Is biomass renewable or nonrenewable? For as long as humans have been making flames, biomass has been used as an energy source. Biomass, a form of green energy, has lots of benefits. Yet there’s still some talk about whether it’s the greenest kind of electricity around. This article concentrates on what biomass is, and how it is used. If you are ready for more learning, keep reading to also find out about this question at Linquip that, “is biomass renewable or nonrenewable?”.
What is biomass?
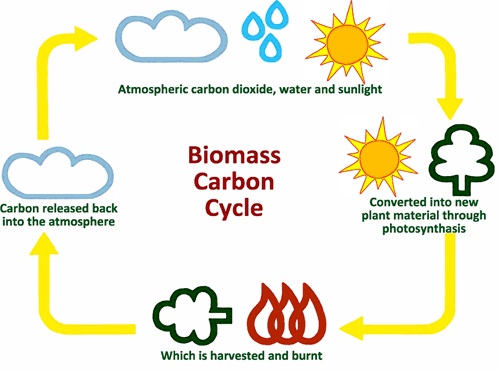
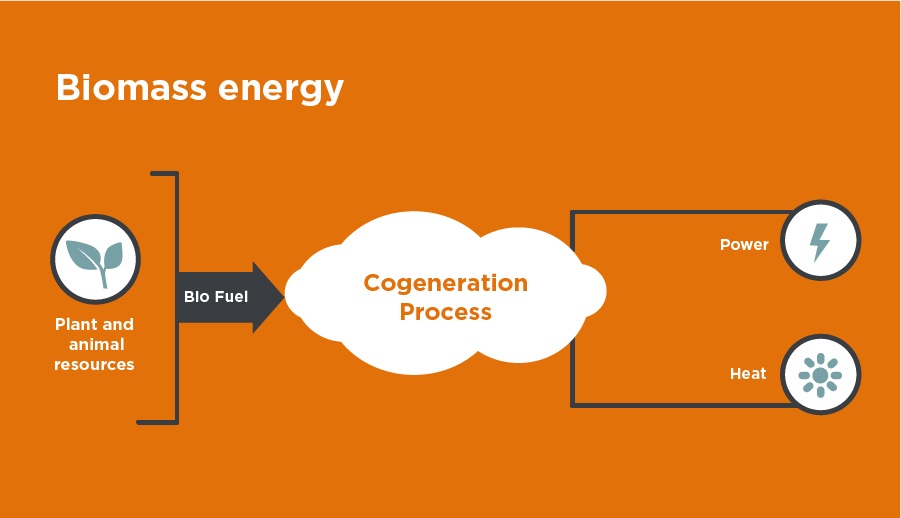
Biomass comes from plants and animals and is a renewable organic material. The biomass comprises the sun’s accumulated chemical energy. By photosynthesis, plants make biomass. Biomass may be burned directly for heat or converted by different methods to clean liquid and gaseous fuels. It can be derived from several sources, including residues from agriculture or forestry, dedicated energy crops, or waste products such as unconsumed food.
Fortunately, emerging technologies have improved to the extent where any emissions from the burning of biomass in industrial facilities are normally less than emissions produced by using fossil fuels.
The use of biomass is also growing ın popularity again these days when the world is finding more green energy options to tackle the climate crisis. Today, biomass in the form of wood and wood products is a frequently used source of energy for many nations around the world, both for domestic use and by power plants on a grid-scale. In developing countries mostly, biomass is an essential fuel, especially for cooking and heating. Besides, in several developing countries, the use of biomass fuels for transportation and energy generation is growing as a way of avoiding carbon dioxide emissions from the use of fossil fuels.
Why is biomass considered a sustainable resource?
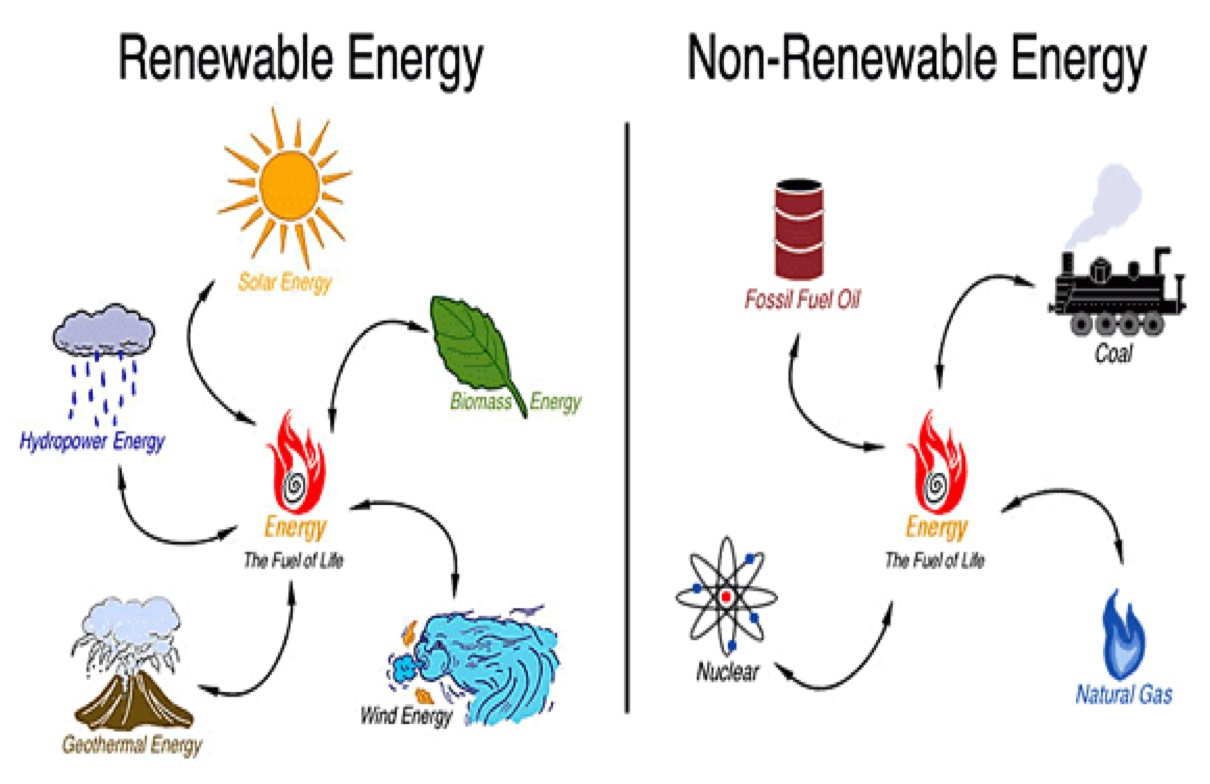
Biomass is considered a sustainable resource, and as long as it is sustainably maintained and controlled, it can be used as a method to mitigate carbon emissions. Biomass energy is a great way to use naturally occurring materials and to make use of waste. It is a much more sustainable alternative as a renewable resource than depending on scarce resources like coal or oil.
But truly, is biomass renewable or nonrenewable? To find out more, carry on reading.
Is biomass renewable or non-renewable?
To answer the question of “is biomass renewable or nonrenewable?”, it should be said that although renewable energy has been praised as sustainable and the solution to the climate change challenge, not all renewable energy is truly “green.” This is true for biomass as well. So, if you ask is biomass renewable or nonrenewable, we should say that biomass is renewable, but not necessarily “Green”.
Traditionally, biomass has been considered a “carbon-neutral” source of energy, ensuring that carbon emitted and carbon extracted from the environment is effectively balanced. The carbon absorbed by trees is believed to be the same as carbon emitted by combustion. But analysis of these arguments has gradually shown differently. Also, the fact is that biomass generation releases greenhouse gases and contaminants into the air, unlike sun, wind, and hydropower.
Is biomass really carbon-neutral?
The carbon effect of bioenergy depends on the technology of combustion, how the biomass is harvested, any re-growing efforts, the form of biomass used, pacing, and the energy resource it is displacing. For example, burning wood to create electricity releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, but trees can re-grow and absorb the carbon dioxide released.
However, it may take decades for trees to re-grow and sequester biomass because the carbon neutrality of the bioenergy supply depends on the time you’re looking. If industries burn forests at a higher pace than re-planting and growing or destroying trees that will otherwise be left intact in a forest, carbon neutrality is undermined.
Is Burning Biomass Bad for Health?
When power plants use biomass as fuel, particularly biomass that comes from forests, carbon emissions will increase compared to coal and other fossil fuels. Any of our most valuable trees are still imperiled by the biomass industry. According to the medical and public health world, “Biomass is far from “clean” – burning biomass creates air pollution that causes a sweeping array of health harms, from asthma attacks to cancer to heart attacks, resulting in emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and premature deaths.” Though biomass is listed as a source of renewable energy, it accounts for around 3% of overall global methane emissions.
Moreover, today, biomass is being produced and used in forestry and agriculture-focused countries, where waste can be used to extract biomass energy from renewable sources. If other green energy alternatives are viable, it should not be appropriate to unnecessarily cut down trees or cultivate crops to harvest biomass, if and when more environmentally sustainable solutions are available.
Other Environmental consequences of biomass energy
Still not sure about is biomass renewable or nonrenewable? Check out the other following environmental consequences of biomass.
Deforestation:
There are plenty of bioenergy plants that use waste as a fuel source whether agricultural or livestock. Many energy producers, though, use plantation wood for power and clear-cut mature trees that eliminate emissions of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere if left unused. Acts like this result in degradation, habitat degradation, soil erosion, natural beauty damage, and more.
Pollution:
Such contaminants and particulate matter, including carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, and nitrogen oxides, can also be released into the air by burning biomass in a solid, liquid, or gaseous state instead of contributing carbon dioxide emissions. Biomass burning will produce more emissions than fossil fuels in some cases. In comparison to carbon dioxide emissions, new plants do not sequester many of these toxins. When not adequately contained, these compounds can lead to a variety of environmental and human health problems.
Water use:
Plants need water to thrive; they use a lot of water for irrigation as energy companies grow trees and other crops for a bio-energy project. This aggravates drought conditions on a wide scale, affecting marine ecosystems and the amount of water available for other uses (food crops, drinking, hydropower, etc.).
Conclusion
All the above information was about the essence of biomass and debates on the question that, “is biomass renewable or nonrenewable?” Is this all? Not. If you feel that you need to gain more about this source of energy and decide to use it or not, click the “register” button. We are truly read to provide you deeper answers about the question that, “is biomass renewable or nonrenewable?” at Linquip.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip