There is a huge difference between AC and DC generators although the names might seem the same to you. These two types of generators provide completely different outcomes. They both provide currents, but the final currents are different in terms of the way they move, their mechanism, their design, and their use. Here, Linquip will explain the difference between AC and DC generators and answer all the questions that may cross your mind while reading about the two. Let us first briefly introduce AC generators and DC generators.
An alternating current Generator produces an alternating current that reverses direction regularly. A DC generator, on the other hand, has a single-direction direct current. The coil through which current travels in an AC generator is normally stationary, whereas the magnet moves. AC and DC generators are important products for electrical systems. AC and DC generators are provided by several Suppliers And Companies, different manufacturers, and a lot of distributors and there are a lot of AC and DC Generators For Sale on Linquip.
There is a complete list of AC and DC generator services on the Linquip website that covers all electrical demands. Linquip vendors can assist you with this. Please contact Linquip’s AC and DC Generators Experts to learn more about how to connect with a diverse group of service providers who consistently deliver high-quality items.
What is an AC generator?
AC generator is considered an electrical generator for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. This energy is in the form of alternating current or alternative EMF. They work according to the principles of electromagnetic induction which states that electromotive force (EMF) is generated in a current-carrying conductor that cuts a uniform magnetic field. This can either be achieved by rotating a conducting coil in a static magnetic field, or by rotating the magnetic field that contains the stationary conductor. The preferred arrangement is to keep the coil stationary because it is easier to draw induced alternating current from a stationary armature coil than from a rotating coil.
What is a DC generator?
DC generators convert mechanical energy into DC electricity which is short for Direct Current. DC generators work according to the principles of energetically induced electromotive force.
Now, let’s dig deeper into the difference between AC and DC generators and learn about their use. Then, you’ll be able to decide which one suits your needs:
AC Generator vs Dc Generator
- The Design and Mechanism
- Use and Maintenance
- Connectivity
AC vs. DC: The Design and Mechanism
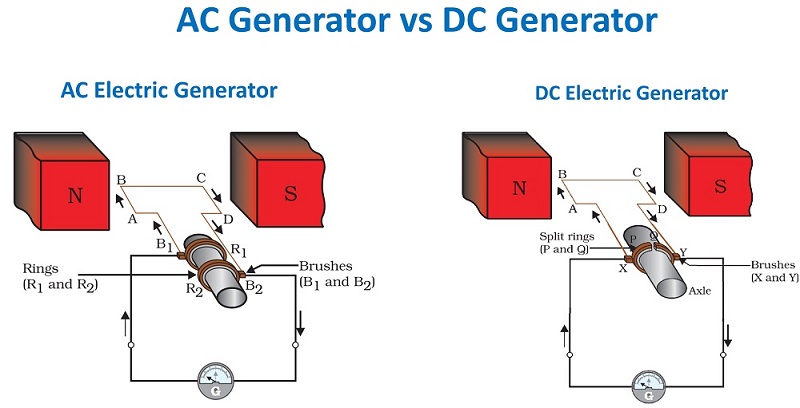
The Diff BW AC and DC Generators in terms of design are that the AC generators’ current moves through the fixed coil. The flow of current remains in the opposite direction, with the help of a moving magnet. While in DC generators the coil moves in a fixed field and the current flow with this movement, so no fixed coils for DC generators.
One of the similarities between AC and DC generators is that they both have slip rings (created from metal) and also an armature coil. The armature connects to the outside circuit with the help of a connection that directly affects the type of the produced current.
The AC generator has two metal rings that rotate with the armature coil simultaneously. Both ends of the armature are connected to a separate slip ring with a carbon brush to enable this process. But the AC generators contain a fixed brush. The brushes are the elements receiving the current flowing through the slip rings. However, both the end of the outside circuit and the end of the armature are connected to one brush.
Another difference between AC and DC generators in this regard is that while AC generators have 2 slip rings, DC generators have only one. The two semi-circular metal rings in the commutator are insulated from one another. The ends of the armature in the DC generator are connected to one-half of the commutator. Then each half-turn rotation results in a reverse direction of the current in the armature.
The 180-degree rotation between magnetic poles by the armature then takes the current from its highest point to zero. The rings in an AC generator don’t have commutators while DC generators have Split-ring commutators. Plus, the smooth and uninterrupted surface of the AC slip-rings is highly efficient and does not wear quickly while both brushes of a DC generator are less efficient than an AC generator since they wear out quickly. The efficiency of the brushes in the AC generator decreases the short circuit possibility but the possibility is high in DC generators.
Although both AC and DC generators have different approach toward collecting and transferring induced electromotive forces in the external circuit, they both use electromagnetic principles to reach the desired outcome. So there’s another difference between an AC generator and a DC generator. This difference is due to the connection between the armature and the external circuit in these two types of generators.
How AC and DC Are Generated?
DC may be produced in a variety of ways: Direct current can be generated by an AC generator with a device known as a “commutator.” The use of a “rectifier,” a device that converts AC to DC. Batteries produce DC as a result of a chemical process within the battery.
The difference between AC and DC generators: Use and Maintenance
The output voltage produced by AC generators is called the alternator. The normal frequency of alternators is 60Hz for America, Europe, and Japan. This output voltage differs in time and amplitude. DC generators produce a steady output voltage, suitable to power large motors. While DC generators are mainly used to supply power for large motors, AC generators are used for smaller ones. You can power your electrical appliances at home with the help of AC like food mixers, electrical fixtures, etc.
The Diff BW AC and DC Generators in terms of maintenance are huge. DC generators require constant maintenance and are less reliable while AC generators need very little maintenance and are more reliable.
AC vs. DC generator: Connectivity
Another difference between AC and DC generators is their connectivity. DC generators have a design that provides seamless connectivity with efficient power flow. This is mostly because they don’t need any transfer switch. In the case of AC generators, however, they require much more effort to transfer electricity to remote sections of the grid, making it less efficient when it comes to connectivity.
Different types of AC and DC generators
AC generators
- Single Phase generator
- Synchronous generator
- Three Phase Generator
- Induction generator
DC generators
- Self-excited DC generator
Series wound generator
Shunt-wound generator
Compound wound generator
- Separately-excited DC generator
AC and DC generators have different types for different uses and needs. Some of them are as follows:
AC generators have different types such as Single Phase generators, Synchronous generators, three Phase generators, Induction generators, etc.
- Single Phase generators: Single-phase generator (also known as a single-phase alternator) is an alternating current electrical generator that produces a single, continuously alternating voltage. Single-phase generators can be used to generate power in single-phase electric power systems.
- Synchronous generators: The synchronous generator or alternator is an electrical machine that converts the mechanical power from a prime mover into AC electrical power at a particular voltage and frequency. The synchronous motor always runs at a constant speed called synchronous speed.
- Three-phase generators: Three-phase generators work by producing three separate waves of AC power that operate in a sequence, ensuring that there is always a continuous flow of energy and that the power level never dips as it does with single-phase generators.
- Induction generators: An induction generator is also known as an asynchronous generator that has a working principle similar to that of an AC generator. The only difference between a normal AC generator and an induction generator is that the induction generator is a rotating device. It is known as asynchronous because the speed of the induction generator is less than that of the synchronous generator. They find applications in mixers and grinders.
DC generators mainly have two types: Self-excited DC generators and Separately-excited DC generators. Their armature connection is the same and that’s why they are categorized as DC generators.
- Self Excited: In a self-excited type, the field coils are energized from the generated current within the generator. These types of generators can further be classified into Series wound generators, Shunt wound generators, and compound wound generators. Series wound: field winding in series with the armature winding
Shunt-wound: field winding in parallel with the armature winding
Compound wound: the combination of series and shunt winding - Separately Excited: In a separately excited type generator, the field coils are energized from an independent exterior DC source.
Which one is better: an AC generator or a DC generator?
Finding the best one between an AC generator and vs Dc generator largely depends on the way you want to use it and your desired outcome. Each of them has several advantages enabling you to get the most out of them, such as:
DC Generators advantages
- Smooth Voltage
- Suitability for large motors
- Simple design
AC Generators advantages
- Suitability for electrical appliances and small motors
- Low maintenance needs
- Easy distribution of the output with a transformer
- Efficiency
- Losses are relatively fewer than DC Generators
- Transmission link size might be thinner because of the step-up feature
- AC generators can be easily stepped up and stepped down through transformers.
- The size of the AC generators is relatively smaller than DC generators.
It’s also good to know that DC generators are more affordable compared to AC generators. AC generators cost a little more.
So, now you know everything you needed to know about the difference between these two! Do you think the difference between AC and DC generators affects other aspects of your life or the industry other than what we mentioned above? Share your thoughts with us in the comment section. And feel free to sign up on our website if you want our experts to answer your most complicated questions regarding this field.
Download the Difference between AC and DC Generators PDF
You can visit this pdf file to explore more about the differences between AC and DC generators.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Difference between single phase and three phase generators: An ultimate guide
- Types of Alternator: Features, Advantages, and Vast Usage
- A Clear Classification of DC Generators
- What are the parts of AC Generators?
- A Simple Guide to the Difference Between Motor and Generator
- Alternator vs Generator: Your go-to guide to learning their difference
- A Clear Classification of AC Generators
- Parts of DC Generator: Explanation of Parts, Working, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages
- What are The Electric Generator Parts?
- DC Generator Repair, Maintenance & Testing (Clear Guide)
- Working Principle of AC Generator
- What is the Working Principle of a DC Generator?
- What is the Difference Between a Whole House and Standby Generator?
- The Difference Between Prime & Standby Generators





Hello, I love your blog! I can totally relate to this as I am currently employed as a customer service representative for an outsourcing company.
Thanks for visiting our website! We also encourage you to visit the Linquip website, where you can find numerous industrial equipment, along with companies and experts.