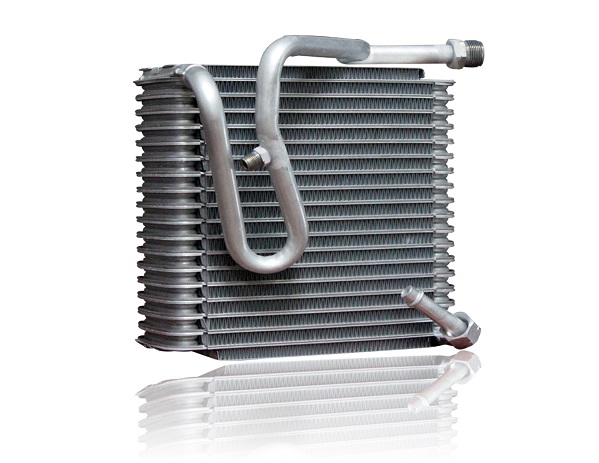
While considering the difference between Condenser and Evaporator, you might see similarities that can surprise you, nevertheless, the differences are vivid and visible. Evaporators are one of the most important devices in the four major sections of refrigeration. During the process inside an Evaporator, the low-temperature condensed liquid moves through the evaporator. Here the liquid exchanges heat with the external air and evaporate and absorbs the heat. This will attain the desired cooling result in the refrigeration system.
Generally, evaporators are composed of an evaporation chamber and a heating chamber. The heating chamber must supply the liquid and the necessary heat to evaporate. In this section, the liquid boils and evaporates. The evaporation chamber is there to separate the two phases of gas-liquid. You can find an example of this in the Ford Focus Auto AC Evaporator, which functions like this process.
Understanding Evaporators
Evaporators are also one of the main heat exchange apparatuses in a refrigeration system. An Evaporator is an instrument that exchanges heat in a refrigeration arrangement between a low-temperature source of heat and a refrigerant. Evaporators vaporize the refrigerant fluid and absorb the heat at a low temperature and a low pressure. During this process, at low pressure and a low temperature, the refrigerant liquid turns into overheated steam or a refrigerant dry saturated vapor. This process generates and releases a cooling balance through the refrigeration device.
If you wish to locate the evaporator in a refrigerator, you can look for it in a cold spot or room, in which freezing or cooling is necessary. Evaporators can usually be found between the return air pipes of the vapor-liquid separation device and the liquid source or between the refrigerator’s return air header and the throttle valve.
Evaporators are heat-absorbing devices that have the purpose of refrigeration. They achieve this goal by converting the liquid low-temperature refrigerant into steam and absorbing the heat of the cooling medium. This purpose is achievable as the said liquid is volatile in low-pressure situations.
Based on their structure they can be categorized into the following groups and other different types:
- box type
- tube type
- plate type
More questions about the Difference Between Condenser and Evaporator?!
If you’ve read this article this far, that means now you can recognize condensers, evaporators, and their differences. But there is no end to learning and knowledge is the key to growth and prosperity in the industrial business. So make sure to read our other content. If you have any other questions, just sign up on our website and submit your questions. Are there any other differences that we didn’t mention? Please tell us more in the comments below about the difference between Condenser and Evaporator for other Linquip readers to know.
Read More In Linquip
- Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a Nutshell 2022
- Difference Between Heat Exchanger and Condenser: A thorough guide 2022
- Steam Condenser: Basics, Parts, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Water-cooled condenser types: A go-to guide to choosing the right one
- Why vacuum is maintained in condenser: an easy-to-understand guide
- Evaporative condenser: An easy-to-understand guide
- Condenser water system: An overview of its components and more!
- What Is a Condenser; Parts, Functions and types
- An Applicable Introduction to different types of Condensers
- Water-cooled condensers: facts that will blow your mind!
- 16 Parts of Heat Pump and Functions (Clear Guide)
- 3 Types of Heat Pump + Working Principle ( Clear Guide)
- 5 Best Electric Boilers of 2022: A Practical Guide
- Heat Exchanger vs. Chiller: Which One is the Best for You?