Developers of distributed generating systems have a choice between two primary power sources: gas engines and gas turbines. Both are proven worldwide in thousands of cogeneration (combined heat and power or CHP) installations. Gas engines and turbines are used in CHP applications that include electric utilities, hospitals, universities, district heating, seawater desalting, food processing, textiles, petrochemical refining, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, pulp and paper, and general manufacturing. Over the years, both technologies have steadily improved in efficiency, reliability, emissions performance, and operating costs. Both gas turbine and gas engine have their characteristic features, and we thereby provide the difference between gas turbines and gas engines to suit the needs of the customer. Read this new blog in Linquip to find out more about them.
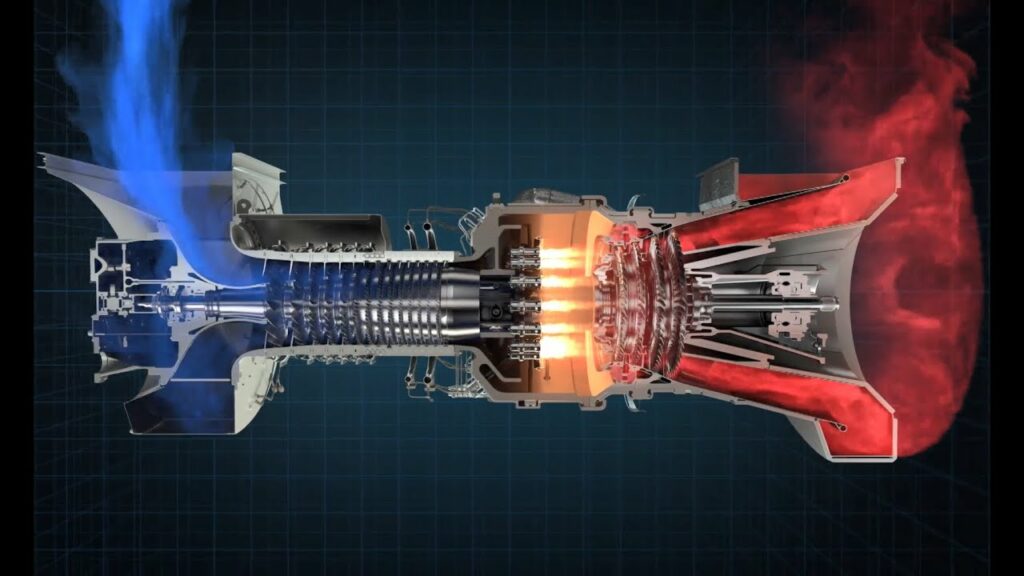
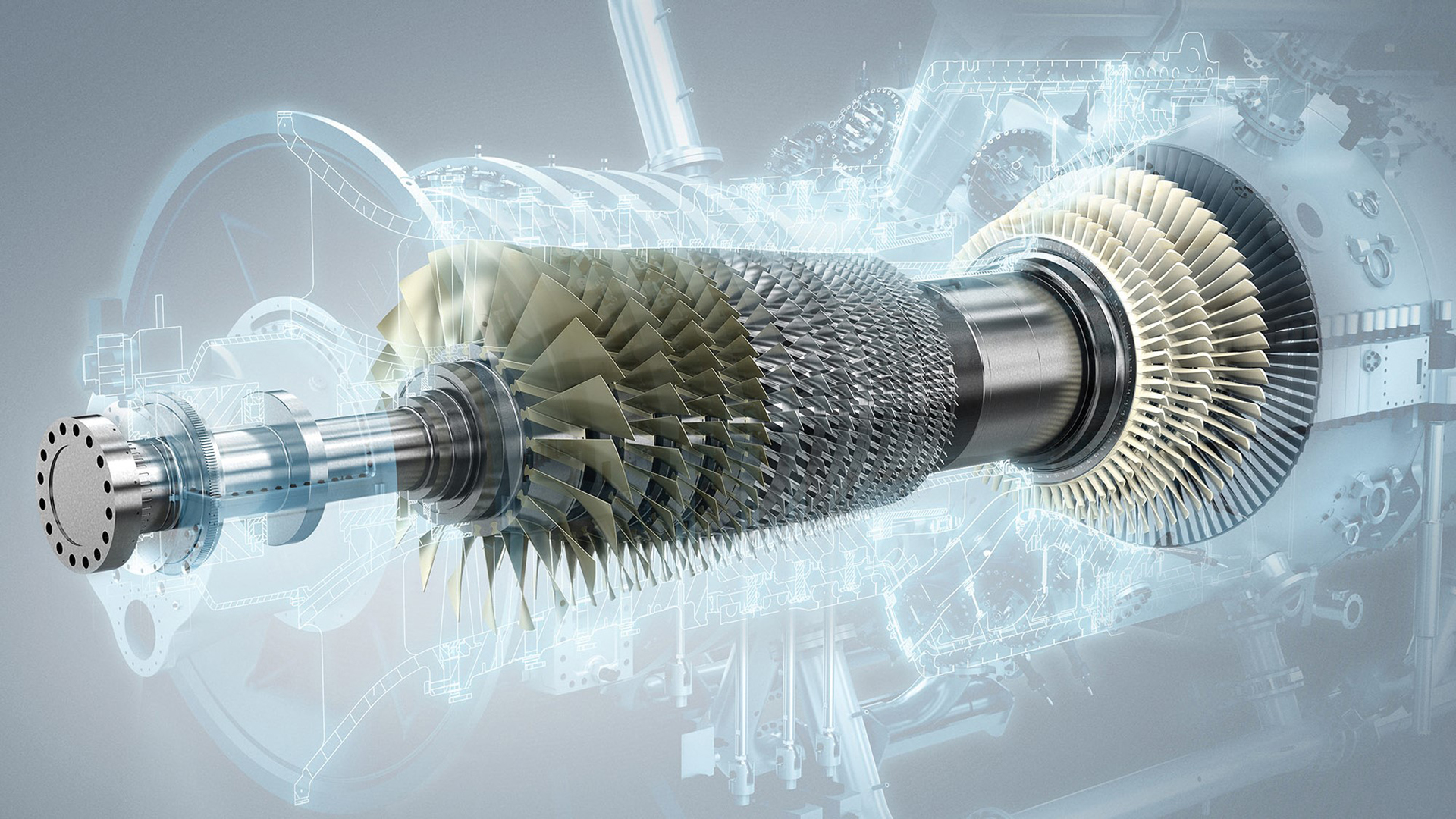
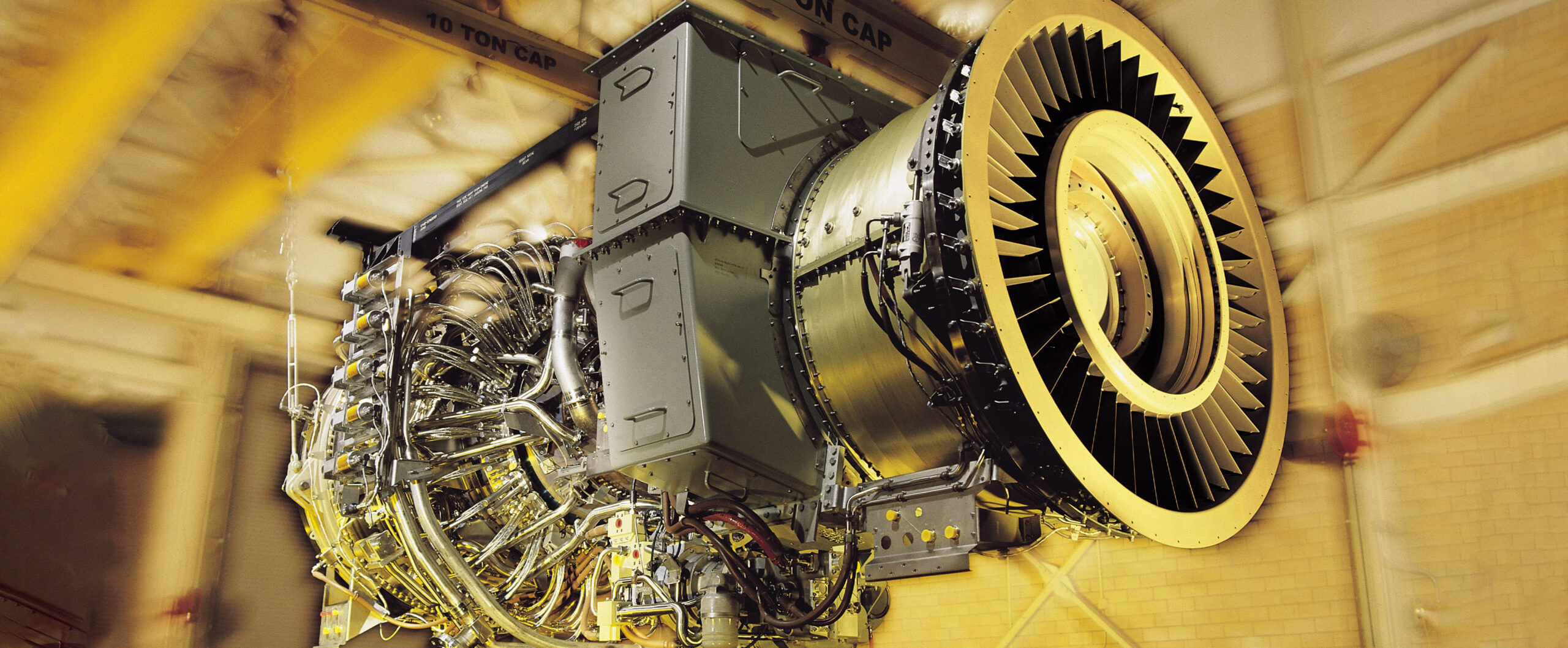
Gas Turbine
A gas turbine is defined as an engine driven by the pressure of burning compressed air and fuel. A gas turbine, the brain of the power plant, is a combustion engine that converts liquid fuels, especially natural gas, into mechanical energy. This energy powers a generator that in turn produces electricity. Within the gas turbine, there is a fuel-air mixture being heated at extremely high temperatures. This causes the turbine blades to spin fast. Gas turbines are used to power aircraft, trains, ships, electrical generators, pumps, gas compressors, and tanks.
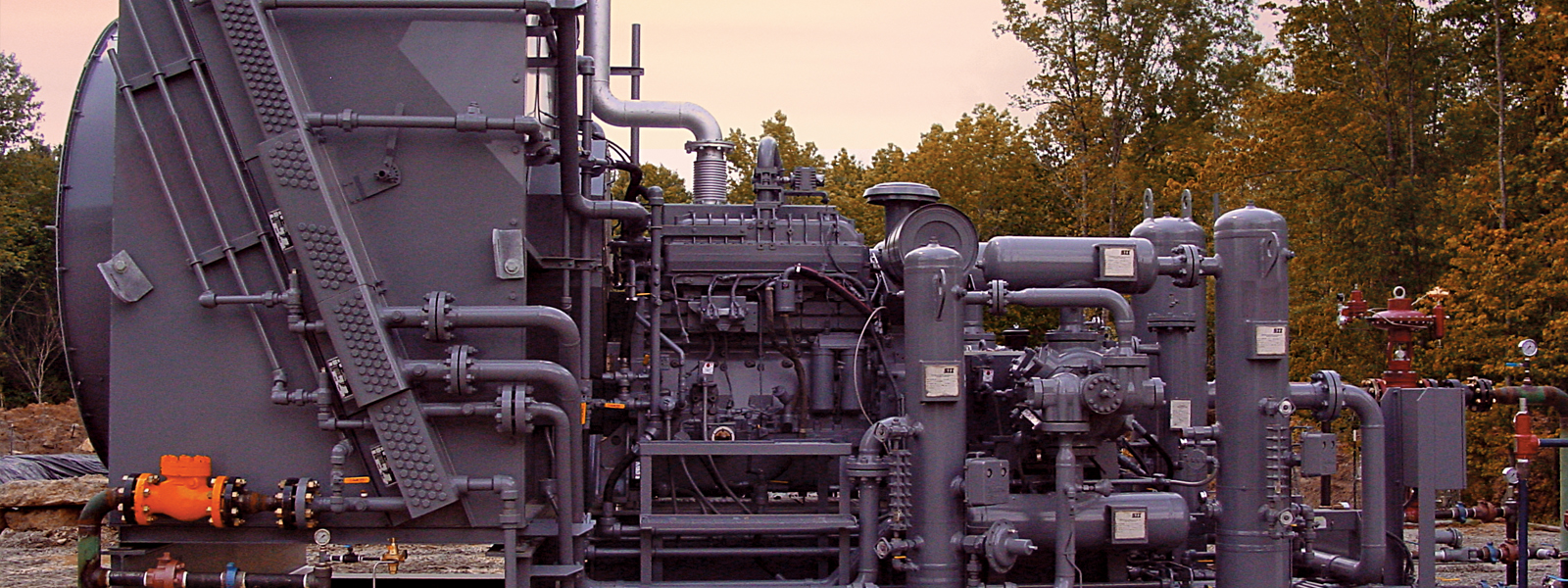
Gas Engine
The gas engine is an engine driven by the production, expansion, or combustion of gas. Gas engines are manufactured in big numbers and cheap while central power plants are one-of-a-kind technology. In the power plant setting, you will find several gas engines interconnected to form generating sets. However, every engine connects to its shaft which connects to an electric generator. The sets are available in standardized sizes of up to 20 MW. The gas engine significantly contributes to CO2 reduction by high-efficiency operation using natural gas and city gas, as well as low-calorie gases such as those generated in gasification melting furnaces.
Gas Turbine VS. Gas Engine
There is a description of the difference between gas turbines and gas engines by considering several factors. Various factors, like those mentioned, are taken into account while selecting a gas turbine or a gas engine for a particular application.
The following factors show the main differences between gas turbines and gas engines.
Electrical Efficiency
- Gas turbine efficiencies range between 29 and 33%.
- Gas engine efficiencies range between 48.5% and 49%.
Energy Ratio of Cogeneration
- In a gas turbine, the energy ratio of cogeneration consists of electricity (33 percent), steam (50 percent), and loss (20 percent).
- In a gas engine, the energy ratio of cogeneration consists of electricity (49 percent), steam (15 percent), hot water (13 percent), low-temperature water (10 percent), and loss (13 percent).
Type of Heat Needed
- In the gas engine, mostly steam provides the needed heat.
- In the gas engine, hot water and some steam provide the needed heat.
Total Efficiency of Cogeneration
- The gas turbine operates at 80% to 83% total efficiency of cogeneration.
- The gas engine operates at 63.5% to 77% total efficiency of cogeneration.
Electrical Efficiency (Partial Load)
- The electrical efficiency of the gas turbine is good.
- The electrical efficiency of the gas engine is very good.
Exhaust Heat
- The gas turbine has a high exhaust gas temperature and amount.
- The gas turbine has a low exhaust gas temperature.
NOx Emissions (O2=15%)
- In a gas turbine, NOx emission is about 15 to 25 ppm.
- In gas engines, NOx emission is about 57 ppm.
Vibration
- The vibration of the gas turbine is ultra-low.
- The vibration of the gas turbine is low.
Machine Size
- The gas turbine includes machines in small sizes.
- The gas turbine includes machines in large sizes.
Start-up Time
- In a gas turbine, start-up time is 20 minutes.
- In a gas engine, the start-up time is 10 minutes.
Maintenance Interval
- The maintenance interval of the gas turbine is very long.
- The maintenance interval of the gas engine is very long.
Few more points about the difference between gas turbines and steam engines to keep in mind:
- With more gas engine products in the larger (more than 3 MWe) size range coming to the market, improved performance (i.e. greater electrical efficiencies), and a greater demand for flexible operation, gas turbine suppliers are increasingly coming under pressure from gas engines.
- Peaking power plants need to have the ability to operate flexibly, often with fast ramp-up/ramp-down rates. Gas engines are well-placed to meet these needs. The transition to gas engines is already well underway although gas turbines will continue to be commonplace, especially within larger peaking plants.
- 30 MWe gas turbines will likely continue to have the majority market share in mid-sized and large industrial sites with electricity and high-temperature steam/heat needs. However, gas engines (100 kWe to 20 MWe) are increasingly stealing market share across a variety of other end-use sectors. Gas engines have increased market share at the expense of gas turbines which are less able to ramp up/ramp down as quickly.
Both gas turbines and gas engines have proven themselves to be valuable to users in power generation applications. Well accepted in the marketplace today worldwide, each technology has found favor with users looking for reliable power and thermal alternatives. All of this means a strong opportunity for gas-fired CHP systems. The time is right for industrial and commercial facilities power users and producers to explore the economic possibilities of CHP with today’s gas engine and turbine technologies.
So, now you know everything you needed to know about the difference between a gas turbine and a gas engine. Do you think there are other differences than what we mentioned above? Share your thoughts with Linquip in the comment section. And feel free to sign up on our website if you want our experts to answer your most complicated questions regarding this field.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip
- Gas Engine Services
- Industrial Gas Engine Services
- Industrial Gas Engine Installation Services
- Industrial Gas Engine Maintenance Services
- Industrial Gas Engine Services in Texas
- Industrial Gas Engine Installation Services in Texas
- Industrial Gas Engine Maintenance Services in Texas
- The Difference Between Diesel Engines and Gas Engines: Discover the distinction, decide the best
- The Difference Between Diesel Engine and Petrol Engine: which one best works for you?
- Difference Between Pump and Turbine
- Differences between Pelton, Francis, and Kaplan Turbine
- The Ultimate Guide to The Difference Between Gas Turbine and Reciprocating Engine
- Quick Guide: The Difference Between Gas Turbine and Diesel Engine
- Warehouse Lighting Fundamentals
- Beginner’s Guide: The Difference Between Gas Turbine and Gas Engine
- The Practical Guide To The Difference Between Gas Turbines and Steam Turbines
- More Information about GE Frame 7 Gas Turbine
- See List of Gas Turbine Products
- See List of Siemens Gas Turbine Products
- See List of General Electric (GE Power) Gas Turbine Products