What is a brushed DC motor? How does it work or what is its working principle? What parts does it consist of and how many types does it have? These are the questions that everyone should ask him or herself before purchasing a brushed DC motor? Linquip, as always, has gathered enough information about these questions so that you can make an easier choice and a more suitable purchase. In the following sections, we will elaborate on each of these issues and delve deeper into each of these areas. Let’s have a look at what a brushed DC motor is and what it does. Read on to have your answers.
What Is a Brushed DC Motor?
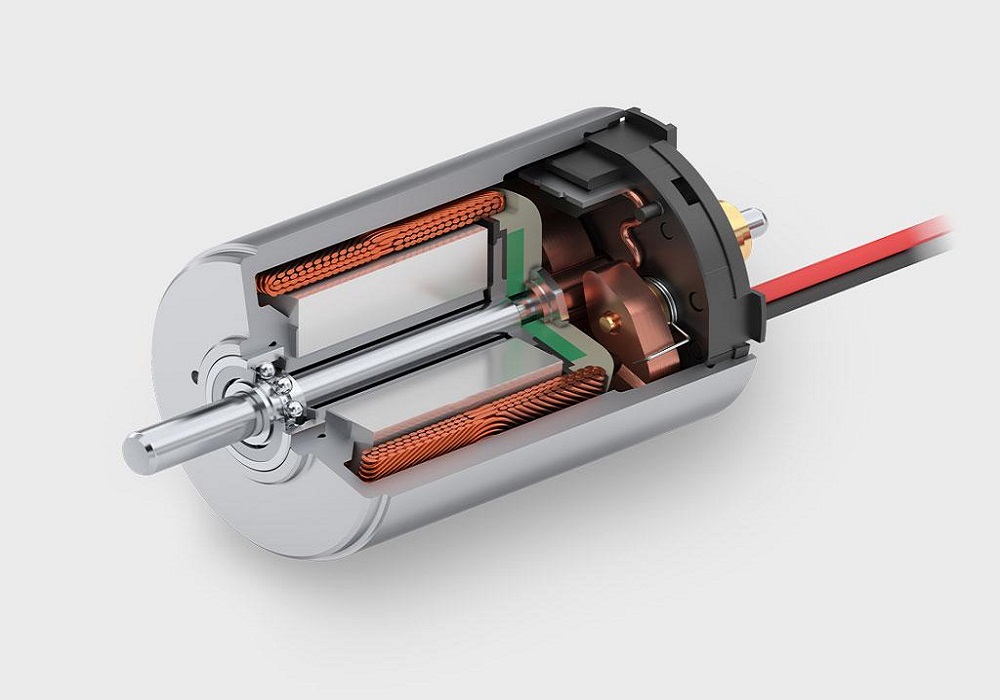
We call this type of motor a brushed DC (BDC) motor as it uses brushes for its commutator. Brushed DC motors are used widely and frequently in home appliances and in automobiles ranging from toys to push-button for adjusting seats in cars. They are inexpensive, easy to use, and have different shapes and sizes. A BDC
motor provides exact control of speed, driven by a direct current. This type of motor can supply three to four times more torque than it’s rated torque and If needed, it even has the potential to supply up to five times more, without stalling. BDC Motors consist of six different components that we will elaborate on the most important ones in the following sections. BDC Motors by using rings to power a magnetic drive that conducts the motor’s armature, provide stable and continuous current. This kind of motor is one of the earliest used motors and is commonly used because of the ability to vary the speed-torque ratio in almost any way.
How Does a Brushed DC Motor Work?
A BDC Motor is made up of two magnets facing the same direction, surrounding two coils of wire that lie in the middle of the Motor and around a rotor. The coils are set to face the magnets which causes electricity to flow to them. This builds a magnetic field, ultimately pushing the coils away from the magnets they are encountering which finally makes the rotor turn.
The current cut off at the rotor makes a turn of 180 degrees. This makes each rotor to face the opposite magnet. once the current starts over again, the electricity flows oppositely and sends another pulse having the rotor turned once again. By transferring the electricity from the rotor, brushes that exist within the motor turn it off and on.
What Are Its Main Components?
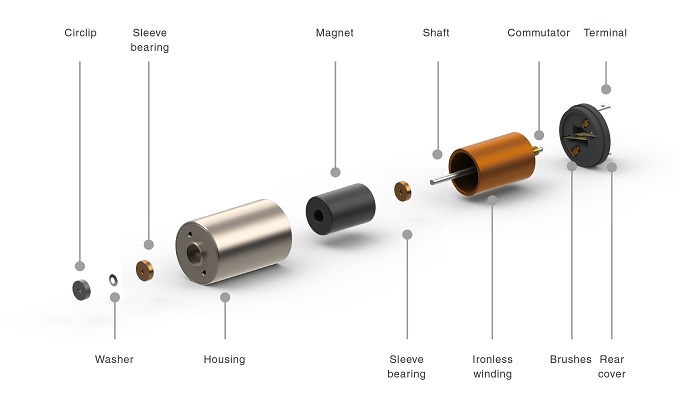
We mentioned before that there are 6 different parts in a BDC motor. But four of them are the most important components that exist in almost all electrical motors. These four components that we are going to talk about are the stator, the rotor and brushes, and the commutator. Let’s see what each of these parts does inside the motor.
-
Stator
The stator as you may know is the stationary part of the engine and generates a stationary magnetic field around the rotor. This magnetic field is generated by either permanent magnets or electromagnetic windings. The construction of the stator or the way the electromagnetic windings are connected to the power source defines the different types of this motor.
-
Rotor
The rotor, aka “armature,” is constructed of one or more windings. When these windings are turning they produce a magnetic field. The poles of this magnetic field will face to the opposite poles generated by the stator and make the rotor to turn. The windings are constantly being energized in various sequences when the motor turns so that the magnetic poles generated by the rotor do not interrupt the poles generated in the stator. We call this switching between the field in the rotor windings commutation.
3 & 4. Brushes and Commutator
Unlike other electric motor types such as brushless DC and AC induction motors, BDC motors do not need a controller to alternate current in the motor windings. Instead, the change of the windings of a BDC motor is accomplished entirely mechanically. The commutator, a segmented copper sleeve, is set on the axle of a BDC motor.As the motor rotates, carbon brushes slide over the commutator and make contact with different segments of the commutator. These segments are connected to different rotor windings, thus, a dynamic magnetic field is generated inside the motor when a voltage is applied across the brushes.
Read More on Linquip
- All About DC Motor Types and Their Applications
- Differences Between Motor and Engine
- Separately Excited DC Motor
- Shunt DC Motors: An Easy-to-Understand Explanation of Working Principle and Components
- Series DC Motors: A Comprehensive Guide
- Compound DC Motors: Everything You Should Know About DC Compound Motors
- Universal Motor: a Simple Guide to Construction, Types and Working
- A Complete Guide to Repulsion Motor
- Differences Between Motor and Generator
- Synchronous Motors: Definition, Working Principle, Types, and Applications
- How Does a Brushless Motor Work: A Full Explained Guide
- Your Guide To The Working Principle Of DC Motor
The Use of BDC Motors
Although the brushless DC motors, because of their longevity and reliability, have been used more commonly in comparison to the bushed DC Motors, the BDC Motors are still appropriately chosen for many applications. Most commonly, the BDC Motors are found in home appliances. Because of their versatility in altering the torque to speed ratio, they can also be found in the industrial world.
Brush DC Motor and Different Industries
The BDC Motor is simple to run and is easily affordable, it is particularly a favorite in the automotive industry. To power windows, seats, and more, automotive manufacturers make use of them. Thus, brush DC Motors can be found in nearly every industry ranging from computers to manufacturing.
The BDC Motors’ Applications
Brushed DC motors are used widely and frequently ranging from toys to push buttons for adjusting seats in cars. Most automatic windows in automobiles and seat adjustments use a BDC Motor. The Brushed Motors’ relatively low cost for purchasing and maintenance as well as their simple design, make them a favorite option for the automotive industry. This type of motor has different shapes and comes in all different sizes. They also have torque and speed specifications.
Conclusion
In this article, we tried to show you what exactly a brushed DC motor does. To answer this question, we analyzed the working principle of a BDC motor and how it works. We explained the rules a BDC motor follows to do its job. After that, we delved into different and main parts of it.
At last, we reached the different types of BDC motors and talked about the main types of it. If you have any experience of using different types of BDC motors, we will be very glad to have your opinions in the comments. By the way, if you have any questions about this topic and if you still have ambiguities about this device in your mind, you can sign up on our website and wait for our experts in Linquip to answer your questions. Hope you enjoyed reading this article.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers