Welcome to Linquip Blog. Today and in this article, we are going to deal with how a servo motor works. The information in this article gives a significant collection of data you need to know about the working principle of Servo Motors, and their construction. The servo motor is most commonly used for high technology devices in industrial applications like automation technology. It is a self-contained electrical device, that rotates parts of the machine with high efficiency and great precision. Moreover, the output shaft of this motor can be moved to a particular angle. Servo motors are mainly used in home electronics, toys, cars, airplanes, and many more devices.
Our team gathered all the necessary information on this topic to eliminate the need for reading diverse content on other websites. Stay with us until the end to find the answer to your question on this topic. We have a long journey ahead of us, so take a deep breath, sit back, and keep reading this article until the end.
What Is a Servo Motor?
To get acquainted with how a servo motor works, you must first get acquainted with its structure and purpose. In this section, we have prepared an introduction to servo motors for you, which will make it easier for you to understand the performance of servo motors.
A servo motor is a rotational or translational motor to which power is supplied by a servo amplifier and serves to apply torque or force to a mechanical system, such as an actuator or brake. Servo motors allow for precise control in terms of angular position, acceleration, and velocity. This type of motor is associated with a closed-loop control system. A closed-loop control system considers the current output and alters it to the desired condition. The control action in these systems is based on the output of the motor. It uses a positive feedback system to control the motion and final position of the shaft.
There are two types of current flow in these motors – AC and DC. AC servo motors can handle higher current surges and are thus more commonly found in heavy industrial machinery. ISL’s DC Servo Motors are best suited for smaller applications and have excellent control-ability and feedback. In a servo motor speed is determined by the frequency of the applied voltage and the number of magnetic poles.
A Full Description of How a Servo Motor Works
Before we get acquainted with the working principle of Servo Motor, it is better to know what servomechanism is. Servomechanism is basically a closed-loop system, consisting of a controlled device, controller, output sensor and feedback system. The term servomechanism most probably applies to the systems where position and speed is to be controlled.
Servo motors are used to control position and speed very precisely, but in a simple case, only position may be controlled. Mechanical position of the shaft can be sensed by using a potentiometer, which is coupled with the motor shaft through gears. The current position of the shaft is converted into electrical signal by the potentiometer, and the compared with the command input signal. In modern servo motors, electronic encoders or sensors are used to sense the position of the shaft.
Command input is given according to the required position of the shaft. If the feedback signal differs from the given input, an error signal is generated. This error signal is then amplified and applied as the input to the motor, which causes the motor to rotate. And when the shaft reaches to the required position, error signal becomes zero, and hence the motor stays standstill holding the position.
The command input is given in the form of electrical pulses. As the actual input applied to the motor is the difference between feedback signal (current position) and applied signal (required position), speed of the motor is proportional to the difference between the current position and the required position. The amount of power required by the motor is proportional to the distance it needs to travel.
How Is a Servo Motor Controlled?
Servos are controlled by sending an electrical pulse of variable width, or pulse width modulation (PWM), through the control wire. There is a minimum pulse, a maximum pulse, and a repetition rate. A servo motor can usually only turn 90° in either direction for a total of 180° movement. The motor’s neutral position is defined as the position where the servo has the same amount of potential rotation in the both the clockwise or counter-clockwise direction.
The PWM sent to the motor determines position of the shaft, and based on the duration of the pulse sent via the control wire; the rotor will turn to the desired position. The servo motor expects to see a pulse every 20 milliseconds (ms) and the length of the pulse will determine how far the motor turns. For example, a 1.5ms pulse will make the motor turn to the 90° position. Shorter than 1.5ms moves it in the counter clockwise direction toward the 0° position, and any longer than 1.5ms will turn the servo in a clockwise direction toward the 180° position.
When these servos are commanded to move, they will move to the position and hold that position. If an external force pushes against the servo while the servo is holding a position, the servo will resist from moving out of that position. The maximum amount of force the servo can exert is called the torque rating of the servo. Servos will not hold their position forever though; the position pulse must be repeated to instruct the servo to stay in position.
The Construction of Servo Motors
Now that we know what a servo motor is and where it is used and how it works, let’s look at its construction and design.
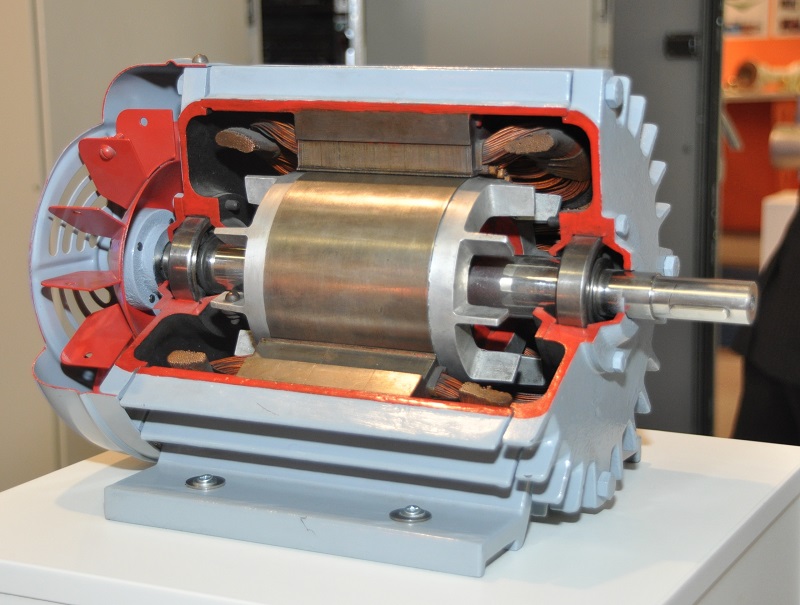
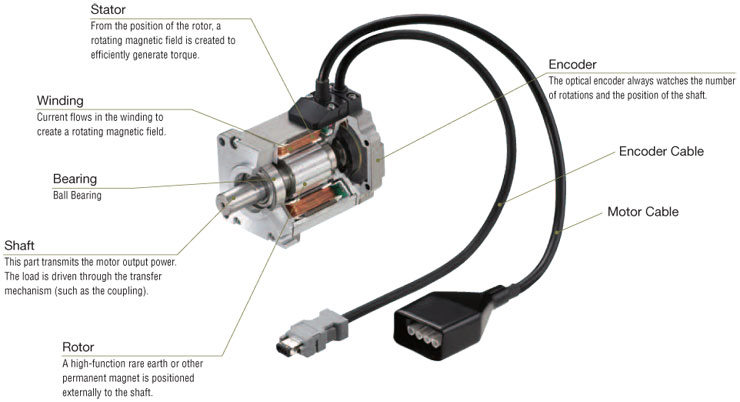
The servo motor consists of two winding stator and rotor windings. The stator winding is wound on the stationary part of the motor, and this winding is also called field winding of the motor. The rotor winding is wound on the rotating part of the motor and this winding is also called the armature winding of the motor. The motor consists of two bearings on the front and backside for the free movement of the shaft. The encoder has the approximate sensor for determining the rotational speed and revolution per minute of the motor.
Conclusion
The present article was an attempt to deal with How a Servo Motor Works and deliver all the essential information about how they are constructed and controlled. A servo motor is a rotational or translational motor to which power is supplied by a servo amplifier and serves to apply torque or force to a mechanical system, such as an actuator or brake. Servo motors allow for precise control in terms of angular position, acceleration, and velocity.
If you have any experience of using different types of Servo Motors, we will be very glad to have your opinions about their performance in the comments on our website Linquip. Moreover, if you have any questions about this topic, you can sign up on our website and wait for our experts to answer your questions. Hope you enjoyed reading this article.





Hello dear Mam, Sir
I would be grateful if you let me know that it is possible to control pH with dosing pump with servo motor.
It would be use for neutralization of wastewater. My point is that is it possible to dose high in the high gap of pH from wastewater and pH 7 and it dose less when the gap of pH from wastewater and pH 7 is low.
Best Regardss
Saeedeh
Why does the servo motor cant operate in auto and manual
Thanks for visiting our website, Steven! You can ask your question from thousands of our experts here.