Every single thing in the world has something to do with wavelengths of light. When light reaches an object, every substance will transmit and absorb light slightly differently. Knowing exactly how much wavelength gets absorbed allows us to identify and quantify different materials. As you can guess we are going to have a look at a device that works with absorption and wavelength named spectrophotometer. Before the spectrophotometer was developed, scientists had no reliable and rapid method to determine the chemical make-up of a substance.
The spectrophotometer radically changed all of that. You can imagine the importance of spectrophotometry and how useful it could be to know what is in a substance. In this article, we will learn what is a spectrophotometer, how it works, and why it is useful in science. Read this new blog in Linquip to find out more about it.
What Is a Spectrophotometer?
A spectrophotometer is an analytical instrument that finds use to quantitatively measure the transmission or reflection of visible light, UV light, or infrared light. Spectrophotometers measure the intensity of electromagnetic energy in a specified region as a function of light source wavelength. By measuring the intensity at each wavelength, a spectrum is created and this can tell us much information about the sample through which the light passed. Important features to look for in a spectrophotometer are broad dynamic range, sample volume capability and lamp type, and lifetime.
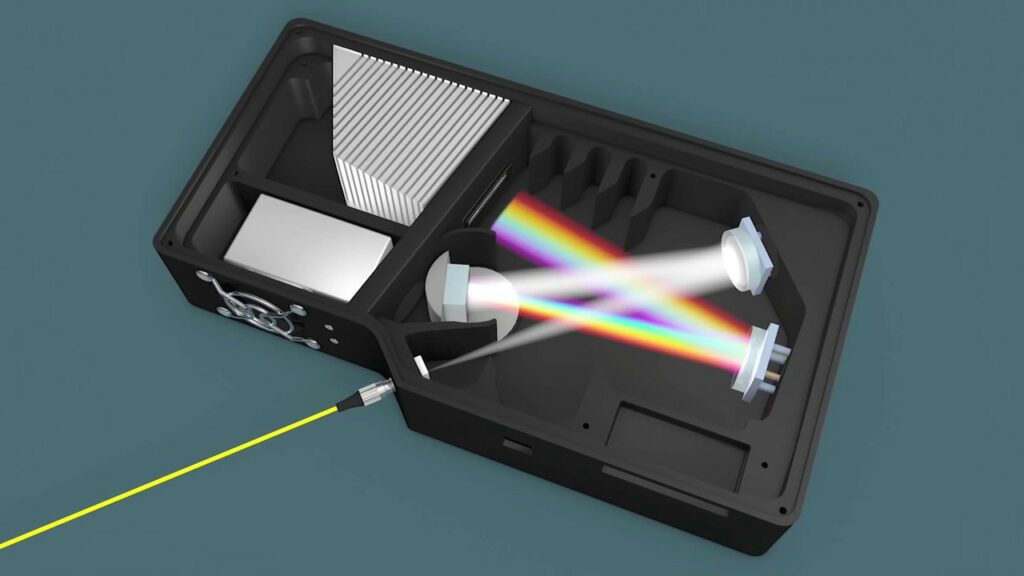
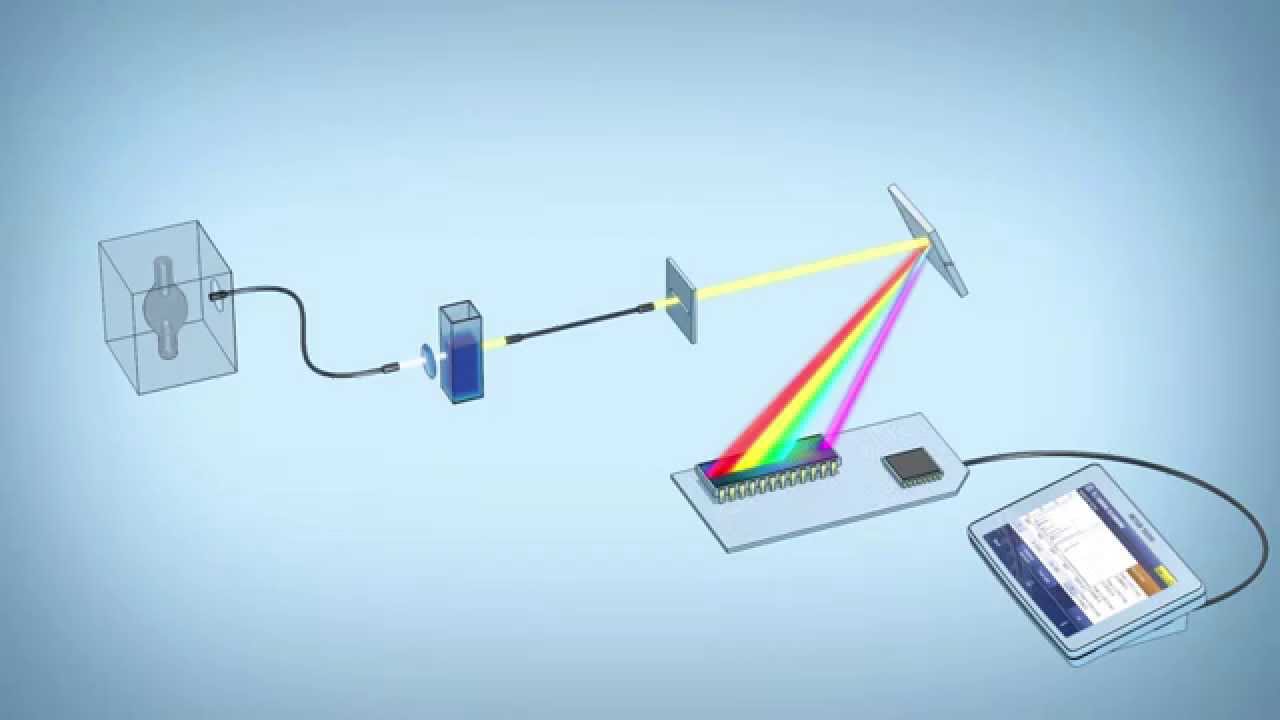
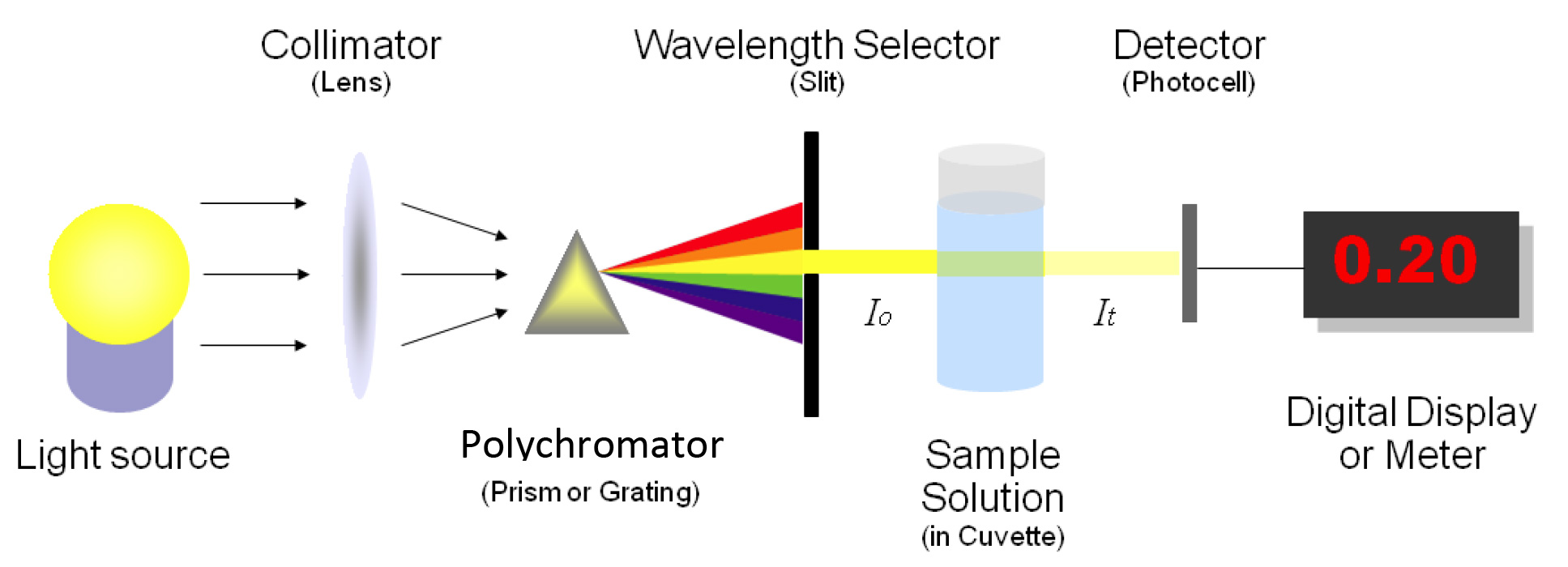
A spectrophotometer, in general, consists of two devices; a spectrometer and a photometer. A spectrometer is a device that produces, typically disperses, and measures light. A photometer indicates the photoelectric detector that measures the intensity of light.
- Spectrometer: It produces the desired range of wavelengths of light. First, a collimator (lens) transmits a straight beam of light (photons) that passes through a monochromator to split it into several component wavelengths (spectrum). Then a wavelength selector transmits only the desired wavelengths.
- Photometer: After the desired range of wavelength of light passes through the solution of a sample in a cuvette, the photometer detects the number of photons that is absorbed and then sends a signal to a galvanometer or a digital display.
Instrumentation of Spectrophotometer
The essential components of spectrophotometer instrumentation include:
- A table and cheap radiant energy source
Materials that can be excited to high energy states by a high voltage electric discharge or by electrical heating serve as excellent radiant energy sources.
- A monochromator
It finds use to break polychromatic radiation into component wavelengths or bands of wavelengths. A monochromator resolves polychromatic radiation into its wavelengths and isolates these wavelengths into very narrow bands. Gratings are often used in the monochromators of spectrophotometers operating in ultraviolet, visible, and infrared regions. A prism disperses polychromatic light from the source into its constituent wavelengths by virtue of its ability to reflect different wavelengths to a different extents.
- Transport vessels (cuvettes) to hold the sample
- A Photosensitive detector and an associated readout system
Most detectors depend on the photoelectric effect. The current is then proportional to the light intensity and therefore a measure of it. Radiation detectors generate electronic signals which are proportional to the transmitter light.
Working Principle of Spectrophotometer
The basic spectrophotometer working principle is that each compound absorbs or transmits light over a certain range of wavelengths. This measurement can also be used to measure the amount of a known chemical substance. The spectrophotometer technique is to measure light intensity as a function of wavelength. It does this by diffracting the light beam into a spectrum of wavelengths, detecting the intensities with a charge-coupled device, and displaying the results as a graph on the detector and then on the display device.
- In the spectrophotometer, a prism or grating is used to split the incident beam into different wavelengths.
- By suitable mechanisms, waves of specific wavelengths can be manipulated to fall on the test solution. The range of the wavelengths of the incident light can be as low as 1 to 2nm.
- The spectrophotometer is useful for measuring the absorption spectrum of a compound, that is, the absorption of light by a solution at each wavelength.
Function of Spectrophotometer
Now that we know what a spectrophotometer is and what its different parts are, let us overview the spectrophotometer function, and this helpful device. Spectrophotometers measure reflected or transmitted light across the spectrum and analyze light in terms of the amount of energy present at each spectral wavelength. They create a visual curve that describes the color on that substrate, under that lighting condition. The emittance curves for light sources are typical spectrophotometer results, as is the reflectance curve of the paint pigment known as emerald green.
Applications of Spectrophotometer
Any application that deals with chemical substances or materials can use this technique. An example of the application of spectrophotometry in biochemistry is to determine enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Spectrophotometers are widely used in various disciplines such as physics, molecular biology, chemistry, and biochemistry. Applications for specs include measurement of substance concentration such as protein, DNA, or RNA, and growth of bacterial cells. Some of the major spectrophotometry applications include the following:
- Detection of concentration of substances
- Detection of impurities
- Structure elucidation of organic compounds
- Monitoring dissolved oxygen content in freshwater and marine ecosystems
- Characterization of proteins
- Detection of functional groups
- Respiratory gas analysis in hospitals
- Molecular weight determination of compounds
- The visible and UV spectrophotometer may be used to identify classes of compounds in both the pure state and in biological preparations.
As you can see the spectrophotometer is a highly flexible instrument with many different applications. It is available in different types and each type finds use in different wavelengths. You may wonder about types of spectrophotometry. We have overviewed this in our previous articles.
So, there you have every single fact about spectrophotometers. If you enjoyed this article in Linquip, let us know by leaving a reply in the comment section. Is there any question we can help you with? Feel free to sign up on our website to get the most professional advice from our experts.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- A Cheat Sheet For Types of Spectrophotometers
- Want To Know Everything About Spectrometers vs Spectrophotometers? Now You Can!
- What Wikipedia Can’t Tell You About How a Spectrophotometer Works
- The Difference Between Colorimeter and Spectrophotometer
- A Quick Look at Types of Spectrophotometers
- Spectrophotometer VS Colorimeter: Which Do You Need?