Here we want to discuss the difference between active and passive filters. First, let’s take a look at the definition of the filter.
The filter is a circuit that alters the amplitude and phase of the input signal and generates output accordingly. It filters or reduces some frequencies and transfers some of them. So it produces various attenuations to various frequencies. We have two types of filters based on their construction components, active filter, and passive filter.
Now, we present the definition of each type, their applications, pros and cons, and finally, we demonstrate the difference between active and passive filters.
Active Filter
Active filters are filter circuits that are designed by employing transistors and op-amps as their essential components. Along with these components, circuits of active filters also contain capacitors and resistors, but there are no inductors.
We know the filter shows the property of frequency selectivity. Therefore, active filter circuits utilize an op-amp and transistors to pass only a selective frequency band while attenuating the other part of the frequency.
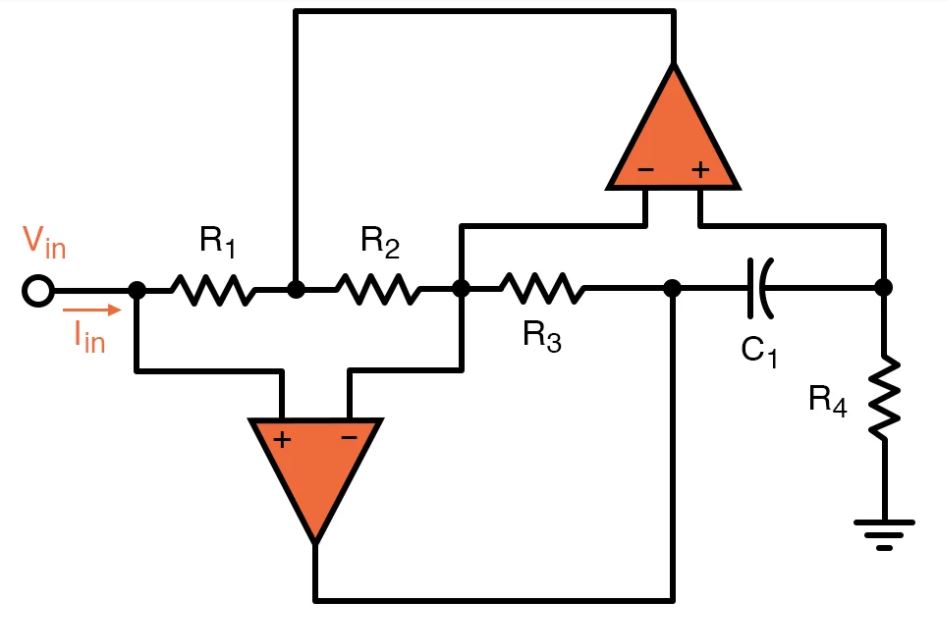
The following figure displays the example of a circuit with an active filter:
In the sample of active filters, in order to create the essential filter characteristic, the interconnection of the integrator, op-amp, inverter, etc., with a capacitor and resistor is formed.
Regularly, the op-amp in the circuit is applied in an integrated model. Therefore, guarantee small size and less massive. We know op-amp offers low output impedance and high input impedance. Hence, such active filters reduce the loading effect at load and source.
Though active components allow finite bandwidth. It sometimes causes difficulties in the operation of the high-frequency signal. Additionally, an external DC source is needed in the case of the active filtering unit since it cannot take the power from the input signal.
Applications of Active Filters
- Active filters are applied in the communication system to overcome noise to isolate signals from various channels to improve the unique message signal from an accentuated signal.
- These filters are employed in instrumentation systems by the designers to determine a required frequency apparatus and detach undesired ones.
- Active filters can be applied to limit the analog signal’s bandwidth before changing them to digital signals.
- Active filters are present in audio systems to send various frequencies to various speakers. For example, recording & playback applications are required in the music industry to control the frequency components.
- These filters are used in biomedical devices to interface psychological sensors with diagnostic pieces of equipment & data logging.
Advantages of Active Filters
Some of the advantages of active filters are:
- No resonance issue
- They can eliminate any harmonics
- They are used for voltage regulation
- They can be used for reactive power compensation
- They provide reliable operation
Disadvantages of Active Filters
There are some disadvantages to active filters, such as:
- They are expensive
- They provide complex control systems.
Passive Filter
Passive filters are the filter circuits formed employing only a resistor, inductor, and capacitor as their major components. As no amplifying element is existing in it, the passive filter offers low signal gain. This leads to the reception of a relatively low signal at the filter circuit’s output than the applied input signal.
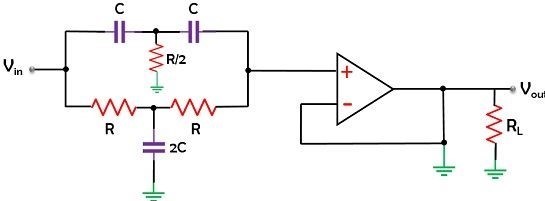
To understand the difference between active and passive filters, let us take a look at the circuit of a passive filter below:
For radiofrequency range, passive filters propose an excellent response. However, the presence of an inductor in the circuit produces some difficulties in low-frequency demands. As the inductance of the inductor must be raised in the case of low frequencies, it needs more turns in the coil.
Below the RF range, both the input and output impedance of passive filters generate an issue. Therefore, these filters are not proper for low-frequency applications. Fundamentally, the band of frequency allowed and restricted forms the classification of filters.
So, if the RLC network passes only a lower band of frequency, it is classified as a low pass filter. Likewise, if the filter attenuates a lower frequency band and passes a higher frequency band, it is classified as a high pass filter.
Applications of Passive Filters
There are many applications for passive filters, such as:
- They can be used in high-pass filters, especially audio amplifiers
- They also can be applied in bandpass filters while rejecting signals at all frequencies above and below this band
- They are used in band stop filters for older radio and TV receivers
- They act as I.F Transformers found in older radio and TV devices to pass a band of radio frequencies from one step of the intermediate frequency (IF) amplifiers.
Advantages of Passive Filters
Some of the advantages of passive filters are:
- Cheapness
- Easy design
- Reliability
- High efficiency
Disadvantages of Passive Filters
There are also some cons to passive filters. Some of them are:
- Resonance problems
- Tuning for fixed frequency
- Large size
- Fixed reactive power compensation
Principal Difference Between Active and Passive Filters
- Active filters are expensive because of the presence of active components. On the other hand, passive filters are cheap enough as a result of passive elements in them.
- The circuit orientation of active filters is quite complex. While comparatively passive filters have a less complicated circuit.
- Active filters have a high value of quality factor in comparison to passive filters.
- Active filters need an external source of power for circuit operation. Nevertheless, passive filters do not demand external energy sources because they drive the energy required for their operation from the applied input signal.
- As the inductor is the key component employed in passive filters, and it generates obstacles at low frequencies, so passive filters are suitable for RF range operation. In contrast, active filters implement a better response at low frequencies.
- Active filters have low weights, while the weight is comparatively high in passive filters.
- Active filters exhibit greater sensitivity to temperature changes. In comparison, passive filters are less sensitive to temperature change.
| Basis for Comparison | Active Filter | Passive Filter |
| Composed of | Active components like a transistor, op-amp, etc. | Passive components like inductors, resistors, capacitors, etc. |
| Cost | Comparatively High | Relatively low. |
| Circuit complexity | More complicated | Less complex than an active filter. |
| Weight | Relatively Low | Relatively heavier because of the presence of inductors. |
| Q factor | High | Very low compared with active filters. |
| External power supply | Is required | Is not required |
| Sensitivity | More sensitive | Relatively less sensitive. |
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip