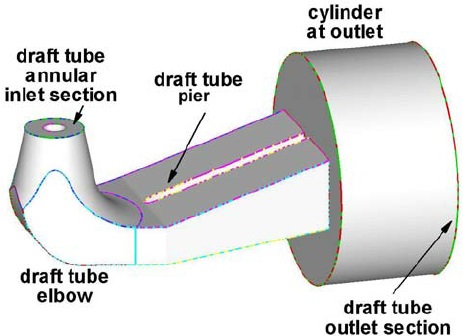
A draft tube is an integral part of a turbine. It helps to get water from the reaction turbines smoothly. However, this is only one of its application in different turbines. Today we will see what is a draft tube, the functions, the types, and the advantages. Later on, we will discover the efficiency of the draft tube. Follow the post here at Linquip.
The Draft Tube is a connecting pipe that is normally installed at the turbine’s outlet or exhaust, and it transfers the water’s kinetic energy to static pressure at the turbine’s output. This prevents the kinetic energy of the water flowing through the turbines’ output from dissipating. It’s often found in power turbines including reaction turbines, Kaplan turbines, and Francis turbines. A draft tube is an important product of employing industrial tools. Draft tubes are provided by several suppliers and companies, different Manufacturers, and a lot of distributors and there are a lot of Draft Tubes for Sale on Linquip.
There is a complete list of draft tube services on the Linquip website that meets all of your needs. Linquip can connect you with a number of draft tube service providers and experts who can help you. Linquip offers a team of Draft Tube Specialists and subject matter experts available to help you test your equipment.
What is a Draft Tube?
A draft tube is a type of tube that connects the exit of the water turbine to the tailrace. The tailrace is the water channel that takes the water out of the turbine. It is usually located at the outlet or exit of the turbines and converts the kinetic energy of the water at the outlet of the turbine to static pressure. The materials used to create a draft tube are cast steel and cemented concrete.
What is the Purpose of the draft tube?
The principal purpose of the draft tube is to convert water kinetic energy into pressure energy. To decrease the velocity of the water and to raise the pressure of the water before joining the tailrace, the pipe is used to steadily increase the cross-sectional area. The draft tube raises the water pressure to the atmospheric pressure. To tolerate the high pressure and speed of the water, the tube must be strong enough.
Types of Draft Tube
Various forms of draft tubes are available. There are mainly 4 types of draft tube, and those are:
- Conical draft tube
- Simple elbow draft tube
- Moody spreading draft tube
- Elbow draft tube with a varying cross-section
conical draft tube
In this type of draft tube form, the flow direction is straight and divergent. This tube style is made of mild steel plates. It is tapered in shape and the outlet diameter is greater than the inlet diameter of the draft tube. The tapered angle of the draft tube should not be too wide to induce a divergence of the flow from the wall of the draft tube. This angle should also not be too short, since it would require a longer draft tube that brings a substantial loss of kinetic energy. So, the angle of the taper is still almost 10 degrees.
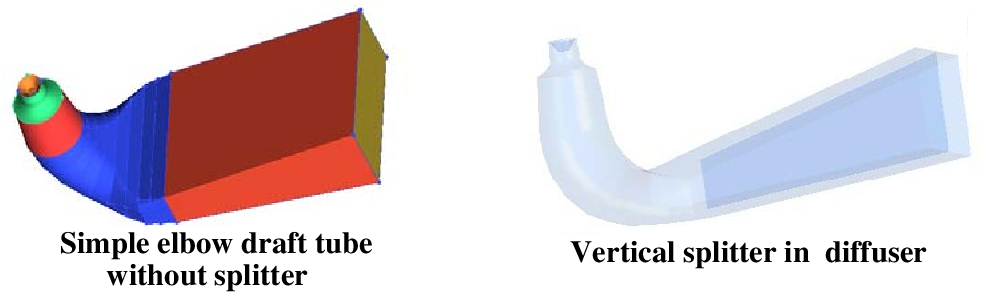
Simple Elbow Draft Tube:
The shape of the tube is like an elbow in a simple Elbow draft Tube. It is used in the Kaplan turbine. In this type of draft tube, the cross-section area remains the same for the entire length of the draft tube. The inlet and outlet of the draft tube are circular. This draft tube is used at low head positions and the turbine is to be mounted next to the tailrace. It helps to minimize the expense of drilling and the exit diameter should be as wide as possible to recover kinetic energy at the runner outlet. This tube has a moderate efficiency of around 60%.
moody draft tube
The outlet of the draft tube is split into two sections in this form of the draft tube. Moody draft tube is similar to a conical draft tube and is with a central core component that divides the outlet into two parts. There are one inlet and two exits for the draft tube. The main aim of this type of draft tube is to reduce the swirling motion of water. The efficiency of this type of tube design is almost 88%.
Elbow draft tube with varying cross-section:
An elbow draft tube with varying cross-section is an improvement of a simple elbow draft. The inlet is circular and the outlet is rectangular in this type. In general, the horizontal section of the draft tube is inclined up to avoid air from approaching the exit area. This type of tube varies in its cross-section from inlet to outlet. The outlet is still beneath the tailrace. The performance of this type of draft tube is used with the Kaplan Turbine at about 70%.
draft tube function
The primary function of the draft tube is to control the flow of water. The turbine has a tailrace. The turbine is attached to this tailrace by the tube, causing the turbine to be beyond the water but still have access to the water. It requires the negative head to be formed at the outlet of the runner and hence raises the net head of the turbine. The turbine can be mounted above the tailrace without any lack of net head and thus the turbine may be adequately inspected.
Moreover, it transforms a significant portion of the kinetic energy wasted at the outlet of the turbine into usable pressure energy. Without a draft tube, the kinetic energy rejected at the outlet of the turbine would be lost to the tailrace. The draft tube stops the water from splashing out of the runner and leads the water to the tailrace.
Advantages of Draft Tube
Some of the advantages of using the draft tube are:
- Using the draft tube prevents the splashing of water from the runner and leads the water to the tailrace.
- The net turbine head is raised as the height is increased between the turbine exit and the tailrace because of the use of the draft tube.
- The use of a draft tube greatly decreases the amount of kinetic energy required at the tailrace.
- The transfer of kinetic energy into pressure energy results in a negative pressure head at the outlet of the turbine, which serves to improve the total performance of the turbine.
Draft Tube efficiency
The efficiency of the draft tube is the ratio of kinetic power transfer to the kinetic energy available at the inlet to the draft tube. The efficiency of a tube depends on how much of the kinetic energy of the water is converted into pressure energy. The more energy is converted, the more efficient the draft tube can be.
draft tube in Kaplan and Francis turbines?
In the case of Kaplan and Francis turbines (reaction turbines), the head usable at the turbine inlet is usually low, so the turbine is far closer to the tailrace to achieve the full head. As much of the water’s pressure energy is converted into the Turbine’s mechanical energy, the pressure at the outlet is lower than the atmospheric pressure. Therefore, if water pressure is less than the atmospheric pressure at the exit of the turbine, then it induces the tail rushing water back into the turbine.
Today, the elevated pressure of water is significantly greater than the atmospheric pressure. It solves the dilemma of the water backflow from the tail to the turbine outlet. It should be noted that the water flow back will do significant damage to the turbine which can interrupt the turbine from working.
Final words
That was all about the draft tube. Within this blog post, we mentioned the main points about the draft tube-like its purpose, the types as well as the merits. If you like this post or have any idea about the draft tube, please register at Linquip and let us know in your comments. Feel free to ask your questions in the comment as well. And don’t forget to share this post, help more people learn about the draft tube.
Download Draft tube PDF
Read More In Linquip
- Heavy Duty Gas Turbine GenSets Equipment for Sale
- Industrial Gas Turbine GenSets Equipment for Sale
- Marine Gas Turbines Equipment for Sale
- Mechanical Drive Gas Turbines Equipment for Sale
- Micro Turbines Equipment for Sale
- Types of Turbines: Classifications and Types
- Impulse Turbine: Working Principle, Components, and Types
- Beginner’s Guide: The Difference Between Gas Turbine and Gas Engine
- What is Heavy Duty Gas Turbine GenSets?
- What is Industrial Gas Turbine GenSets?
- What is Marine Gas Turbines?
- What is Mechanical Drive Gas Turbines?
- What is Micro Turbines?
- 6B.03 Gas Turbine for Sale
- TG20 Industrial Gas Turbine for Sale
- TG50 Industrial Gas Turbine for Sale
- Gas Turbine Blades & Buckets for Sale
- Nozzles & Shrouds Gas Turbine for Sale