Inductance VS Capacitance – RLC circuits rely heavily on inductance and capacitance. Waveform generators and analog filters frequently employ inductors and capacitors, components related to inductance and capacitance. The capacitance of a device is its ability to hold and store electric charges, while the inductance of a current-carrying conductor is its ability to produce a magnetic field around the conductor.
To provide you with a comprehensive view of Inductance and Capacitance, Linquip provides you with a great deal of information. Our “Electrical” page provides more information on Linquip’s solutions for your situation. Choosing the right electrical component may be difficult for you. Linquip offers a wide selection of Electrical Products, so you can find the one that fits your needs. Through the Linquip Platform, you will be able to receive free quotes from multiple Electrical Suppliers and Companies in this industry.
What Are Capacitors?
The capacitance of a capacitor is often rather high. The capacity to store energy as an electric field, measured in farads, is known as capacitance. When a dielectric separates two conducting paths, a capacitance results.
This capacitance is usually unintended and undesired. A capacitor is a device that offers high capacitance in a compact form factor, making it ideal for usage when the need arises to increase capacitance to a circuit. The parallel-plate construction, which consists of two conducting plates with a thin dielectric between them, is the simplest physical design for a capacitor.
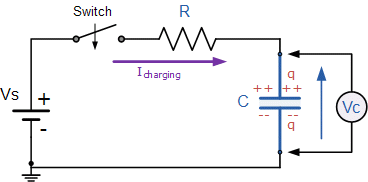
When a capacitor is first connected to a power source, the current flowing through it causes the voltage across the capacitor to rise. Now the circuit’s current is progressively dropping. When the capacitor has been charged to its maximum capacity, it acts like an open circuit, preventing any more current from flowing until the charging condition is altered.

The RC Circuit
An RC circuit is formed by connecting a resistor and a capacitor in series. This deceptively straightforward network plays a significant role in many real-world circuits. As an illustration, it can function as a low-pass filter when connected to an alternating current signal.
However, the voltage produced by a charging capacitor does not rise steadily. instead, an exponential form may be seen in a plot of capacitor voltage vs time. Equally, an exponential connection controls the amount of current flowing through the capacitor.
Take note of how the current varies in the opposite direction of the voltage. Voltage and current in a totally resistive circuit are proportional to one another, thus if you increase the voltage, the current will rise as well, and vice versa. Now that a capacitor is part of the circuit, things are different; voltage rises with the falling current.
What Are Inductors?
In this article, we learned that capacitance is the capacity to store energy in the form of an electric field. The capacity to store energy as a magnetic field, symbolized by the letter L and measured in henries, is known as inductance.
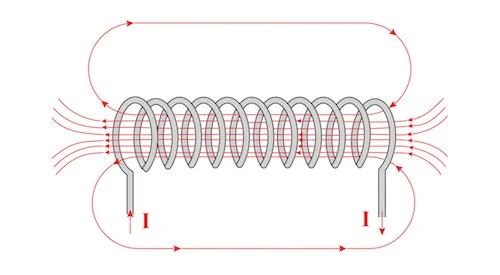
An inductor is a piece of conductor built to produce a large magnetic field, as more inductance requires a larger magnetic field. An inductor’s essential physical structure is a wound wire coil.
Since a current-carrying wire produces a circular magnetic field, this configuration is useful because it concentrates the magnetic field within the coil by arranging many loops side by side.
Because there is nothing magnetic within the coil of wire, the component depicted in the accompanying diagram is known as an air-core inductor. Most inductors include a magnetic core material that boosts the inductance of the device, although air-core inductors are favored in some situations.
What is Inductance?
An electrical conductor has inductance if “a change in current through it causes an electromotive force in the conductor itself.” A magnet is created by connecting the two ends of a coil made from copper wire wound around an iron core to battery connections. The property of inductance is responsible for this phenomenon.
What is Capacitance?
A device’s capacitance is the amount of time it can store an electric charge. Fundamentally, a capacitor is made up of two metallic films separated by a dielectric layer. As a result of the continuous voltage applied, the two metal plates will accumulate opposing charges. These charges persist even when the power is turned off. Additionally, the capacitor discharges when resistance R is connected between the charged capacitor’s plates. The capacitance (C) of a device is the ratio of the voltage (v) used to charge it to the charge (Q) it can store. Farads is the standard unit of capacitance (F).
C = Q/v
The charging time of a capacitor may be expressed as the time constant, R x C. The resistance (R) in a charging circuit. A capacitor’s time constant is the amount of time it takes to charge to 63% of its full capacity.
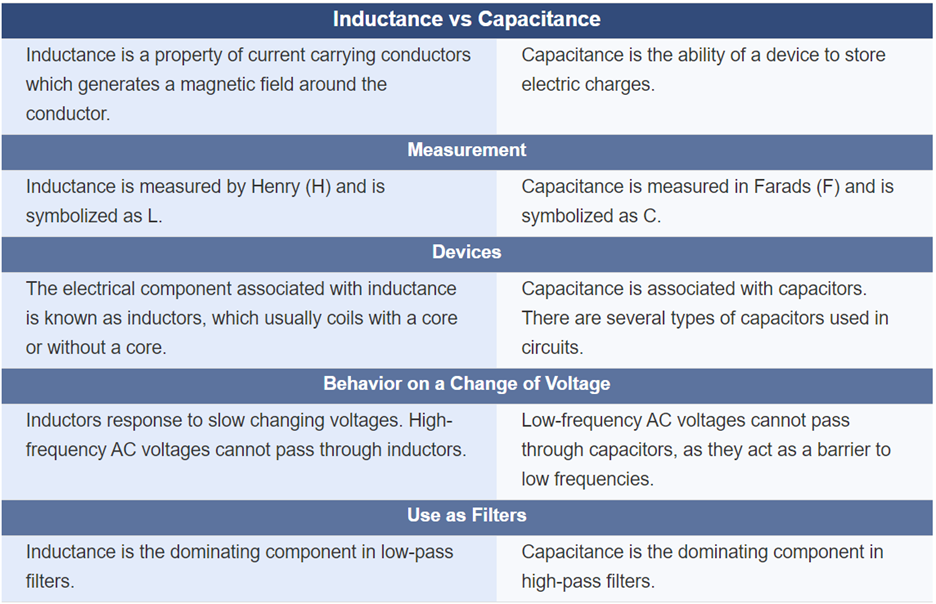
What Is The Difference Between Inductance And Capacitance?
The following table summarizes the key differences between Inductance and Capacitance.
FAQs about Inductance vs Capacitance
Is capacitance the opposite of inductance?
Being “equal but opposing,” capacitance and inductance are relatively related phenomena that may be understood with relative ease by those who are already familiar with the fundamentals of capacitance. To put it simply, a capacitor uses an electric field to store energy, whereas an inductor uses a magnetic field.
What is the main difference between inductive and capacitive reactance?
The term “inductive reactance” is used when the energy is released in the form of a magnetic field; the term “capacitive reactance” is used when the energy is released in the form of an electric field.
How does capacitance affect inductance?
Capacitance is a quality of a device to holds and store electric charges, whereas inductance is a feature of a current-carrying conductor that creates a magnetic field around the conductor.
Conclusion
This article is aimed at providing you with the key points about the difference between inductance and capacitance. In this regard, we discussed the basic characteristics of inductance and capacitance. Linquip Electrical Experts are available to answer all your questions about selecting the right component for your particular application. Moreover, Linquip platform also provides you with access to a variety of Electrical Service Providers if you need any services regarding your equipment and electrical devices.
Download PDF for Inductance VS Capacitance
You can download the PDF format of this post from the link provided here.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip
- Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a nutshell 2023
- Difference between Capacitor and Inductor- Capacitor vs. Inductor
- Film What is Film Capacitor? Different Types & Working
- What is a Paper Capacitor?
- What is Non-Polarized Capacitor? Types & Function
- Types of Capacitors: All You Need to Know
- What is Mica Capacitor Used for?
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor? Usage & Application
- What is Polarized Capacitor? Function and Applications
- What is Ceramic Capacitor Used for?