The main difference between step up and step down transformer is their performance while operating. The step up transformer increases the output value, while the step down transformer decreases the output value. Some other differences are discussed below, considering important characteristics, including winding, voltage, the thickness of the conductor, the number of turns, and application.
What is the Difference Between Step Up and Step Down Transformer?
A transformer is a static electrical instrument that transmits AC electrical energy from one system to the other at an equal frequency, but the voltage rating is commonly modified. Electric power is needed to be transformed at high voltage for economic reasons, while it should be used at low value from a safety point of view. This raise in voltage for transmission and reduction in voltage for use can only be obtained using a step up and step down transformer.
The main difference between step up and step down transformer is that the step up type improves the output value, while the step down type reduces that value. Visit here to explore more about the difference between step up and step down transformer.
Step Up Transformer vs. Step Down Transformer

Output Value
The output value of the step up transformer is more than that of the supply voltage, while the output value of the Step-down transformer is less than that of the main voltage.
Winding
LV winding of the step up type is the primary, and the HV section is the secondary. Otherwise, the HV section of the step down transformer is the primary, and the LV side is the secondary.
Voltage
The secondary voltage of the step up type is more considerable than its primary voltage. The secondary voltage of the step down form is less than its primary value.
Number of Turns
The number of turns in the primary winding of the step up type is less than the secondary winding. The number of turns in the primary section of the step down transformer is higher than the secondary side.
Current
The primary current of the step up transformer is higher than the secondary value. On the other hand, the secondary current of the step down type is more than the primary current.
Application
A step up transformer is typically employed for power transmission. For example, the generator transformer in the power plant is one application of a step up type.
A step down transformer is applied in the power distribution systems. The device in the residential colony is one application of a step down transformer.
Definition of a Step Up Transformer
When the voltage is increased on the output section, the transformer is introduced as the step up transformer. In this type, the number of turns in the secondary side is often higher than the turns in the primary section since a great voltage is induced on the secondary winding of a transformer.
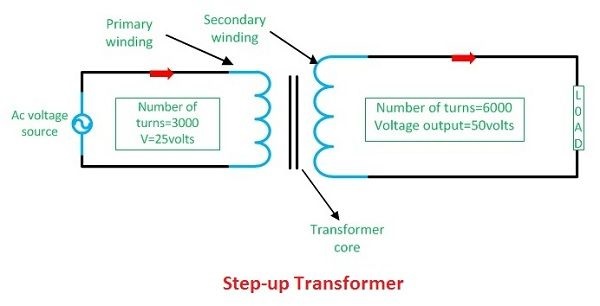
The T1 and T2 are the numbers of turns, and the E1 and E2 are the voltages on the primary and secondary coils of the transformer.
The number of turns on the secondary side of the transformer is higher than that of the primary one, i.e. T2 > T1. Therefore, the voltage turns level of the step up type is 1:2. The primary coil of the step up type is constructed of thick insulated copper wire since the low magnitude current moves across it.
Applications
- The step up transformer is employed in transmission systems for transforming the high voltage generated by the alternator. The power waste of the transmission network is directly related to the square of the current flows across it (RI2).
- The output current of the step up type is less, and hence it is applied for reducing the power waste. The step up device is also employed for starting the electrical motors, X-rays devices, microwave ovens, etc.
- In countries like India, commonly, power is produced at 11kV. AC power is transformed at very high voltages (220v-440v) over long distances for economic reasons. As a result, a step up transformer is used at the generating source.
Definition of a Step Down Transformer
A step down transformer drops the output voltages, or in other words, it transforms the high-voltage and low-current input into a high-current and low-voltage output. For instance, if the power network carries 220-110V, but the doorbell needs just 16V. Therefore, a step down transformer must be used to decrease the value from 110V or 220V to 16V.
Voltages are stepped down to 440v/230V for safety reasons to support different regions. As a result, the number of turns on the secondary coil is less than the primary one. So, less voltage is produced at the output (secondary) end of the device.
The voltage turn ratio of the step down type is 2:1. The voltage turn ratio specifies the magnitude of voltage transformation from the primary to the secondary sections of the device.
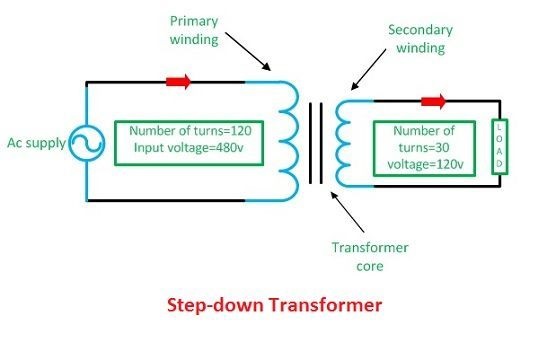
The step down type is constructed of two or several coil wounds on the iron center of the device. It operates based on the magnetic induction principle between the coils. The voltage applied to the primary section of the winding magnetizes the iron part, which induces the secondary coils of the device. Therefore, the voltage converts from the primary to the secondary side of the transformer.
Applications
The step down transformer is applied for electrical isolation cases, for controlling the home appliances, in a power distribution network, in a doorbell, etc.
Key Difference Between Step Up and Step Down Transformer
- Once the output (secondary) value is higher than its input (primary) value, it is called a step up transformer, whereas the output (secondary) voltage is less in the step down transformer.
- In a step up type, the low voltage section is the primary side, and the high voltage section is the secondary side, whereas the low voltage winding is the secondary side in the step down transformer.
- In the step up form, the magnetic field and current are less developed in the secondary section, and it is extremely increased in the primary side, whereas, in the step down type, the voltage is low on the secondary side. Therefore, the current and magnetic field is great.
Note1: The current is directly related to the magnetic field.
Note2: Based on Ohm’s laws, voltage is directly related to the current. If we improve the voltages, then the current will also raise. But in the transformer for transmitting the equal amount of power, if we raise the voltage, the current will be reduced and vice versa. Therefore, the power remains identical in the sending and receiving lines of the system.
- In a step up transformer, the primary coil is constructed of thick insulated copper wire, and the secondary section is constructed of thin insulated copper wire, while the thick insulated copper wire is applied for creating the secondary side in the step down transformer since the output current is too great.
Note: The wire thickness is based on the potential of current flow across them.
The step up type extends the values from 220 Thickness -11k Thickness or above, while the step down transformer decreases the voltages from 440-220V, 220-110V, or 110-24V, 20V, 10V, etc.
Point to Remember
The same transformer can be applied as a step down or a step up device. It is based on how it is configured in the network. If the input source is provided on the low voltage winding, then it becomes a step up device. On the other hand, if the input source is provided on the high voltage section, the device becomes a step down one.




Thanks a lot for your consideration. Please read our other posts and comment on them.
Good Day Dears
I HAVE 2500KV STEP DOWN TRANSFORMER CAN I USED AS A STEP- UP TRANSFORMER?
thanks
Thanks for visiting our website. You can visit our Industrial Equipment page, where you can find various TRANSFORMERs based on your application and demand. You can also visit our expert page and take advice from hundreds of professionals on your issue.