Circuit Breaker vs Fuse- Circuit Breakers and Fuses both present the same purpose: to support the electrical systems by preventing over-currents and overloads that can cause damages like fires. They both interrupt the current flow, but in very different ways from each other. Whereas a fuse is constructed from a piece of metal that melts when over-warmed, circuit breakers have the internal structure for switching the mechanisms that can be cut by an unsafe rate of electricity. We will discuss the main differences between them in this post to explain the Circuit breaker vs Fuse issue precisely.
What are the Differences Between a Circuit Breaker and a Fuse?
The differences between the circuit breaker and fuse are discussed considering several factors such as the Requirement of Auxiliary Equipment, Reusability, Working Principle, Operating Time, Their Function, Indication of Status, Temperature, Cost, Breaking Capacity, Characteristic Curve, Protection, and Mode of Operation.

Fuses can be faster for interrupting the flow of electricity, but when they melt, they should be replaced; on the other hand, circuit breakers just require to be reset. When contrasting these two devices, we’ll take a look at some of the main benefits and problems between circuit breakers and fuses to distinguish between them.
A Fuse is an electrical instrument that includes porcelain, glass, or plastic substance containing a thin layer of wire. If any faults happen in the setup and an overvalue of current flows within the circuit, the fuse melts automatically and breaks the main contact of the system, thus, protecting the devices from any damage. The Circuit Breakers also operate on the same function as that of the fuses but are based on the electromagnetism process. The circuit breakers also protect the devices from getting damaged because of the overrated current. Visit here if you want to explore more about the circuit breaker vs fuse subject.
Circuit Breakers Working Principle
Circuit Breakers have two various methods of operation: the first is using an electromagnet section, and the second is employing a bi-metal blade. In both ways, when turned on, the breaker permits the electrical current to move from a bottom section to an upper terminal through the strip. When the current rises to any unsafe rates, the magnetic force of the strip or solenoid becomes great enough to pull the metal blade in the switching mechanism and cut the current off. The other mode that can happen is that the metal blade can bend, pushing the switch and cutting the connection off.

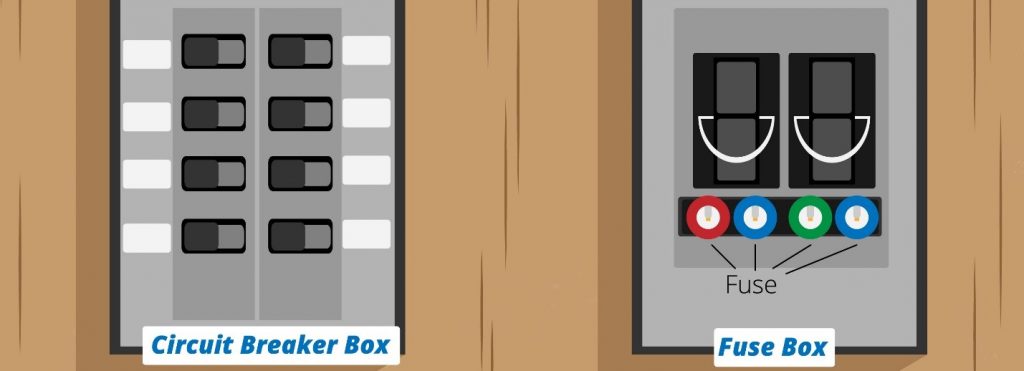
In order to recover the flow of current, the switch button can only be turned back on, which reopens the system. Circuit breakers in many applications are found in an individual cabinet, including different switches introduced as the breaker box. This simple switch process permits turn-off the individual circuits in a house simply when required for operation on particular wiring in the location.
Circuit breakers have other constructions like using Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (commonly known as GFCIs). The operation of them is to avoid the electric shock, rather than just overheating. They cut off the system in an outlet if the current becomes unbalanced. They can be reset by pushing a button and are typically useful in bathrooms or kitchens, where electrocution or immediate shocks are too risky from the use of electrical devices near water pipes such as the faucets or sinks.
Fuse Types
Fuse types are too different for both commercial and residential use. The most common type is constructed from a filament or a metal wire that is covered with glass, ceramic, or a metal casing. The fuses are commonly plugged into a central fuse box in residential homes, where the wiring of the building passes through this box. When the current flows, the fuse will allow the power to pass without any limitation through the filament between wires. The filament melts when overloads occur and stops the current flow.

It will take a little time for the filament to cut, and therefore, any power surge is ceased. When the fuse is broken, it is to be eliminated and replaced with a new one. Various ratings and voltages are available in the market to handle the different capacities of the current. The best fuse for a system is typically one that is rated for slightly greater than the normal value of the current.
Key Differences to Compare Circuit Breaker vs Fuse
The key difference to compare Circuit Breaker vs Fuse are summarized below:
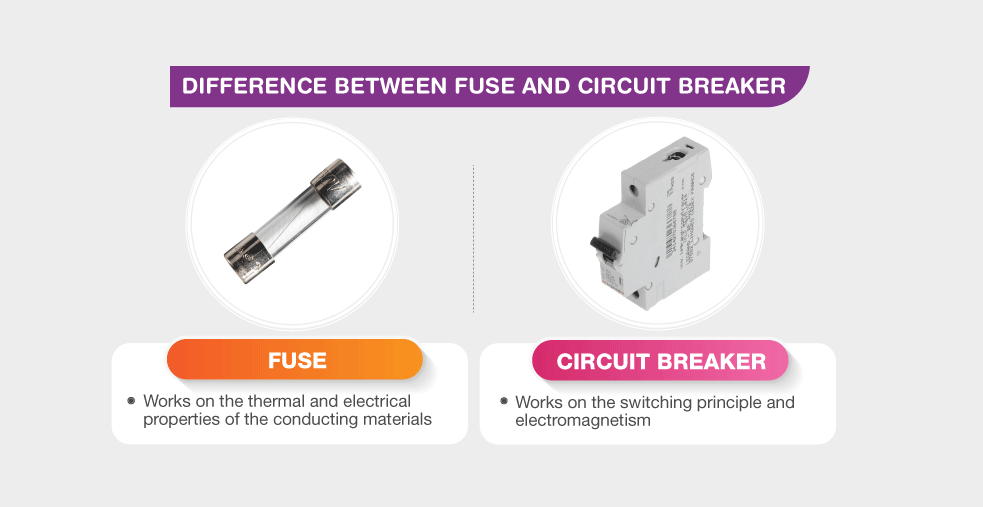
- The Fuse operates on the principle of thermal and electrical properties of the conducting substances, whereas the Circuit breaker operates on the electromagnetism principle and the switching mechanism.
- The broken fuses cannot be reused again, but the Circuit breakers can be used more than one time. As a result, there is no requirement to replace a circuit breaker after the occurrence of any fault.
- The auxiliary contact is needed in a circuit breaker, while no auxiliary contact is required in the fuse.
- The circuit breaker can be employed as an ON/OFF switch, whereas the fuse cannot be used as an ON/OFF button.
- A circuit breaker operation is based on the ambient temperature, but fuses are independent of ambient temperature.
- The characteristic diagram of the fuse changes due to the Ageing Effect, and, as a result, it needs to be replaced after a while because of the nuisance and tripping. However, the performance of a Circuit Breaker does not shift.
- The fuse presents protection against just the power overloads, while a circuit breaker provides an appropriate operation to protect against both short circuits and power overloads.
- A circuit breaker performs to interrupt the circuit, and a relay system is required for the detection of any fault in that circuit. But the fuse supports both interruption and detection processes.
- The breaking capacity of a fuse is less than a circuit breaker.
- Circuit Breakers are more costly, whereas the cost of a fuse is low.
- The operating time of a fuse is too little, about 0.002 seconds, while the working time of a circuit breaker is relatively more than that of a fuse. It is between 0.03 to 0.06 seconds.
- The mode of working of a fuse is fully automatic, but the circuit breaker can be run manually as well as automatically by using a relay system.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of a Circuit Breaker and a Fuse?
The advantages and disadvantages of a circuit breaker and a fuse are listed below:
- Fuses are less expensive, and accessible in nearly any hardware market. They perform quickly to overloading, providing more protection to sensitive electric instruments. The only problem in this is that if the system is prone to surges that uniformly cause fuses to blow, then the fast reaction to the overloading can be introduced as a disadvantage.
- When fuses are broken, they require to be replaced. This can be complex, particularly in a dark room, or if the new fuse is not available at the time of requirement. Another disadvantage is that people usually replace a fuse themselves with the new one that actually has a greater current or voltage rating, which is too high for the need or application. It can then cause an overheated system.
- Fuses are commonly speaking, simple to see which switch has been broken and which would require to be reset. The average homeowner can find it secure because there is no doubt about selecting the best fuse rating and all of the electrical junctions are in the breaker box.
- The main disadvantage of employing a circuit breaker is that it can be more expensive to set, replace, and repair. Circuit breakers don’t operate as quickly as fuse in power limitations. This means it would be feasible that electronic devices connected to an electric diagram could be damaged by the power that is just let through in the circuit. It can be more sensitive to movement and vibration, which may permit the switching process to detect new reasons that are unrelated to the overloads in the system.
- Fuses and circuit breakers are not interchangeable for all industrial applications. For instance, a fuse should not be utilized in applications that need a GFCI. Electricians are best qualified to select whether a circuit breaker or a fuse is more suitable for any particular application or electrical installation. If you have any questions about a special project and would like to explore more, you should talk to an accomplished expert.
What About Safety Precautions?
- Always check the local building codes when adding circuits or wiring in your home.
- Never eliminate the cover of your electrical box to expose it unless you are a skilled electrician.
- When a fuse blows or a breaker trips, find out what the main cause is. Many times, homeowners either replace the fuse or reset the breaker, which does not solve the basic problem. Check to ensure that all circuits are not overloaded with too many devices or other electrical appliances.
- Never try to change your panel. You should talk to a licensed electrician to resolve the problems.
- Always ensure that the breakers are in the proper working order.
In conclusion, circuit breakers or fuses are one of the most vital safety mechanisms in your house. If you have added new places or electrical outlets, you might consider having your service updated if required. If so, give an electrician a call to ensure you have the electrical service that is appropriate for your home and family.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip



Great post! Very informative. What an amazing and well-thought-out write-up. thanks for sharing
Thank you for your comment. Please visit our other posts on Linquip.
I am in favor of circuit breakers, they are more reliable and multifunctional. I have seen many scenarios where circuit breakers performed much more efficiently than fuses.
Thanks Aria for sharing your experience with us. It was a pleasure having you visit us.
The greatest auto reset circuit breaker should be installed in your vehicle’s electrical system. You won’t have to be concerned about blown fuses because of overloading and short circuits if you have this gadget.
Thanks for visiting our website and leaving your comment, David! We hope to hear from you again in our other posts.