Coal is something that we might have come across at least once in our lifetime. Coal has many applications, from producing heat for households to firing industrial boilers and generators to manufacturing cast iron and synthetic fuel. Coal energy specifically finds use in heating, cooling, metallurgical processes, lighting, transportation, communication, farming, industry, healthcare, export, and much more. So given all these uses, let’s take a look at how does coal energy work. In this article, we discuss how coal energy work to have a better understanding of this fossil fuel. Read this new blog in Linquip to find out more about them.
What Is Coal?
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock composed mostly of carbon and hydrocarbons. Coal is readily combustible, black or brownish-black, and has a composition that, including inherent moisture, consists of more than 50 percent by weight and more than 70 percent by volume of carbonaceous material. It is formed from plant remains that have been compacted, hardened, chemically altered, and metamorphosed by heat and pressure over geologic time.
Where Does Coal Energy Come From?
Coal is a non-renewable energy source because it takes millions of years to create. If you wonder how is coal formed, the energy in coal comes from the energy stored by plants that lived hundreds of millions of years ago when the earth was partly covered with swampy forests. For millions of years, a layer of dead plants at the bottom of the swamps was covered by layers of water and dirt, trapping the energy of the dead plants. The heat and pressure from the top layers helped the plant remains to turn into what we today call coal.
Coal Mining
Most coal is buried under the ground. If coal is near the surface, miners dig it up with huge machines. First, they scrape off the dirt and rock, then dig out the coal. This is called surface mining. After the coal is mined, they put back the dirt and rock. They plant trees and grass. The land can then be used again. This is called reclamation. If the coal is deep in the ground, tunnels called mine shafts are dug down to the coal. Machines dig the coal and carry it to the surface. Some mine shafts are 1,000 feet deep. This is called deep mining, or underground mining.
How Does A Coal Power Plant Work?
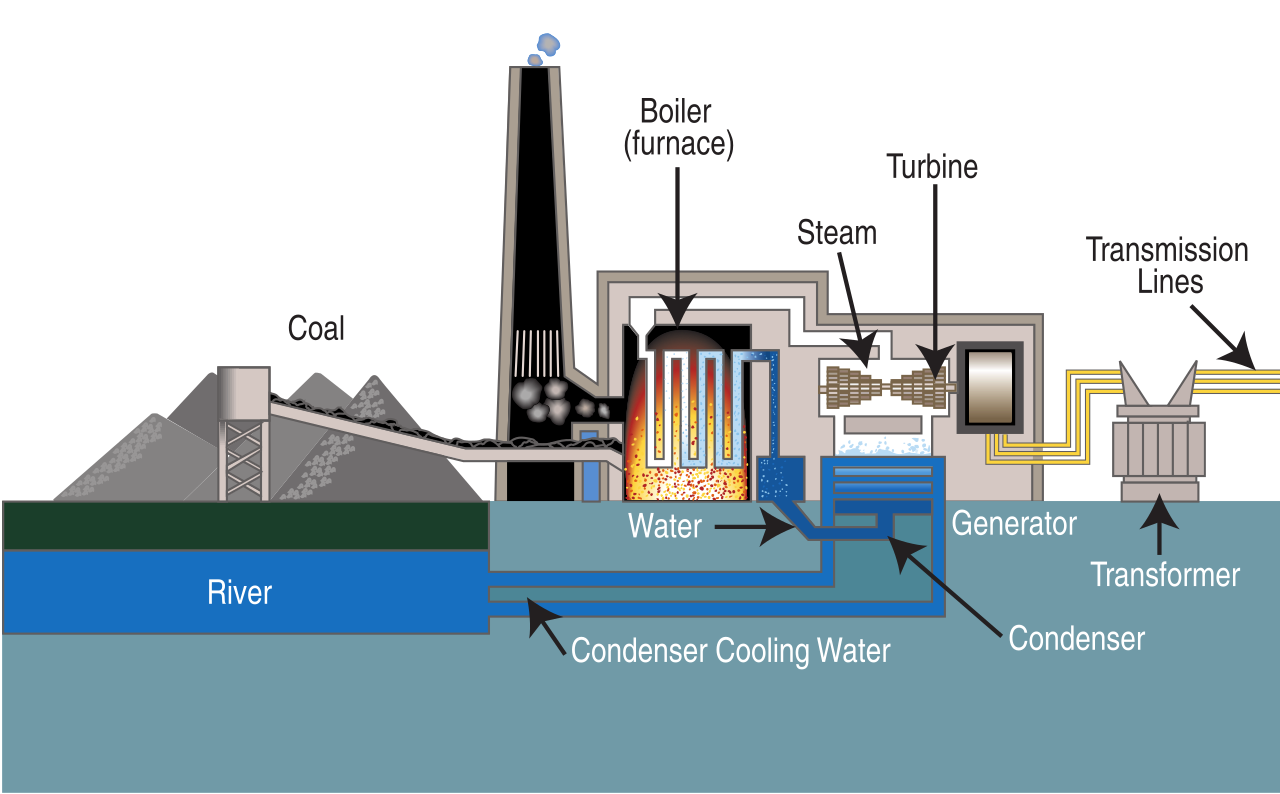
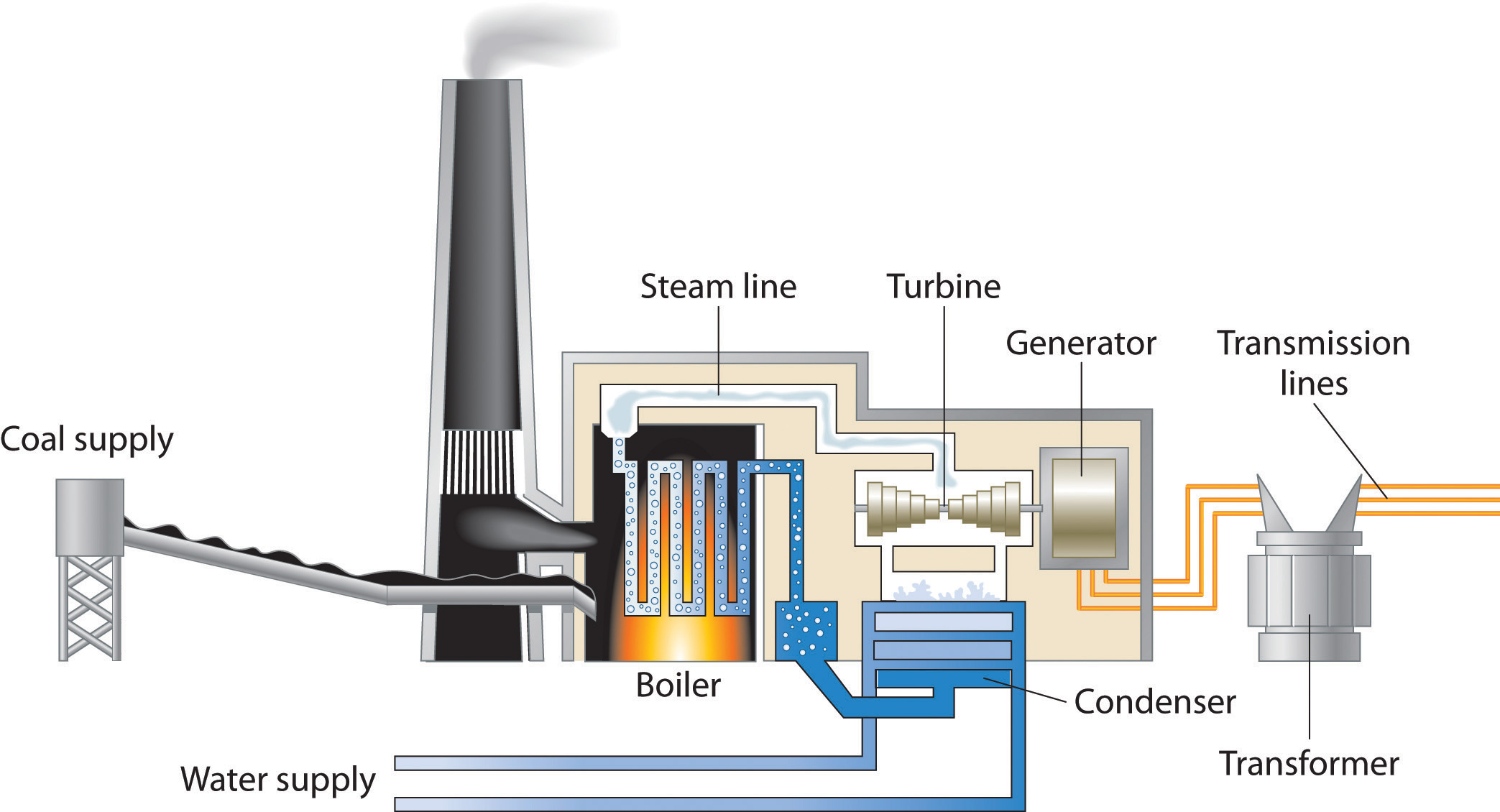
To answer how coal energy work, it is better to have a look at coal power plants. The principle is simple. After coal comes out of the ground, it typically goes on a conveyor belt to a preparation plant that is located at the mining site. The plant cleans and processes coal to remove dirt, rock, ash, sulfur, and other unwanted materials, increasing the heating value of the coal. Coal power plants produce electricity by burning coal in a boiler to produce steam.
The steam produced under tremendous pressure flows into a turbine which spins a generator to create electricity. The steam is then cooled, condensed back into the water, and returned to the boiler to start the process over.
The process of converting coal into electricity has multiple steps. If you are interested in how coal produce electricity step by step, the steps are the following:
- A machine called a pulverizer grinds the coal into a fine powder.
- The coal powder mixes with hot air, which helps the coal burnt
more efficiently, and the mixture moves to the furnace. - The burning coal heats water in a boiler, creating steam.
- Steam from the boiler spins the blades of an engine called a turbine, transforming heat energy from burning coal into mechanical energy that spins the turbine engine.
- The spinning turbine is used to power a generator, a machine that turns mechanical energy into electric energy. This happens when magnets inside a copper coil in the generator spin.
- A condenser cools the steam moving through the turbine. As the steam is condensed, it turns back into water.
- The water returns to the boiler and the cycle begins again.
When coal is burned, this results to waste gases that contain sulfur and nitrogen oxide. These wastes become acid rain when mixed with atmospheric water and can pollute the air. Despite the disadvantages of coal, it remains to be a necessity for mankind. What is important is to think of alternative ways to produce energy while minimizing the bad effects of coal. You may wonder What are the coal energy advantages and disadvantages. You can check our website, we have overviewed this in our previous articles.
So, there you have every single fact about where coal comes from, and how it works. If you enjoyed this article in Linquip, let us know by leaving a reply in the comment section. Is there any question we can help you with? Feel free to sign up on our website to get the most professional advice from our experts.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip





Coal is more cost-effective fuel but it also affects global warming.
Thanks for sharing your experience with us, Samarth! You can also visit our industrial directories, where you can find thousands of various industrial equipment based on your application and demand.