The Difference Between Gas Turbines and Diesel Engines: Diesel engines and gas turbines are both classified as internal combustion engines. Diesel engines are the well-known motive power, commonly used around us, and gas turbine engines may not be familiar to us. In this article, we will discuss two types of power-generating engines and their differences.
In general, the overall installed mass of Gas Turbines is lower. This has an advantage over Diesel Engines for shipping and installation in distant regions. Gas Turbines and Diesel Engines are important products to use in industrial applications. Gas Turbines and Diesel Engines are provided by several Suppliers and Companies, different manufacturers, and a lot of distributors and there are many of them for sale on Linquip.
Linquip offers a comprehensive selection of Gas Turbine and Diesel Engine services that will meet all of your needs. Linquip can help you connect with several industrial service providers. Linquip provides a list of Specialists and Subject Matter Experts who can help you test your gas turbines and diesel engines.
Follow this new blog on Linquip to find out more about the difference between gas turbines and diesel engines.
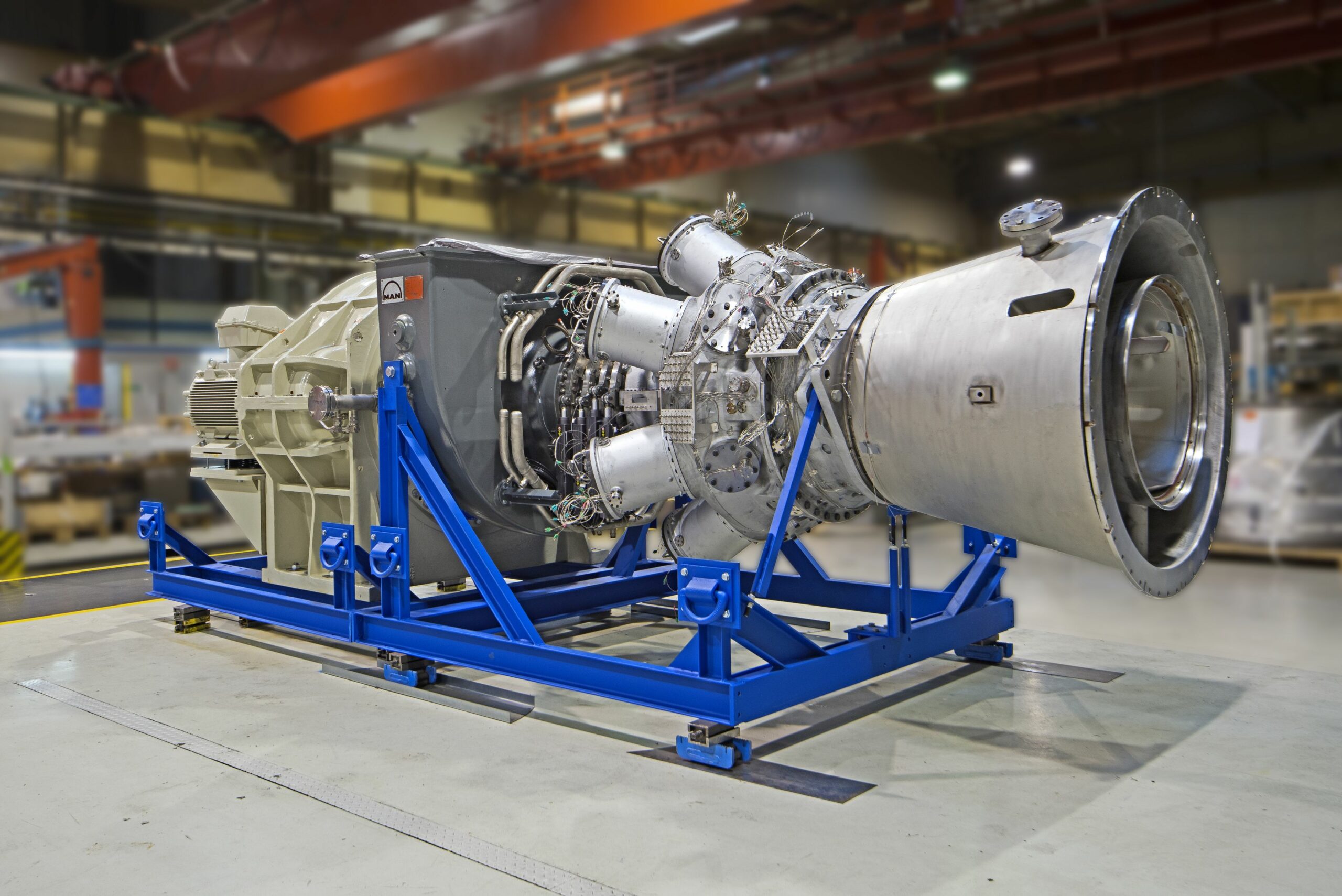
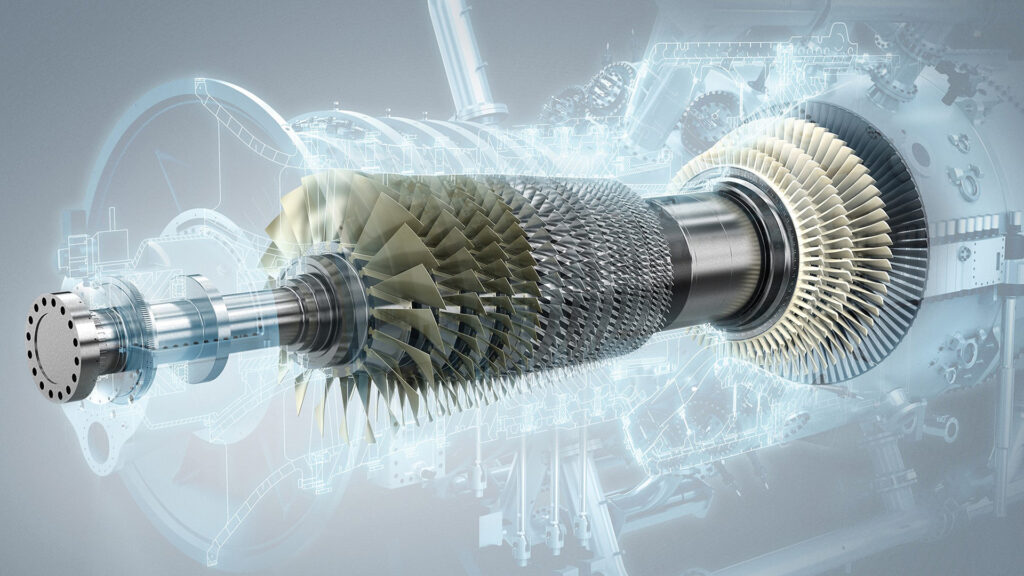
Gas Turbine
The gas turbine as a major power producer came about just before the turn of the 20th century, and they are continually being improved to provide reliable energy to communities around the world today. In all modern gas turbine engines, the engine produces pressurized gas, and it does so by burning something like propane, natural gas, or jet fuel. The heat that comes from burning the fuel expands the air, and the high-speed rush of this hot air spins the turbine. Variations of gas turbines have been used by Leonardo Da Vinci, Nikola Tesla, and Sir Charles Parsons, and they have entered into common use in many fields today. These turbines are used to create thrust for jet engines, for mass power creation, or in ships, locomotives, helicopters, and tanks. A small number of cars, buses, and motorcycles also use gas turbines.
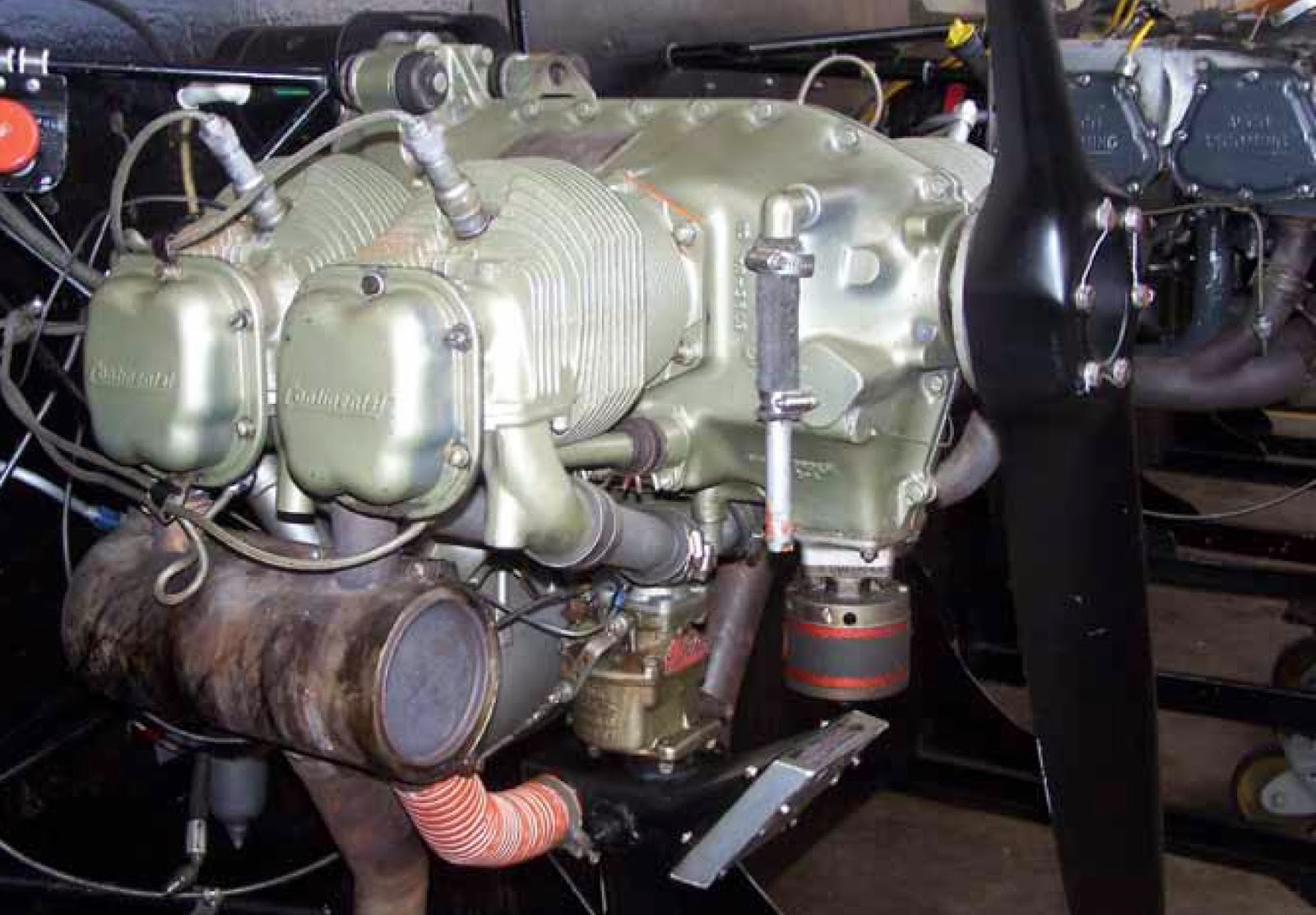
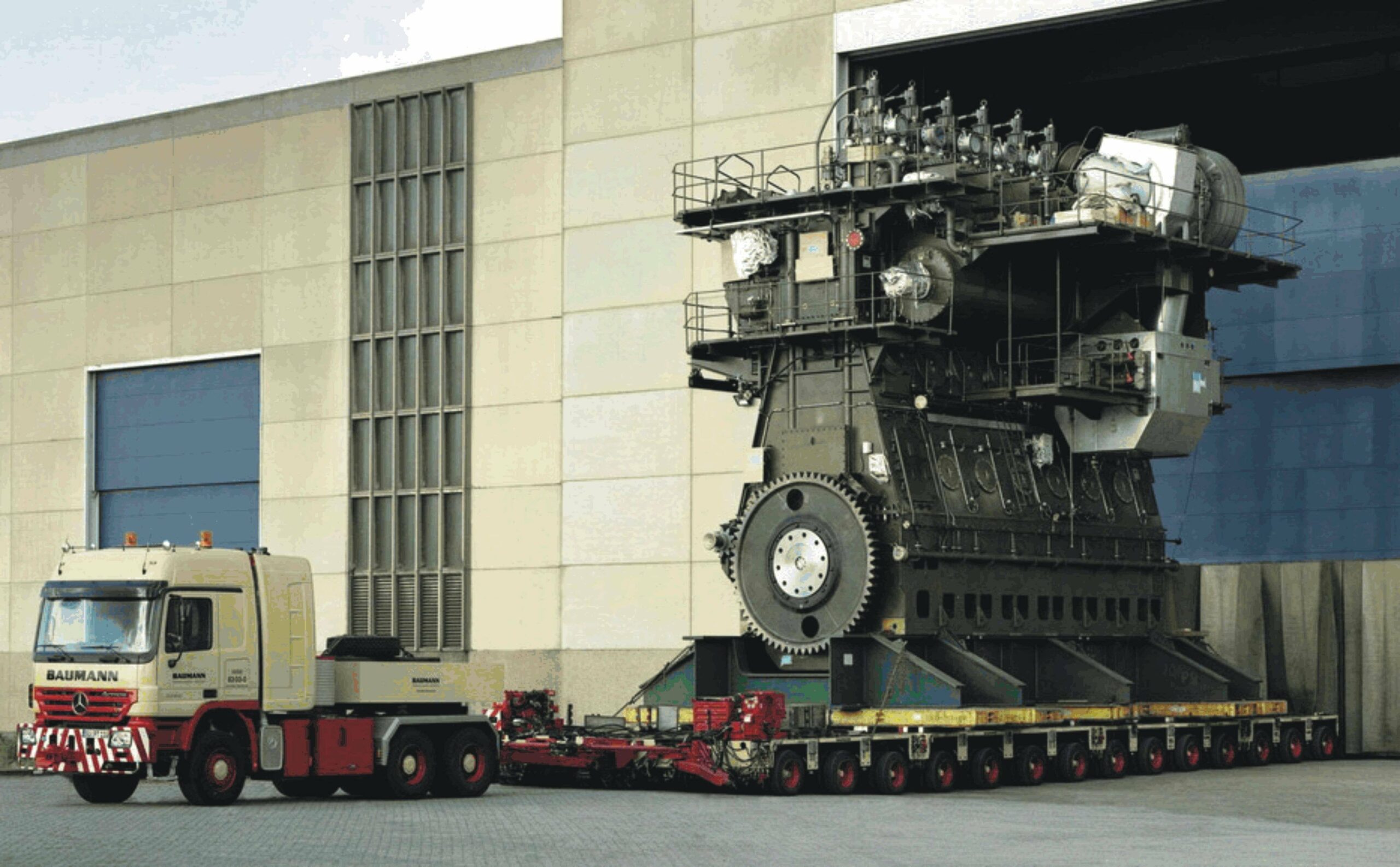
Diesel Engine
Since 1897 when Rudolf Diesel built his first well-known prototype of the high-compression engine, the diesel engine has evolved into one of the world’s most capable and reliable forms of power generation. In diesel engines, internal combustion results in the expansion of high-temperature, high-pressure gases, which in turn move pistons, transforming chemical energy into mechanical energy. Today, they are used extensively in the Navy, serving as propulsion units for small boats, ships, and land vehicles. Diesel engines are also used as construction and farming equipment and prime movers in auxiliary machineries, such as emergency diesel generators, pumps, compressors, and countless industrial applications.
Gas Turbine VS Diesel Engine
Both of these engines are heat engines, for example, they work by taking heat as an input. Here we will point out the difference between the gas turbine and diesel engine. Several factors play an essential role in choosing the best engine for your application. Here we compare some attributes between these two.
Components
- In the gas turbine, the compressor, combustion chamber, and power turbine are important components.
- In the diesel engine, pistons, connecting rods, crankshafts, cylinders, exhaust valves, combustion chambers, and bearing caps are important components.
Longevity
- The gas turbine lasts for about 20 years or more.
- The diesel engine lasts for 30 years or more.
Maintenance Costs
- The gas turbine requires more maintenance costs.
- The steam turbine requires fewer maintenance costs.
Fuel
- The gas turbine can use many kinds of flammable gases and liquids as fuel. For example, gasoline, light oil, kerosene, alcohol, natural gas, and hydrogen. Regenerative fuels such as alcohol and methane have lately attracted considerable attention and gas turbine is well fit for them.
- The most common type of diesel engine fuel is a specific fractional distillate of petroleum fuel oil, but alternatives that are not derived from petroleum, such as biodiesel, biomass to liquid (BTL), or gas to liquid (GTL) diesel, are increasingly being developed and adopted.
Efficiency
- A simple cycle gas turbine can achieve efficiencies ranging between 20 and 35 percent.
- The diesel engine has an efficiency of up to 41 percent but more typically 30 percent.
Starting
- The starting of the gas turbine is easy and quick.
- The starting of the diesel engine is not easy and takes a long time.
Ignition and Lubrication System
- In the gas turbine, the ignition and lubrication system is simpler.
- In the diesel engine, the ignition and lubrication system is complicated as compared to the gas turbine.
NOx Emissions
- In the gas turbine, NOx emission is less.
- Diesel engines produce unacceptably high levels of NOX.
Work Developed Per Kg of Air
- In the gas turbine, the work developed per kg of air is more than in the diesel engine.
- In the diesel engine, the work developed per kg of air is less.
Fuel Cost
- In the gas turbine, cheaper fuel can be used.
- In the diesel engine, comparatively costlier fuel is required.
Machine Size
- The gas turbine includes machines in small sizes.
- There are three basic size groups of diesel engines based on power; small, medium, and large.
Internal Temperature
- In the gas turbine, the internal temperature reaches 1,500 degrees Celsius.
- In the diesel engine, the temperature rises to 600 degrees Celsius.
Exhaust Gas Production
- The gas turbine produces exhaust gases five times greater than the diesel engine.
- The diesel engine produces lesser exhaust gases.
Fuel Control
- In the gas turbine, fuel control is comparatively difficult due to wide operating speeds.
- In the diesel engine, fuel control is easier.
Working Fluid
- The gas turbine uses air or some other gas as the working fluid.
- In the diesel engine, the fuel is burned internally and the combustion products are used as the working fluid.
Higher Speeds
- The gas turbine can be driven at higher speeds. (40000 rpm)
- The diesel engine can’t be driven at higher speeds.
Few more points about the difference between gas turbine and diesel engines to keep in mind:
- The most discriminating feature of gas turbines against diesel engines is the amount of gas to be processed in the same engine size. A gas turbine can process a large amount of gas in a small engine, resulting in a very high power-weight ratio. In the diesel engine, the size will be the same as a large truck.
- Gas turbines have a very high power-to-weight ratio and are lighter and smaller than diesel engines of the same power.
- The diesel engine has a higher thermal efficiency (engine efficiency) than the gas turbine due to its very high expansion ratio and inherent lean burn which enables heat dissipation by the excess air.
- The gas turbine is most efficient at the maximum power output of any practical internal combustion engine.
- Diesel engines use much higher compression ratios than gas turbines and that higher ratio compensates for air pumping losses within the engine.
- Gas turbines do have an advantage in power density compared to diesel engines.
- Gas turbines are expensive compared to diesel engines of the same size. Because they spin at such high speeds and because of the high operating temperatures, designing and manufacturing gas turbines is a tough problem from both the engineering and materials standpoint.
- In the gas turbine, blades are continuously in contact with hot gases throughout the operation, whereas the piston and the cylinder of the diesel engine are subjected to high pressure and high temperature for a very limited period throughout the cycle. Hence the highest temperature in the diesel engine is higher than that in the gas turbine.
- The volume flow rate is quite high in gas turbines as compared to diesel engines.
- The gas turbine is an open system, or you could call it a control volume system. On the other hand, the diesel engine is an example of a closed system, for example, a control mass system.
- In the gas turbine, due to its open system feature, it continuously produces work. While the diesel engine produces work only in a particular stroke of the cycle.
So this is all you need to know about the difference between gas turbines and diesel engines. If you enjoyed this article in Linquip, let us know by leaving a reply in the comment section. Is there any question we can help you with? Feel free to sign up on our website to get the most professional advice from our experts.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- Industrial Diesel Engine Services
- Industrial Diesel Engine Installation Services
- Industrial Diesel Engine Maintenance Services
- Industrial Diesel Engine Services in Texas
- Industrial Diesel Engine Installation Services in Texas
- Industrial Diesel Engine Maintenance Services in Texas
- How do Valves Work in an Engine?
- The Difference Between Gearbox and Transmission
- What is Gear Shaft? Clear Principle & Advantages
- The 10 Best Diesel Engines
- Efficiency of Stirling Engine (Formula & Diagram)
- Beginner’s Guide: The Difference Between Gas Turbine and Gas Engine
- Differences Between Motor and Engine
- Differences Between Engine and Transmission
- The Difference Between Diesel Engines and Gas Engines: Discover the distinction, decide the best
- The Difference Between Diesel Engine and Petrol Engine: which one best works for you?
- Diesel Engine Working: everything you need to know
- Gas Turbine Cycle: Everything You Need to Know About Gas Turbine Working Principle
- Combined Cycle Gas Turbine
- Gas Turbine Types: Overview of Types and Profitable Applications
- Gas Turbine Parts: Fast Basic Guide about Components





A question about the difference between gas turbines and diesel engines: Are diesel engines fuel flexible? The gas turbine engine has proven to be fuel flexible, but is the diesel engine as well?