The difference between refrigeration and air conditioning depends on their application, operating fluid cycle, and structure. However, Refrigeration and air conditioning are very similar in many ways, including working with chemicals, physical effects such as expansion and evaporation, and liquefaction of gas to receive energy and reduce the temperature.
This factor causes the development of two separate categories of refrigeration and air conditioning. In this article, we study every difference between refrigeration and air conditioning.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in the Definition
The names of refrigerators and air conditioners are each based on the concept introduced here.
Refrigeration
Generally, refrigeration means cooling an environment or a system, or an object at a temperature below ambient temperature. That is heat transfer from a cold environment to a warm environment. This process is contrary to the natural process of heat transfer from a point with a higher temperature to a lower temperature. So refrigeration is artificial cooling.
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning provides the appropriate conditions for the occupants or equipment within an environment to bring the conditions to comfort. This goal is achieved by removing heat or dehumidifying the environment. Air conditioning is indicated as AC, A/C, or air con.
Air conditioning works for both domestic and commercial environments. Of course, air conditioning is also used for electronic equipment in which heat generation takes place, such as personal computers.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in the Operation Goals
The primary task of refrigeration is to transfer heat from a cold to a warm environment. But in the case of air conditioning, the heat is taken from the environment, and the environment remains cold. So, the heat goes to an environment with a lower temperature.
Refrigeration
Refrigeration, an action to cool the products, is the system that deals with body cooling successive processes. Thus cooling is the extraction of energy to decrease the internal energy of an object. It is done by reducing the temperature.
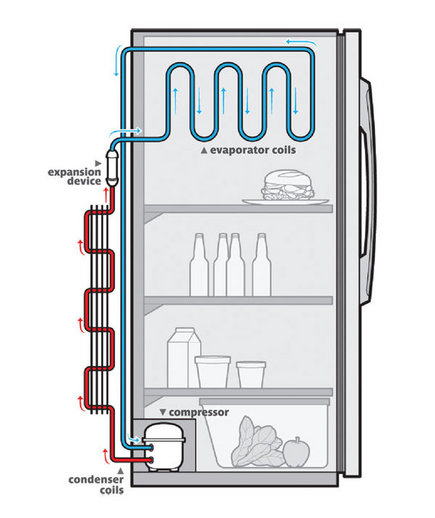
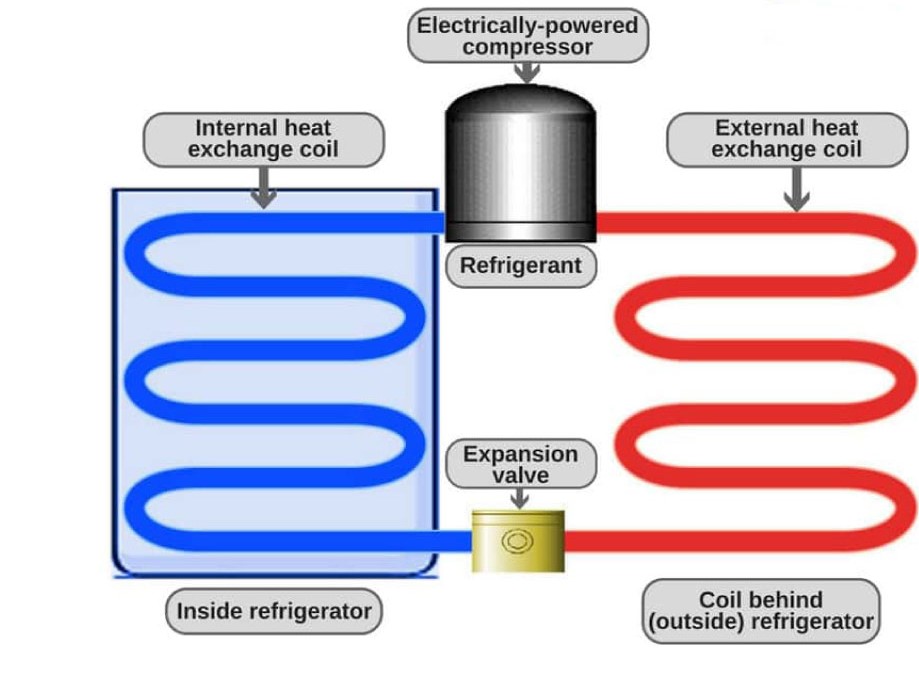
To complement refrigeration a set of equipment is used to convert liquids to gas at very low temperatures. The coolant substance is usually chlorofluorocarbons, i.e. Freons. Refrigerators typically consist of a series of sealed twisted tubes in which Freon is circulated continuously. Freon is frequently altering the phase between liquid and gas. Liquid Freon receives the heat, and with a temperature rise, it changes into a gas phase. Consequently, the temperature of the objects inside the refrigerator drops.
Air Conditioning
The air conditioning system ordinarily spreads the conditioned air in various indoor spaces to provide comfort and high-quality air. In a more general scheme, this term includes any possible technology that adjusts air with its application, such as cooling, heating, dehumidification, and ventilation. But to put it simply, the air conditioning system takes the hot air and cools it with evaporation operation.
It has two principal parts: evaporator and condenser, which both are working as an exchanger. The entire unit circulates the working substance called coolant in different states such as including liquid and gaseous. The cooling process is like what happens in heat pumps for heating, and they both work based on the Carnot cycle. The evaporator takes the air heat and causes the air and its surrounding ambient to be cooled.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in the Applications
Another difference between refrigeration and air conditioning is their applications.
Refrigeration
Typical uses of refrigerators include household, industrial, and cryogenic refrigerators and freezers.
Air Conditioning
Common applications of air conditioning are classified into two general groups: comfort and process.
Comfort applications include commercial buildings, tall buildings such as dormitory blocks or high-rise apartments, transport such as airplanes, institutional buildings such as government buildings, and low-rise buildings such as residential apartments, industrial buildings, and sports stadiums.
Process applications include biological and chemical laboratories, clean rooms to provide highly accurate temperature and humidity conditions, animal laboratories, cooking or food process environments, nuclear power equipment, textile manufacturing, and plant growing environments.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in Cycles
Here, working principles as another difference between refrigeration and air conditioning are discussed.
Refrigeration
The basis of refrigerator working is based on two simple physical principles.
The first principle is that with compression, a gas gets hotter, and its volume decreases. Conversely, by the expansion of a gas, it takes up more volume. As a result, the heat inside its molecules is divided among a larger volume of space, so the entire gas temperature falls, and it gets cooler.
The second principle is that two objects with different temperatures that are in contact with (or adjacent to) each other exchange energy in such a way that the warmer object decreases in temperature and the colder object increases in temperature. This is a reading of the second law of thermodynamics.
The refrigeration cycle involves the passage of refrigerant through several sections, which are explained below.
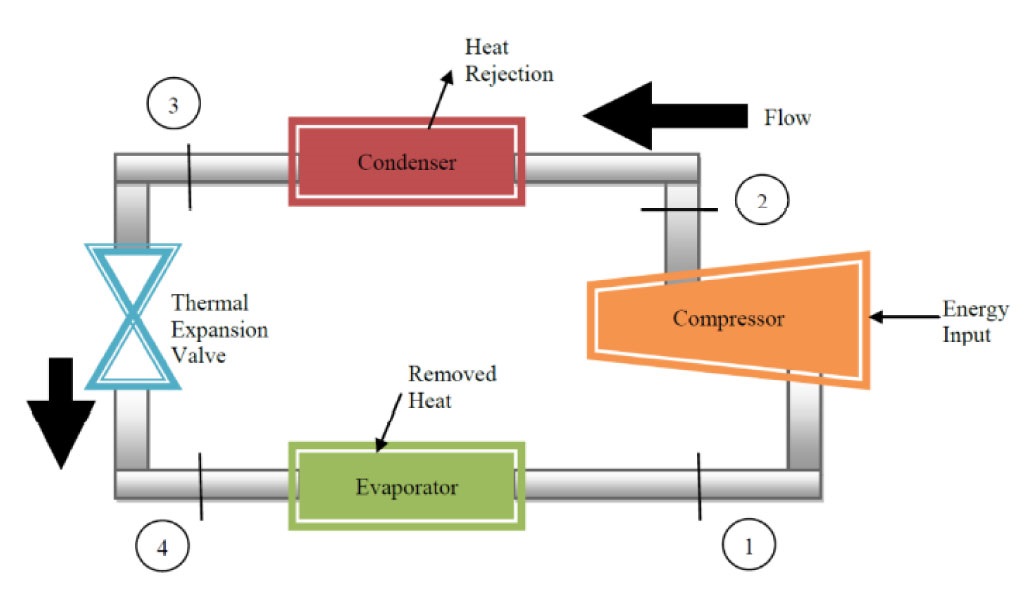
1→2 The compressor compresses the coolant vapor to increase the pressure and temperature and drives it into the condenser coils locating outside the refrigerator.
2→3 The hot gas circulating in the condenser coils touches the ambient cooler air temperature outside the refrigerator, and it gets to the liquid form.
3→4 The coolant in the liquid form cools, and its pressure drops as it flows through the expansion valve.
4→1 The coolant takes the heat from inside the fridge when it passes over the evaporator coils and cools the fridge air.
Finally, the coolant evaporates to gas due to an increase in temperature and returns to the compressor, then the cycle repeats itself.
The principal element in a refrigerator that requires power is the compressor. It is like a pump that is run by a motor. The sound of the fridge is because of the compressor working. Moreover, the thermostat manages the temperature of the refrigerator by turning the compressor on-and-off.
Air Conditioning
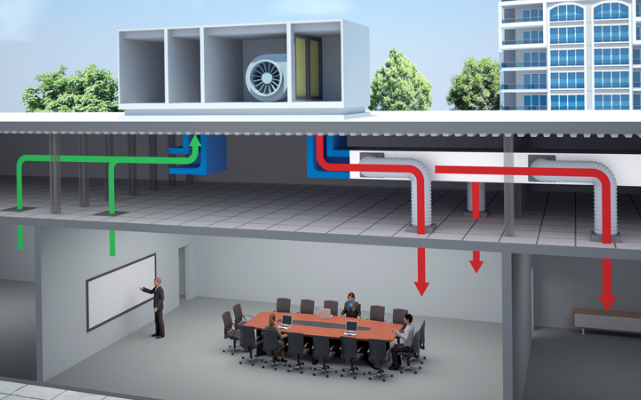
Based on the following figure, some successive steps are taken to perform air conditioning.
1→2 The air with the high temperature inside the building is pulled employing a vent and blows on the cold evaporator coil. The application of the evaporator coil is to take heat from the air or cooling the air. In order to blow the colder air into air channels, a fan is used so that it is distributed throughout the room space.
The refrigerant absorbs the heat of the passing air; it turns into a gas and moves towards the compressor.
2→3 The compressor reduces the gas volume. The result is increasing in the pressure and temperature of the coolant. Now it is prepared to become condensed.
3→4 The coolant as a superheated gas enters the condenser, in contact with the outside air. The outside air takes the heat from the coolant. So the temperature of the coolant reduces, and its phase changes from a gas into a liquid.
4→1 Once the heat from the coolant is pushed to the outdoors, the cold coolant moves back indoors toward the evaporator. So the process repeats until the inside temperature of the building reaches the desired degree. At this point, the thermostat sends a blackout message to the air conditioner.
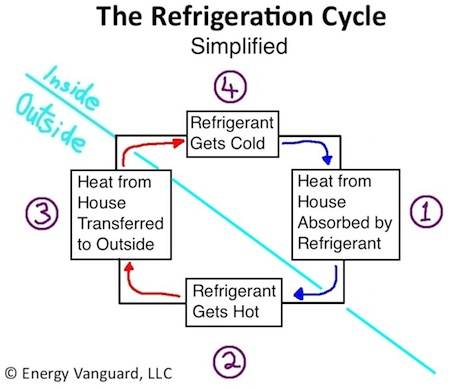
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in Gas Supply
A significant difference between refrigeration and air conditioning is the supply of gases.
Refrigeration
In the case of refrigeration, systems have installed gas in a group of tubes. In old refrigeration systems, this gas was Chlorofluorocarbon or CFC, but this has adverse influences on people and the environment because of the harmful effect on the atmosphere. Therefore today, refrigerators do not include CFC gases. However, HFC-134a is the single gas employed as a coolant in refrigerators.
Air Conditioning
Air conditioners use built-in chemicals to cool the air inside an environment such as a heated room. These gases take heat from the air and circulate the cooled air inside the room or environment.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in Circulation Systems
Air conditioning systems have circulation devices to throw cool air away from the cooling system. But, refrigeration systems are equipped with circulation systems to keep the coolant in an enclosed space.
Refrigeration
Refrigerators circulate cool liquids and gases within a group of tubes. Cool air is sucked from inside a refrigerator into a compressor to be recycled through the pipes.
Air Conditioning
In the case of air conditioners, although they employ tubes in the coolant system, they have fans for air dispersal. Unlike refrigeration systems, which retain gases in a confined space, air conditioning systems disperse cool air to the vast areas.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in Evaporation Process
The role of operators in refrigeration and air conditioning systems is summarized as follows:
Refrigeration
Refrigeration systems circulate HFC into a chamber with low pressure to boil the fluid. The process of boiling makes HFC vaporize, converting a liquid to a gas. It can be accomplished in one of two forms: boiling or evaporation. Thus air conditioners vaporize the liquid with the mechanism of evaporation, but the vaporization in refrigerators occurs through boiling.
Air Conditioning
The air conditioning system uses an evaporator in order to convert the liquid into gas. An evaporator is a little and tight hole, and its application is to change the pressure of liquid until it evaporates.
The Difference between Refrigeration and Air Conditioning in Terms of Structural Integrity
Both systems include a condenser, an evaporator, and a compressor, which fit into the system in two different ways.
Refrigeration
In the case of refrigerators, the compressor and condenser units are integrated with the evaporator.
Air Conditioning
In an air conditioner, the compressor and condenser units are both separate from the evaporator.




Very good explanation of refrigenation and air-conditioning.