Capillary tubes are the most simple refrigerant metering device used in many pieces of equipment. So it is of great importance to understand what capillary tube refrigeration is and how it works. In this article from Linquip, we want to dive deeper into the world of the capillary tubes and their functions. Keep on reading to learn more.
There is a wide range of information available on Linquip’s website about capillary tube refrigeration equipment and devices. Any questions related to capillary tube refrigeration you may have can be answered by Linquip’s team of experts. Linquip has an excellent article, “What Is Capillary Tube Refrigeration”, that you may find worthwhile.
For full access to all of the benefits offered here, you can also register as a Linquip Refrigeration Expert. Would you be open to Guest Posting on Linquip? You can submit your articles as a guest on the Linquip platform.
What is Capillary Tube Refrigeration?
The capillary tube is one of the most commonly used throttling devices in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. The capillary tube is a copper tube with a very small internal diameter. It is of very long length and it is coiled to several turns so that it would occupy less space.
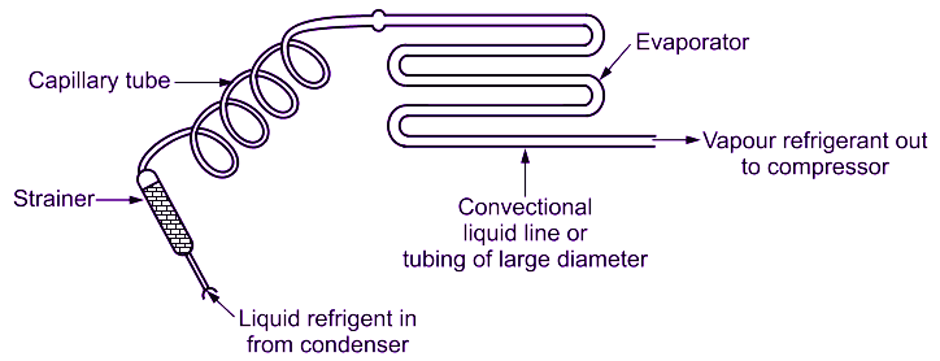
How Does Capillary Tube Work?
When the refrigerant leaves the condenser and enters the capillary tube, its pressure drops down suddenly due to the very small diameter of the capillary.
In the capillary, the fall in pressure of the refrigerant takes place due to the small opening of the capillary.
The capillary tube is a non-adjustable device that means one cannot control the flow of the refrigerant through it as one can do in the automatic throttling valve. So the flow of refrigerant would change according to the variation in the surrounding. That is why the capillary tube is designed for certain ambient conditions. However, if it is selected properly, it can work reasonably well over a wide range of conditions.
Capillary Tube Size
The size of the capillary tube is fairly critical. Unlike orifices, such as expansion valve seats, capillary tubes depend on their length as well as their diameter to determine their total restriction. A capillary tube is 1–6 m long with an inside diameter generally from 0.5–2.28 mm (0.020–0.09 inches).
A change in diameter on a percentage basis can change the flow more than an equal change in length. Restriction can also be changed by lengthening or shortening the capillary tub. The longer the tube, the slower the flow; the shorter the tube, the faster the flow.
Capillary Tube Function
The capillary tube actually meters the refrigerant from the condenser to the evaporator. The diameter and length of the tube would determine the flow at a given pressure.
Because the capillary tube restricts and meters the flow of liquid to the evaporator, it helps maintain the needed pressure difference for proper system operation. The capillary tube and compressor are the two components that separate the high side from the low side of the refrigeration system.
The capillary tube is used when the load is relatively constant. Capillary tubes are used as the throttling device in domestic refrigerators, deep freezers, water coolers, and air conditioners.
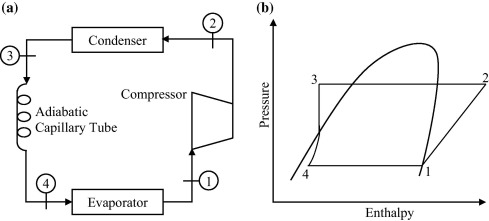
Advantages Of The Capillary Tube
The advantages of using the capillary tube as the throttling device in the refrigeration and the air conditioning systems are as follows.
- The capillary tube is a very simple device that can be manufactured easily and it is not very costly.
- The capillary tube has no moving parts. Therefore it doesn’t need maintenance.
- The capillary tube limits the maximum amount of the refrigerant that can be charged in the refrigeration system due to which the receiver is not required in these systems.
- The capillary tube provides an open connection between the condenser and the evaporator hence during off-cycle, pressure equalization occurs between condenser and evaporator. This reduces the starting torque requirement of the motor since the motor starts with the same pressure on the two sides of the compressor. Hence, a motor with low starting torque (squirrel cage Induction motor) can be used.
- It can be used for hermetic compressor-based systems that are critically charged and factory assembled.
- It is compact in size.
Disadvantages Of The Capillary Tube
Some of the disadvantages of a capillary tube are:
- These valves are not capable of adjusting themselves to the change of flow as per changing ambient temperature and load.
- It is susceptible to clogging because of the narrow bore of the tube, hence, utmost care is required at the time of assembly. A filter-drier should be used ahead of the capillary to prevent the entry of moisture or any solid particles
- During off-cycle liquid refrigerant flows to evaporator because of pressure difference between condenser and evaporator. The evaporator may get flooded and the liquid refrigerant may flow to the compressor and damage it when it starts. Therefore critical charge is used in capillary tube based systems. Further, it is used only with hermetically sealed compressors where refrigerant does not leak so that critical charge can be used. Normally an accumulator is provided after the evaporator to prevent slugging of the compressor.
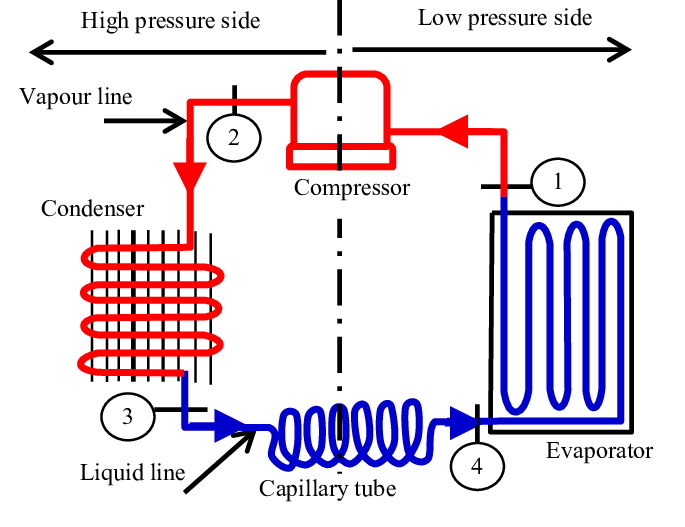
What Should You Consider When Choosing a Capillary Tube for Refrigeration?
It is usually a very small diameter pipe available in diameters ranging from 0.76 to 2.16 mm that is used as a capillary tube. It is chosen to fit the condenser system capacity.
How Do Expansion Valves and Capillary Tubes Differ?
While both of these systems control refrigerant flow, their methods of operation differ. While a thermal expansion valve can adjust the flow of refrigerant to match the temperature, a capillary tube remains unchanged regardless of heat load fluctuations.
Now that you know the answer to the question of what is capillary tube refrigeration, how about sharing your thoughts and comments on the subject with us? Comment below and let us know what you think! And if you have any questions about the capillary tubes, sign up on Linquip right now and we’ll help you in the blink of an eye!
Download Capillary Tube Refrigeration PDF
You can download this article as a PDF so that you can access it whenever you like.
Read More In Linquip
- Water Chiller System and the Essential things You Should Know about it
- Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Comparison
- How to Calculate the Efficiency of Heat Exchangers?
- Cooling Tower Approach: Basic Elements of Efficiency in Cooling Towers
- Transformer Efficiency: Essential Things You Should Know
- Cooling Tower Partsand Functions: A Concise 10,000-Foot yet Essential View
- The Counterflow Cooling Tower: A Quick Intro
- What is HVAC? Types, Parts & Diagram
- How an Air Conditioners Compressor Work?
- Crossflow vs Counterflow Cooling Towers: Which to Use Where
- The Counterflow Cooling Tower: A Quick Intro
- Top Air Conditioner Manufacturers and Companies in the US
- 5 Best Electric Boilers of 2022: A Practical Guide
- How to Choose the Best AC Repair Service
- Common Problems with Solar Air Conditioners
- Benefits of Installing Lennox Air Conditioning
- Difference Between Air-Cooled vs Water-Cooled Compressor
- Advantages of Air Conditioner: Everything You Need to Know
- What Are Air Source Heat Pumps? A Complete Guide
- 5 Types of Ventilation and All We Should Know About
- The Essential Guide to the 4 Types of Air Compressors
- Can I Use Water Instead of Coolant in an Emergency?
- A General Overview of Heat Pump Problems
- At What Temperature is a Heat Pump Not Effective? Easy Answer
- What Is a Condenser; Parts, Functions and types
- Easy Introduction to HVAC Maintenance and Services ( Heating and Cooling Repair )
- Cooling Tower Parts and Functions: A Concise 10,000-Foot yet Essential View
- How an Air Conditioners Compressor Work?
- Advanced Guide: What Is Tube In Tube Heat Exchangers
- Quick Guide On What Is Floating Head Exchanger
- What is u-tube heat exchanger? An undeniable advantageous system
- Types of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
- Water Tube Boiler: What You Need to Know






Nice article, cleared some things up for me.
what happens if we install two capillary tubes in the same system with a gap?
Thanks for visiting our website, Fayyaz! You can ask your question from our thousands of experts available on the Linquip website.
Why are the low/high side pressures that are stamped on the side plate of a window unit A/C with R410A, why do run so much higher than the HVAC units that key off standard temperature and pressure charts which end up being half or less of what a window unit states as the pressures?
Thanks for visiting our website, Don! You can visit our expert page and take advice from hundreds of professionals on your issue.
What is necessary peremeter for calculating the size and lenght of capillary tube to be employed a refrigeration system?
Thanks for visiting our website. You can solve your issue by asking from one of our experts here.