The question “what cooling system is better for removing heat from a liquid?” is frequently asked by individuals who are about to buy a cooling system for their companies or facilities and they are confused about the chiller or a cooling tower. The problem is that they cannot recognize the functions and applications of a chiller vs. cooling tower.
There is no need to be worried anymore because in this article, Linquip will help you to have a better choice. Read on so that the ambiguities of this issue get resolved once and for all.
To figure out which one of these cooling systems meet your cooling requirements better, we have to look at the differences and understand how differently they operate.
Both of these cooling systems are possessed for almost similar purposes. They both are used to remove heat from a liquid, which is used as a coolant in large devices and processes such as food processing units, metal plating, power stations, etc. So, both of these cooling systems perform similar functions. However, they vary in their mode of operation, according to their types, parts, and also the equipment they cool. In the following sections, we are going to discuss how distinctions between these two systems put a chiller vs. a cooling tower.
How Does a Chiller Work?
Basically, chillers reject heat from the coolant by using the air around the system or water as the refrigerant before it is transferred into the surrounding. This process is essential to the whole cooling process. Chillers can be air-cooled or water-cooled. In air-cooled chillers, the hot coolant bearing a phase change into a gas, is exposed to the ambient air around the system and the air cools it and brings it back into a liquid. In water-cooled chillers, the water to cool down and condense the coolant is provided by a cooling tower.
How Does a Cooling Tower Work?
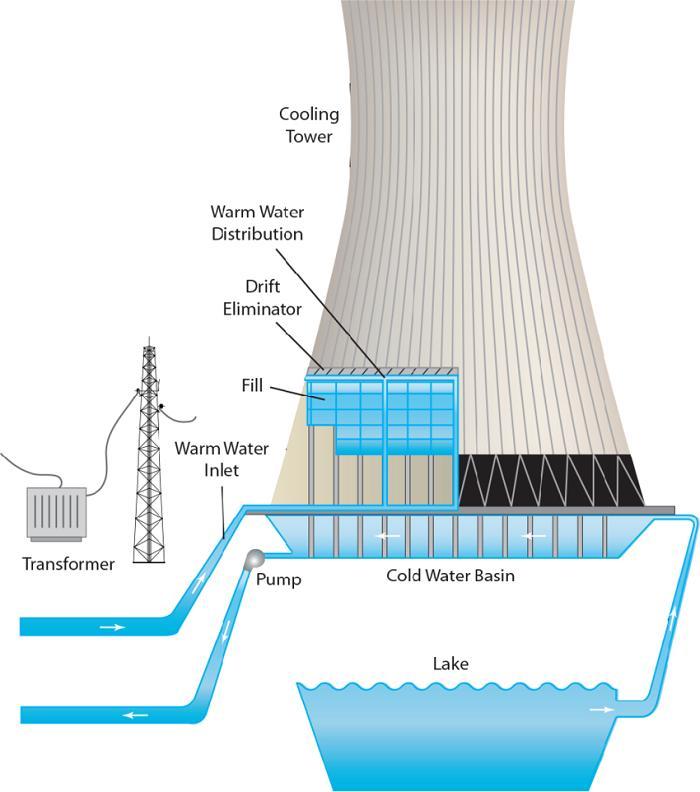
In the previous section, you read what a chiller does and how different types of chillers work. In this section and to find out why we put a chiller vs. cooling tower, we try to analyze the performance of cooling towers. A cooling tower is a huge heat exchanger structure using a condenser to discharge coolant to cooling tower to reject heat from coolant. This coolant has already been used to cool down processed fluid or another structure. The whole process is done via the combination of spraying water and the assistance of fans. The water is sprayed on the surface of coolant and fans flow the air to remove the heat from it.
To find some other differences that leave a chiller vs. cooling tower, we make some comparisons in various aspects. Let’s have a look at the diverse types, main components, uses and applications and power consumption of each of these cooling systems.
Types a Chiller vs. Cooling tower
There are two different types for each of these cooling systems: chillers are like radiators and cool down the coolant by using air or water. Water-cooled chillers need more maintenance in comparison to air-cooled ones but the best aspect of water-cooled ones is that they consume less power to run.
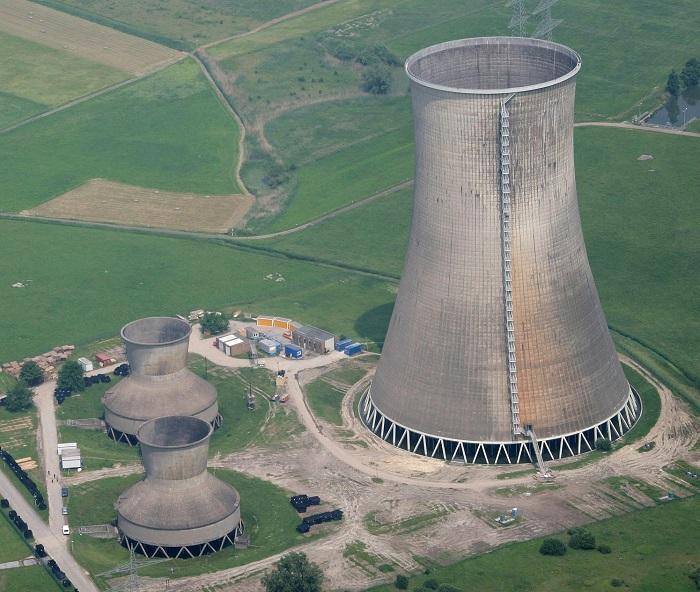
Cooling towers have two different types too: natural and mechanical drafts. Natural drafts are huge and massive structures that are usually associated with nuclear power plants. These cooling towers are called natural drafts as the process of rejecting heat is done by the natural convection process.
The other type of cooling tower is called the mechanical draft. In the process of cooling in this type, large fans are used to pull the cooler ambient air into the tower. The ambient air cools down the coolant inside the tower before it is circulated throughout the power plant or any other similar industrial equipment or structure.
What Are the Main Components?
The main parts of a cooling tower are pumps, a large basin and enormous fans. The basin collects the water discharged from coolant system. Pumps supply water for the cooling tower to make a water flow for facilitating cooling process. And finally, the fans bring the ambient air onto the surface of discharged water to drop the temperature of the water. A chiller has three main parts: compressors, condensers and evaporators that all cooperate to reject the heat from coolant.
So far, we have analyzed the types and components of a chiller vs. cooling tower to have a better distinctive understanding of these to cooling system. The two remaining aspects are applications and power consumption which make differences between these two.
Applications and Uses
Cooling towers are commonly used for large-scale operations such as nuclear power plants located near rivers or lakes, refining plants of oil and gas and thermal power stations while chillers are used in refrigeration, metal and plastic industries and more.
Although these two cooling systems are sometimes used interchangeably in the same industries and same locations, if you want to maximize the efficiency and keep the costs down, it’s vital to pair the right cooling system with its related and specific industry.
Cooling towers are often used where a high amount of cooling is required. Most of the industrial plants needing continuous cool water flow use cooling towers as their cooling system while chillers are used in smaller applications.
Power Consumption of a Chiller vs. Cooling Tower
As mentioned before, chillers possess compressors and heat exchangers. So, it consumes more power in comparison to cooling towers’ power consumption of fans and pumps considering their greater cooling capacity. Besides, water-cooled chillers do the cooling job better than air-cooling ones and consumes 10% less power than air-cooled ones but the costs of maintenance for water-cooled ones are higher.
The Combination of Cooling towers and Chillers
Depending on the scale of your industry and its requirement for cooling processes, you have a lot of option in using cooling systems. For smaller application you can combine a water-cooled or air-cooled chiller with a small cooling tower on the roof of your industrial building. You can also use a water-cooled chiller associated with cooling towers.
For higher efficiency in a cooling process, you can apply a huge chiller accompanied with a massive cooling tower. Choosing between all of these combinations and more directly depends on your budget and the amount of cooling your industry requires. Sometimes it is needed to have a small cooling center in the lowest place of an industrial building and sometimes it requires having giant chillers with a tall and big cooling tower.
Another determining factor that can affect your choice is the coolant temperature you desire to have for your equipment. If you require the temperature of 32 to 30° C, cooling towers can afford it but the temperatures below 30° C require using chillers, especially water-cooled ones.
Conclusion
What you read in this article was a collection of information on a chiller vs. cooling tower. We analyzed these two cooling systems from different aspects to make it clear which cooling system or any possible combinations of those are more suitable and effective for your application and use.
It is vital to understand the difference between obtainable options we have to select the best. We want you to know if there are still some ambiguities for you on this topic, you can share your questions with our experts in Linquip. All you need to do is to sign up now and our experts are ready to answer your questions and give you advice. Moreover, if you have any experiences of using chillers and/or cooling towers, or have opinions on this topic, you can share them with us in the comments. Hope you enjoyed reading this article.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
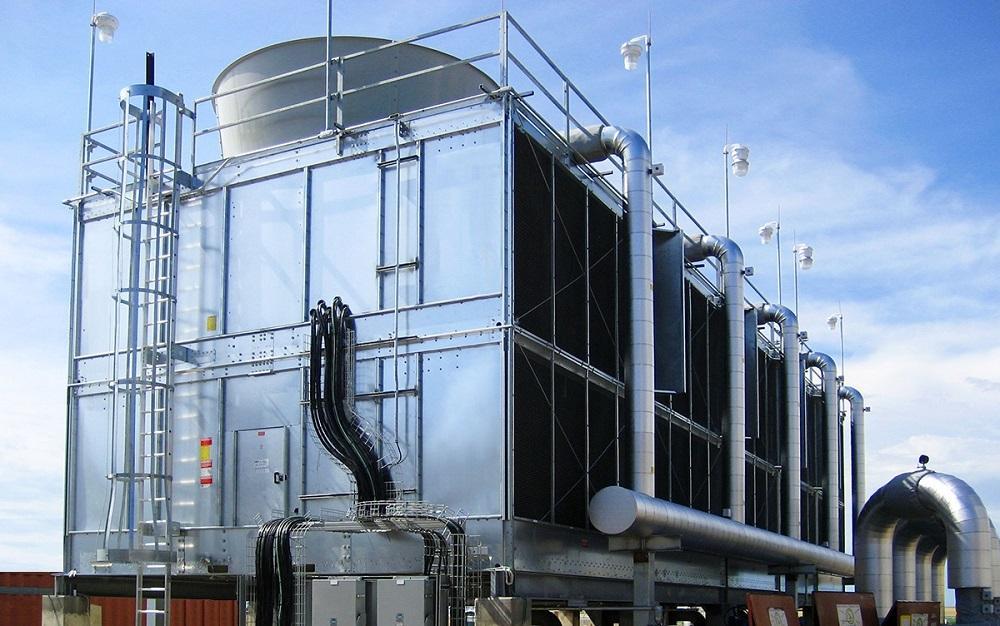





Anaa, you were really informative! The chiller and the cooling unit perform the same thing: they remove heat from the system so that the machinery continues to run at peak efficiency without interruption. However, there are differences in heat removal technologies between the two systems. A chiller, for example, is a system in which heat is removed directly from the coolant before it is transported to the surrounding air, which is necessary for the chilling process. On the other hand, a cooling tower is intended to remove heat from any water released from the condenser unit.
Thanks for sharing your experience with us, Alistar! You can also visit our industrial directories, where you can find thousands of various industrial equipment based on your application and demand.