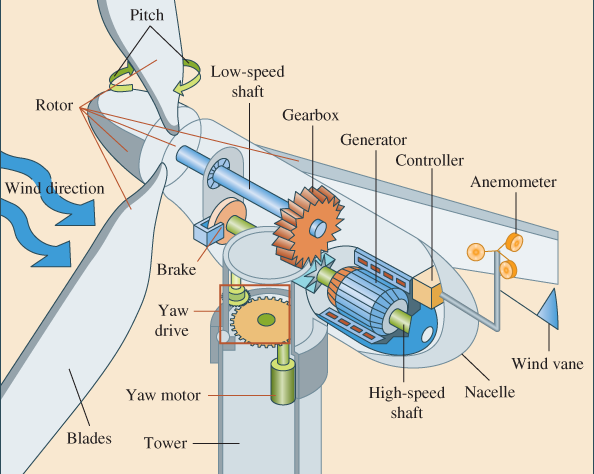
How do Wind Turbine Generators Work? Wind turbines commonly operate on a simple principle: instead of employing the electricity to create wind—such as a fan—wind turbines utilize the wind to produce the electricity. The wind rotates the propeller-like blades of a turbine within a rotor, which turns the generator to create electricity.
How do Wind Turbine Generators work?
Wind flow speeds and patterns vary considerably across the world and are changed by vegetation, bodies of water, and differences in terrain. Humans employ this wind flow, or motion power, for many goals: flying a kite, sailing, and even producing electricity. The terms “wind power” and “wind energy” both explain the procedure by which the wind is utilized to produce mechanical power or electricity. This mechanical power can be employed for different applications (such as pumping water or grinding grain), or a generator can transform this mechanical energy into electricity.
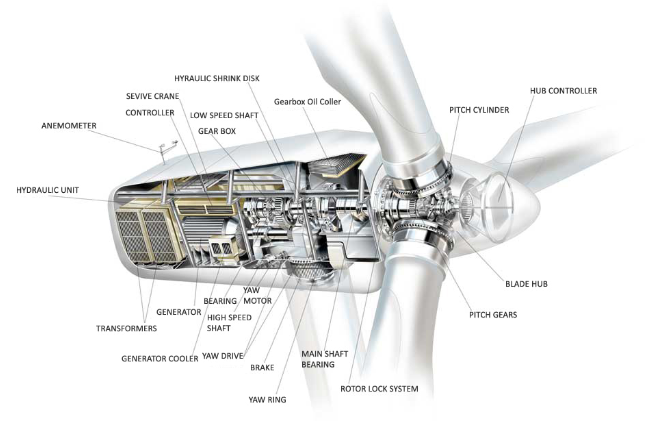
A wind turbine converts the wind power into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the blades of the rotor, which perform like a helicopter rotor blade or an airplane wing. When the wind moves across the blade, the air pressure on one section of the blade reduces. The difference in air pressure in the two parts of the blade makes both drag and lift forces.
The lift force is stronger than the drag, and this forces the rotor to rotate. The rotor is attached to the generator, either straightly (if it’s a direct drive type of turbine) or within a shaft and a series arrangement of gears (or a gearbox) that increase the speed rotation and permit a physically smaller generator. This aerodynamic force effect rotates a generator to produce electricity. Visit here to see this effect theoretically.
How does a Wind Turbine Create Electricity?
The main component of a wind turbine is the generator which transforms mechanical energy into electricity. We’ve known since the early 20th century that if you rotate a conductor in a magnetic environment, then it produces electricity, based on Faraday’s Law. So, the wind supplies the torque and movement, and the generator does the rest.
For an industrial form of turbines, like the ones you may see on wind farms, there is typically an anemometer that is joined to a control panel. The turbine is run at wind velocities of over 8 miles per hour, but the system is shut off with velocities over 50 miles per hour to prevent damage.
The gearbox is utilized to modify the slow-motion we see from the blades turning to the quicker motion of the axis, which practically controls the generator. This is one of the most expensive components of the system, turning speeds of 25 to 50 revolutions per minute into a thousand rpm. It’s one of the fields that developers and researchers are looking to create more efficiently so that a higher current of electricity can be generated at slower speeds.
A yaw drive is typically employed to turn the blade array into the oncoming wind to cope with varying wind directions. The generator makes an AC that is fed into the system and is utilized to energize the surrounding homes. If you want to explore more about the working principle of wind turbines generator, you should first look at the different types of them.
Types of Wind Turbine Generators
When we want to provide the answer to this main question: “How do Wind Turbine Generators Work?”, we should look into the structure of different types more precisely. A wind turbine is constructed from two major parts: the rotor blade and the wind turbine generator or WTG. WTG is the electrical system employed to produce electricity. A low rpm electrical generator is employed for transforming the mechanical rotational energy made by the power of the wind into usable electricity to provide electricity for our homes and is at the heart of any wind energy system.

The transformation of the rotational mechanical energy created by the rotor blades (introduced as the prime mover) into useful electrical energy for use in lighting applications and domestic power or to charge batteries can be operated by any of the following main kinds of rotational electrical systems typically used in wind energy generating systems:
- The alternating current (AC) induction system, also introduced as an Alternator
- The direct current (DC) system, also introduced as a Dynamo
- The alternating current (AC) synchronous system, also introduced as an AC Generator
All these electrical systems are electromechanical instruments that operate based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. That is, they work with the interaction of an electric current and magnetic flux, or flow of charge. As this procedure is reversible, the same system can be employed as a conventional electrical motor for transforming the electrical energy into the mechanical one or as a generator converting the mechanical energy back into the electrical type.
The electrical system most commonly employed for wind turbine applications are those running as generators, with induction generators and synchronous generators being commonly utilized in larger wind turbine generator setups. Typically, the homemade or smaller wind turbines tend to employ a low-speed DC system or Dynamo as they are compact, cheap, and a lot simpler to connect up.
So, does it make a difference which kind of electrical system we can employ to create wind power? The best answer is both No and Yes, as it all depends on the form of the setup and application you want. The low voltage DC output from a generator or older form dynamo can be employed to charge batteries, whereas the higher AC sinusoidal type from an alternator can be joined directly to the local grid.
Also, the output voltage and energy demand are entirely based on the appliances you have and how you want to use them. Additionally, they are related to the place of the wind turbine generator: would the wind source keep it continuously turning for long periods, or would the generator velocity and therefore its output speed down and up with the variations in the present wind.
Electricity Generation
A Wind Turbine Generator is what makes electricity by transforming the mechanical energy into an electrical one. Let’s be precise here; they do not make energy or generate more electrical energy than the amount of mechanical power being utilized to move the rotor blades. The greater the “energy”, or electrical demand placed on the system, the more mechanical load is needed to spin the rotor. This is why the generators come in various sizes and generate various amounts of electricity.
In the case of a “wind turbine generator”, the wind pushes straightly against the turbine blades, which transforms the linear motion of the wind into the rotary type, which is necessary to turn the generator’s rotor, and the harder it pushes, the more electrical power can be produced. Then it is vital to have an appropriate wind turbine blade model to extract as much power out of the wind as possible.
All the electrical turbine generators operate due to the effects of turning a magnetic field past an electrical coil. When electrons move within an electrical coil, a magnetic environment is made around it. Likewise, when a magnetic field flows past a coil of wire, a voltage is stimulated in the coil, as explained by Faraday’s law of magnetic induction forcing the electrons to move.
Simple Generator using Magnetic Induction
Then we can see that by flowing a magnet past a single loop of wire, a voltage introduced as an EMF (electro-motive force) is induced across the wire loop based on the magnetic field of the system. As a voltage is produced across the wire loop, an electrical current in the case of an electron flow begins to flow around the loop, creating the electricity.
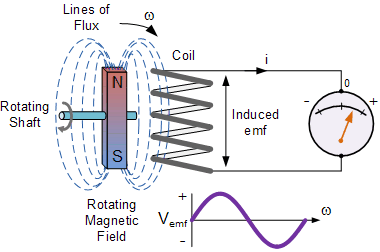
But what if instead of a simple individual loop of wire as presented, we had several loops joined together on the same size to create a coil of wire? For sure, much more voltage and therefore current could be produced for the same amount of magnetic field in this case.
This is because the magnetic flux cuts within more wire, creating a higher EMF and this is the main principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic effect and an AC system employs this principle to transform a mechanical power such as the movement from a wind turbine or hydro turbine, into the electrical power generating a sinusoidal waveform.
So, we can see that there are three basic requirements for electrical production, and these are:
- A coil or an arrangement of the conductors
- A magnetic field setup
- Relative motion between the field and the conductors
Then the quicker the coil of wire circulates, the higher the rate of modification by which the magnetic flux is cut by the coil, and the higher is the made EMF across the coil. Likewise, if the magnetic flux is produced stronger, the made EMF will improve for the same rotational velocity. As a result, induced EMF is proportional to Φ and N. Where “Φ” is the flux of the magnetic field and “N” is the velocity of the rotation. Also, the polarity of the produced voltage is based on the direction of the magnetic wires of flux and the movement direction of the conductor.
There are two main forms of electrical generator and alternator for that matter: the wound-field generator and the permanent-magnet generator with both forms, including two main parts: the rotor and the stator.
The rotor is the section of the system that “rotates”. Again, the rotor can have output coils that move or particular types of permanent magnets. The stator is the “stationary” component of the system and can have either a set of permanent magnets within its model or a set of electrical windings generating an electromagnet. Normally, generators and alternators employed for wind turbine generators are explained by how they produce their magnetism, either permanent magnets or electromagnets.
There are no practical advantages and disadvantages of both forms. Most residential wind turbine generators on the market utilize the permanent magnets across their turbine generator structure, and which makes the needed magnetic field with the movement of the system, although some do utilize the electromagnetic coils.
These high-strength magnets are typically constructed from rare earth substances such as Samarium Cobalt (SmCo) or Neodymium Iron (NdFe), removing the need for the field windings to supply a fixed magnetic field, leading to an easier, more rugged structure. Wound field windings have the benefit of matching their magnetism (and therefore energy) with the differing wind velocity but need an additional power source to create the required magnetic field.
We now understand that the electrical generator supports a means of power conversion between the mechanical load produced by the rotor blades, introduced as the prime mover, and some other electrical loads. The mechanical junction of the wind turbine generator to the blades of the rotor is constructed with a basic shaft which can be either a simple direct drive or by employing a gearbox to reduce or increase the generator velocity relative to the movement velocity of the blades.
Using a gearbox permits better matching of the generator velocity to that of the turbine, but the drawback of employing a gearbox is that as a mechanical part, it is subjected to wear and tear, which ends to decrement in the efficiency of the device. Direct drive, however, may be easier and more effective, but the generator’s rotor bearings and shaft are subjected to the total weight and the rotational load of the rotor blades.
Wind Turbine Generator Output Curve
So, the form of the wind turbine generator needed for a special location is based on the power contained in the wind and the features of the electrical system itself. All wind turbines have special characteristics related to the velocity of the wind.
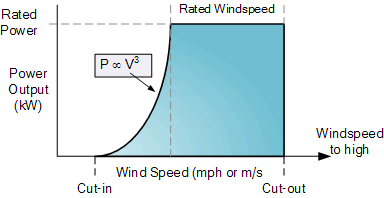
The alternator or generator does not generate output power until its rotational velocity is above its cut-in wind velocity, where the load of the wind on the blades of the rotor is adequate to overcome the friction and the rotor blades are precise enough for the generator to start producing usable energy.
Above this cut-in velocity, the generator must create a power related to the wind velocity cubed (K.V3) until it reaches its potential rated energy output.
Above this nominal speed, the wind power on the blades of the rotor approaches the optimum strength of the electrical system, and the generator generates its maximum or rated energy output as the rated wind velocity window is reached. If the wind speed tends to improve, the wind turbine generator will cease at its cut-out value to prevent electrical and mechanical damage, resulting in zero electrical production. The application of a brake to cease the system from damaging itself can be either an electrical speed sensor or a mechanical governor.
Buying a wind turbine generator such as a 400-Watt type of Wind Turbine Generators for battery charging is not simple, and there are several features that should be taken into account. The price is just one of them. Be sure to select an electrical system that meets your requirements. If you are setting a grid-connected configuration, select an AC mains voltage generator. If you are setting a battery-based device, look for a battery-charging DC system. Also, consider the mechanical structure of a generator, including size and weight, working speed, and protection from the surrounding.
To explore more about “How do Wind Turbines Generator work”, or achieve more wind power information about the different wind turbine generating systems accessible, or to explore the disadvantages and advantages of wind energy, click here.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip



Please read this post to know the working principle of Generators.
https://www.linquip.com/blog/what-is-a-generator/
Terrific concept. I ought to believe on it thoroughly.
Thanks for visiting our website and leaving your comment, Roderick! We hope to hear from you again in our other posts.
Thank you so much for such valuable information.
Thanks for visiting our website and leaving your comment! We hope to hear from you again in our other posts.