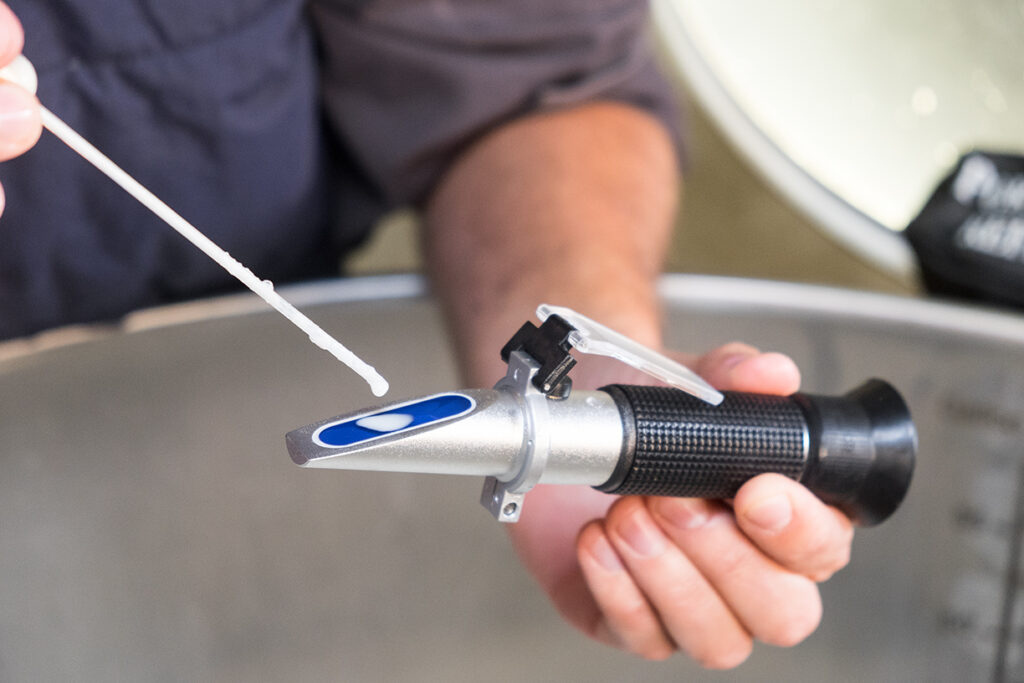
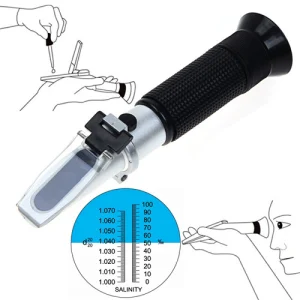
This article is dedicated to the proper way of using a refractometer. Let us begin by defining what it is.
What Is a Refractometer?

A refractometer is used to determine a concentration of a particular substance within a given solution. It operates based on the principle of refraction. When rays of light pass from one medium into another, they are bent either toward or away from a normal line between the two media.
The angle between the normal ray and the incident ray is called the angle of incidence. The angle between the normal ray and the refracted ray is called the angle of refraction. The Figure below demonstrates this using a pencil resting in a container of water. As you can see, the light ray passes from the air into the water and is bent toward the normal ray or the angle of incidence.
The angle of refraction is related to an index value called the index of refraction. Each compound has a specific index of refraction. The angle of refraction is dependent on the composition of the media and on the temperature. This composition dependency is what makes refractometers so useful. As the concentration of a particular compound in a solution increases, so does the degree to which the light is bent. Also, it is important to determine the temperature of the testing environment since temperature affects the angle of refraction.
An example of How to Use a Refractometer
As an example, refractive light can be used to determine the sodium chloride (NaCl) concentration/salinity in a brine solution. For each percent salinity value, there is a corresponding angle of refraction. That angle of refraction is converted to percent salinity. This percentage is the concentration of NaCl in the brine solution. To make the conversion easier, refractometers are available with scales that are calibrated to read the desired value, in this case, percent salinity.
The concentration of a coolant, cleaner, or other aqueous solution is usually determined in the field with the use of a handheld refractometer. The range of the refractometer must cover that expected by the diluted solution. If the dilute solution is too concentrated for the refractometer that is being used, a further dilution of the fluid can be made and the appropriate factors applied.
Equipment
- 0-16 or 0-32 range (Brix) handheld refractometer
- Clean tap or distilled water
- Clean Lint Free Tissue
- Dropper Pipette
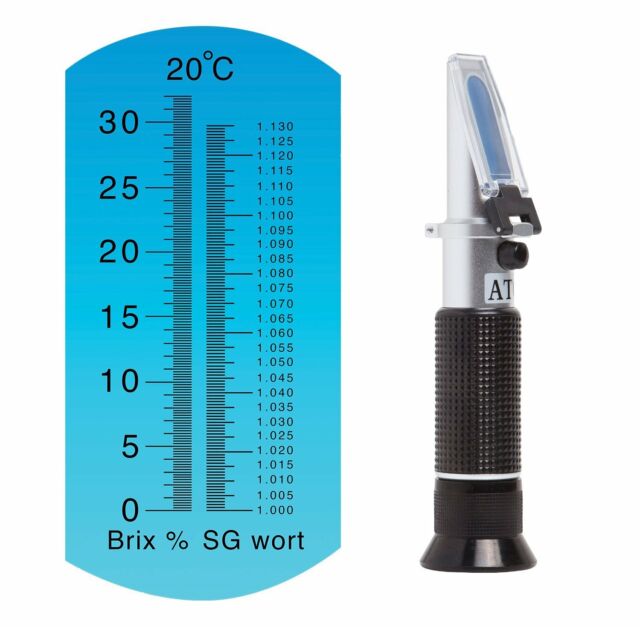
Refractometer Brix scale
How to Use a Refractometer: Simplified Measurement Method
- Using a dropper pipette, transfer one or two drops of room temperature water to the prism (clear glass) of the refractometer and close the cover plate. The sample must spread all over the prism surface.
- Look at the scale through the eyepiece and read the scale where the boundary line intercepts it.
- Set the boundary line to read zero by using the adjusting screw for calibration.
- Wipe the prism clean with a clean lint-free tissue.
- Using a dropper pipette, transfer one or two drops of the system coolant sump to the prism (clear glass) of the refractometer and close the cover plate. The sample must spread all over the prism surface. Do not dip the refractometer into the coolant sump. Do not place the refractometer under a coolant stream. Not following these directions can damage the refractometer prism and calibration.
- Look at the scale through the eyepiece and read the scale where the boundary line intercepts it.
- Wipe the prism clean with clean lint-free tissue and water.
How to Use a Refractometer: Concentration Control
The use of a 0 to 10 or a 0 to 32 refractometer is suggested to manage coolant concentration. Use the control chart for the coolant in question to determine the appropriate refractometer reading for the concentration that you desire. If a coolant control chart is not available use the refractometer factor to determine the concentration of the fluid. If no factor or control chart is available contact your sales representative on how to determine your coolant concentration.
How to Use a Refractometer: Types of Refractometers
Handheld Analog Refractometer With an analog refractometer, the sample is placed on a cover plate and a prism and then held to the light to view the scale inside the meter.
Handheld Digital Refractometer Digital refractometers require a drop of the tested solution to be placed in a well. That well is illuminated by a light source, usually, an LED light and the meter interprets the light transmission into refractive index or whatever unit of measure the instrument is programmed to read.
Abbe (Laboratory) Refractometer Abbe Refractometers are bench-top meters that look similar to a microscope and provides highly precise measurements of refractive index.
How to Use a Refractometer: Various Scales
Refractometers are available with a variety of scales:
- Salinity: Measures sodium chloride solutions
- Brix: Measures percent sucrose. Used in the food and beverage industry for quality control
- Coolant: Freezing Point Determines the effectiveness of ethylene glycol and propylene glycol coolants
- Clinical: Measures Serum albumen and urine-specific gravity (e.g. to test for urine drug sample tampering)
- Specific Gravity: Measures the density of a liquid in relation to the density of water, which has a specific gravity of 1.
How to Use a Refractometer: Calibration and Use of Analog Refractometers
- Calibrate the refractometer with a standard solution before use. Since the reading will be affected by temperature changes, it is best to calibrate at the temperature of the test environment. If this is not possible, correction charts may be used. Some refractometers have automatic temperature correction (ATC), a feature that allows the instrument to automatically correct temperature differences.
- Place a small amount of liquid (usually 2–5 drops) on the prism and secure the cover plate. This will evenly distribute the liquid on the prism.
- Point the prism end of the refractometer toward a light source and focus the eyepiece until the scale is clearly visible.
- Read the scale value at the point where the dark and light portions meet. Below is an example of a salinity scale as seen through the eyepiece:
How to Use a Refractometer: Commonly Asked Questions
Q: I need to test the concentration of lubricating oil but I have a Brix refractometer. Can I use it?
A: Yes, you can use it if the refractive range is similar. In this case, you need to prepare known samples of the lubricating oil and determine the corresponding Brix values. From this data, a chart can be created to convert the Brix value to the percent oil value.
Q: How do I maintain a refractometer?
A: Refractometers require very little maintenance. When the measurement is complete, wipe the prism with soft lens tissue. When the instrument is not in use, keep the cover closed to avoid scratching the prism.
See the video below
How to use a Refractometer – YouTube
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip
- 3 Different Types of Hygrometers and Their Applications
- A Quick Look at Types of Spectrophotometers
- An Easy Guideline to How to Use a Refractometer
- What is the Similarity Law of Fluid Mechanics?
- Your Convenient Preventive Maintenance Checklist
- How to read and use a micrometer
- How to Use and Read a Hydrometer: Your Concise But Complete Guide