Different Types of Power Plants – Modern existence is dependent on electricity. Electricity now powers everything from watches to automobiles. The dynamics of how and where power plants function are continuously changing as a number of nations continue to switch from highly polluting fossil fuels to low-carbon alternatives. The world has many distinct kinds of power plants that cooperate to meet the rising demand for electricity. In this post, we’ll learn in-depth information on how these power plants operate.
On Linquip website, among the many options available to you, you will find all the information you need to know about Power Plants, as well as information regarding this marketplace. You can count on Linquip to provide you with as much general and reliable information about this topic, whether you’re a professional or a customer looking for a proper company. We recommend you review a list of all Industry Directories available in Linquip.
We would be delighted to provide you with more information on how we can help you generate revenue within your industry. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions! With Linquip’s Solutions for Each Company Level, you will be able to upgrade the capabilities of your organization in order to gain a competitive edge by taking advantage of a wide range of options to enhance your organization’s performance. If you are looking for the simplest or the most sophisticated marketing and advertising package for your business, we can help you ensure that your company gets as many customers as possible to grow your business.
What is the Power Plant?
An assembly of systems or subsystems that work together to produce energy or power that meets economic needs makes up a power plant. The power plant itself needs to benefit society economically and ecologically.
A power plant, which is the location where power is produced from a certain source, is where electricity or energy is produced.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only move from one form to another, hence the word “generated” in the previous phrase is a misnomer.
In actuality, a power plant is a location where another kind of energy is transformed into electrical energy, depending on the kind of power plant being evaluated and the type of energy that is transformed.

These are often found in sub-urban areas at a distance of several kilometers from cities or load centers because of their requirements, which include high demand for land and water as well as a number of operational restrictions, such as waste disposal.
Because of this, a power-producing station must be concerned with both the efficient generation of power and its transmission. Transformer switchyards frequently accompany power plants because of this. These switchyards raise the power’s transmission voltage, which improves the efficiency of its long-distance transmission.
The fuel type is the primary determinant of the energy source that is utilized to turn the generator shaft. The power plant is defined by the fuel used, and the many types of power plants are categorized in this way.
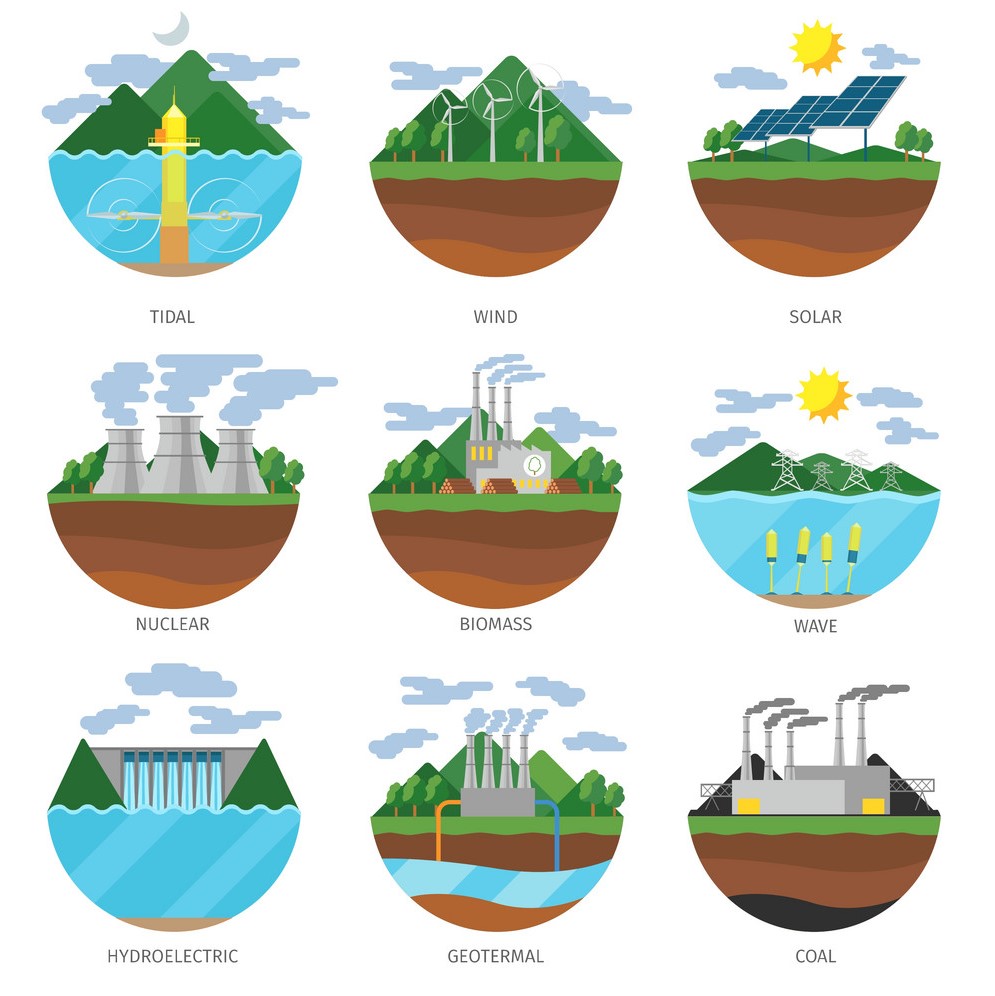
Different Types of Power Plants
9 Types of Power Plants include:
- Nuclear Power Plant
- Hydroelectric Power Plants
- Thermal Power Plants
- Green Energy Power Plants
- Geothermal Power Plants
- Solar Power Plants
- Wind Power Plants
- Tidal Power Plants
- Biomass Power Plants
Different types of power plants are categorized depending on the type of fuel utilized. The most effective energy sources for bulk power generation include thermal, nuclear, hydropower, and renewable sources. The three types of electricity producing stations stated above can be broadly categorized. Let’s take a closer look at various kinds of power plants.
Nuclear Power Plant
The list of power plants that can generate enormous quantities of energy also includes nuclear power plants at the top. Nuclear energy is transformed into electricity at a nuclear power station.
Water is turned into steam using the nuclear reactor’s heat. The turbines are then linked to a generator and powered by the pressured steam.
Unlike coal or natural gas power plants, a nuclear power plant doesn’t need to burn anything to generate heat. Nuclear fission powers the entire process.
Nuclear power plant is filled with pellets of low-enriched uranium. Nuclear fission is then produced when the uranium atom splits. Significant energy is released during this process.
A nuclear power plant has the benefit of not needing to burn anything in order to produce electricity. As a result, nuclear power plants emit extremely little carbon.
The production of radioactive waste and the high expense of establishing a nuclear power plant are its drawbacks. Approximately 10% of the world’s energy demands are met by nuclear power.
The Kashiwazaki-Kariwa power station in Japan is the biggest nuclear power plant in the world. Using seven boiling water reactors, it is able to produce 7,965MW of electricity.

Hydroelectric Power Plants
Among all power facilities, hydroelectric ones are among the most efficient and environmentally friendly. Water is the source of electricity in a hydroelectric power plant.
In more detail, water’s potential energy is changed into electrical energy. The armature, which is attached to a generator, spins when water is forced to fall from a height onto a turbine.
The generator begins to generate power as soon as the turbine turns. Then, in order to distribute the power, this electricity is sent to all of the various substations.
The Three Gorges Dam, a hydroelectric power plant, is the biggest power plant in the world. Amazingly, the dam generates 22,500MW of power.
This accomplishment is accomplished with 34 power generators. The dam is so enormous that once it was built, it alone delayed the earth’s rotation.
One benefit of a hydroelectric power plant is that no waste is produced during the energy production process.

Thermal Power Plants
The most traditional and relatively efficient way to produce electricity is through a thermal power station or coal-fired thermal power plant. To boil the water needed to create the superheated steam that powers the steam turbine, coal is used as the main fuel.
The alternator rotor, whose rotation produces electricity, is then physically connected to the steam turbine. Commonly used as boiler fuel in India, bituminous coal or brown coal has an ash level of 5 to 16% and volatile content of 8 to 33%. The pulverized coal is utilized in the boiler to increase the plant’s thermal efficiency.
In a coal-fired thermal power plant, pulverized coal is burned to produce steam under extremely high pressure within the steam boiler. After that, this steam is extremely heated in the superheater. The pressure of the steam is then permitted to enter the turbine, rotating the turbine blades as it does so.
The alternator and turbine are mechanically connected so that the alternator’s rotor will turn with the turbine blades. After entering the turbine, the steam pressure quickly decreases, increasing the amount of steam in a similar manner.
The steam is produced to exit the turbine blades and enter the steam condenser after being given the energy to turn the turbine rotors. The low-pressure moist steam condenses in the condenser as a result of the pump’s circulation of cold water at room temperature.
The condensed water is then sent to a low-pressure water heater, where low-pressure steam raises the temperature of the input water before it receives another high-pressure heat source. This describes the fundamental operating procedures of a thermal power plant.

Green Energy Power Plants
We now have more energy-producing options than merely thermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric power plants because of technological breakthroughs. These are referred to as non-traditional power plants.
These power plants can produce clean energy (or Green Energy). Find out more about them by reading this!
Geothermal Power Plants
Flash steam power stations, dry steam power stations, and binary cycle power stations are the three primary categories of geothermal plants, and they are all powered by steam turbines to generate electricity.
Over the past ten years, geothermal energy installed capacity has steadily expanded worldwide, rising from less than 10 GW in 2010 to about 14 GW in 2019.
Compared to coal-fired power plants, geothermal power plants are said to be more ecologically benign and generate less hazardous emissions.

Solar Power Plants
Solar energy plants use one of the cleanest and most plentiful renewable energy sources—the sun—to transform solar energy into thermal or electrical energy.
They often endure for 20 to 25 years and don’t need a lot of upkeep.
Between 2018 and 2050, the capacity of the world’s solar power plants will rise from 480 GW to more than 8,000 GW, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
But financing solar power plants comes with hefty upfront expenses, and the installation takes up a lot of room.
Solar thermal technology is a related approach. It is a system of enormous mirrors strategically positioned to focus the sun’s rays on a relatively tiny area to generate a substantial amount of heat, producing steam to drive an electrical generator.

Wind Power Plants
The number of wind farms has increased quickly in recent years, thanks to technological breakthroughs all around the world.
According to the IRENA, the installed wind production capacity worldwide has expanded by a factor of over 75 during the previous 20 years, rising from 7.5 GW in 1997 to 564 GW by 2018.
Wind power facilities are often seen as being very cost-effective since when the wind turbines are constructed, operational expenses associated with maintaining them are minimal.
Wind farms may also be built on sites used for agriculture without hindering farming operations.
But because certain wind turbines need to be examined often and because wind power projects generally demand significant upfront costs, the maintenance of wind turbines may vary.

Tidal Power Plants
In contrast to wind and solar power, the generation of tidal energy is thought to be more predictable. Tidal energy is produced by turning energy from the strong tides into power.
But despite the fact that the first sizable plant of its kind in the world went into service in 1966, tidal power is still not commonly employed.
The development of innovative techniques to harness tidal energy is anticipated to accelerate as the focus on producing electricity from renewable sources increases.
Although tidal power research is still in its infancy, it has the potential to increase considerably over the next several years.

Biomass Power Plants
A renewable and sustainable energy source used to produce electricity or other types of power, biomass is a fuel made from organic materials. This type of bioenergy exists. Using bio based feedstocks can help rural companies become more resilient by generating income from their waste streams and helping the environment by displacing fossil fuels and sequestering carbon.
In biomass power plants, wood or other waste is burnt to create steam that powers a turbine and turns it into electricity or heats buildings and businesses. Fortunately, new technologies have developed to the point that any emissions from burning biomass in industrial facilities are lower than emissions created while utilizing fossil fuels. These technologies include pollution controls and combustion engineering (coal, natural gas, oil).

PDF for Different Types of Power Plants
If you are interested to have this article in PDF format, you can download it from here.
Conclusion
The need for energy has increased steadily over the world over the years. There is currently no indication that this tendency will slow down any time soon. The yearly increase in pollution levels demonstrates our worrying rate of fossil fuel usage.
What we can do is switch from carbon-intensive energy sources like fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. To make this goal a reality, several organizations and nations have invested a great deal of energy.
We may anticipate more green energy power plants rather than CO2 industries in the upcoming years.
FAQs about Different Types of Power Plants
1. What Is The Most Efficient Power Plant Type?
The oldest and most popular renewable energy source, hydro turbines, have the most efficient power conversion methods.
2. What Type Of Power Plants Provide The Most Of Our Electricity?
In 2021, natural gas accounted for around 38% of the country’s electrical production. Gas and steam turbines both use natural gas to produce power. In 2021, coal accounted for around 22% of the energy used to generate power in the United States. Steam turbines are used in nearly all coal-fired power facilities.
3. What Is The Safest Type Of Power Plant?
The safest type of energy is nuclear energy. More than 330 times fewer people die from it than from coal, 250 times fewer than from oil, and 38 times fewer than from gas.
4. What Is The Most Harmful Power Plant?
The most lethal energy sources are coal and hydroelectric: According to estimates published by Business Insider, coal power plants cause between 2.8 and 32.7 fatalities every 10 kilowatt-hours. Nuclear power was regarded as the least lethal kind of energy, with hydroelectric power causing 1.0 to 1.6 fatalities per 10 kilowatt-hours.
5. Which Power Plant Is Least Reliable?
Wind energy is the least reliable source of energy, but it still makes a lot of electricity.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- Nuclear Power Plant Diagram: A Complete Guide
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram: All You Need to Know About It
- What is a Power Plant? (Clear Guide)
- How Does a Power Plant Work? (Step-by-Step Guide)
- What is Combined Cycle Power Plant? + Efficiency & PDF
- What is Distributed Generation? (Clear Guide) + PDF
- What is CHP? (Combined Heat and Power) + Types & Working Principle
- Combined Cycle Power Plant: Efficiency & Working Principles + PDF
- More Informtion about Power Plant System
- More Details about Power Plant Generator
- More Details about Thermal Power Plant Generators
- Read More Information about Steam Power Plant Generators
- More Information about Nuclear Power Plant Generators
- Read More Information about Hydro Power Plant Generators
- See List of Siemens Generators Products