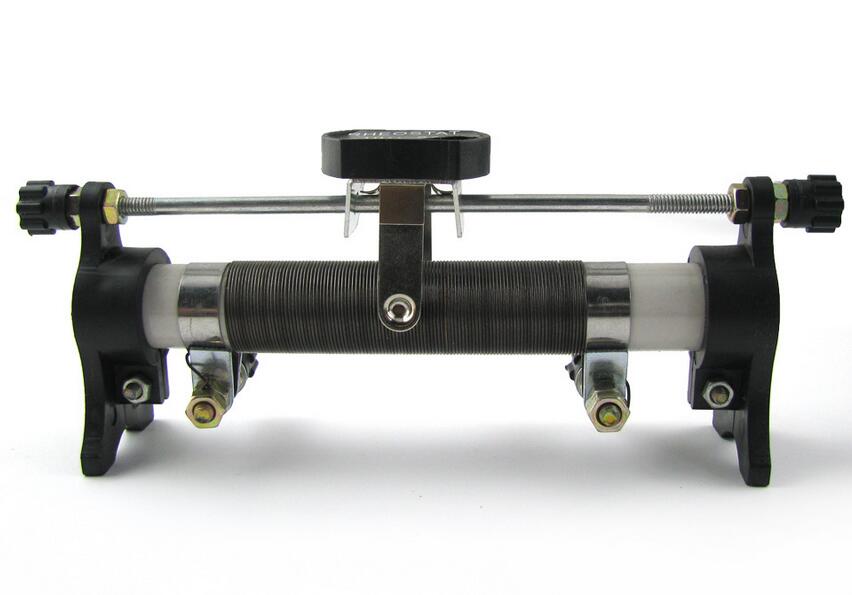
In this article from Linquip, we will talk about rheostat functions, how they work, and all the other information you need to know about them. These components can be found even in your house! They are widely used across the world. So, it’s important for everyone to know how they work and what they really are. Continue reading to know more about rheostats.
Before we get into details, let’s briefly review what a rheostat is…
What is a Rheostat?
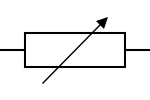
A rheostat is a unit that is considered a variable resistor. They are a bit like potentiometers. You can change the resistance in a rheostat to control the flow of the current through it. Rheostats are great for controlling the downstream in different devices such as lamps or even transistors. The good thing about rheostats is that they can vary the resistance in a circuit without causing any interruption! A rheostat symbol according to the IEC standard is a rectangle that is placed between two linear lines and an arrow, that will cross the rectangle in a semi-tilted way. Here’s an image of its symbol:
One of the most important things about rheostats is that they have two terminals and are connected throughout these two.
What is the rheostat function and how it works?
We all know that to change a current, we should either change the circuit’s resistance or the applied voltage. Rheostat’s function is to change the resistance of the circuit in order to change the circuit’s current. When you need to decrease the current in a circuit, you should increase the rheostat’s resistance. And just like that, if an increase in the current is demanded, you need to decrease the resistance of the rheostat.
The rheostat function depends on changing the resistance of the rheostat. In order to do that, one of the three factors (length, type, and area of cross-section) that affect the resistance will be changed and that factor is the length. A sliding contact in different types of rheostat is used to change the length and therefore, change the resistance. For understanding how it changes the length, you need to know the rheostat’s construction:
Rheostat’s Construction
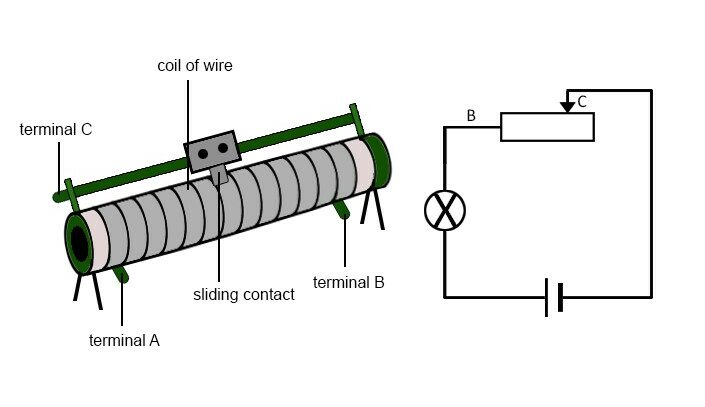
Rheostat’s construction is similar to the potentiometer, but the difference is that it uses two connections instead of three. One of these connections is used for the resistive element and the other one is used to connect to the sliding contact (also known as the wiper). So, one of these terminals is fixed and the other one is a moving terminal.
The length that affects the resistance is between the fixed terminal and where the sliding terminal on the resistive path is. For changing this length, the slider should move, resulting in a change in the rheostat’s resistance. Resistance and length are directly proportional so increasing the length results in an increase in the resistance and vice versa. You can see the rheostat diagram below:
Now, the rheostat function is a bit different than the potentiometer since it has to carry a significant amount of current. That’s why they have wire-wound resistors. The name is because the resistive wire will be wound around an insulating ceramic core and then, the sliding contact (wiper) will slide over the windings to achieve the desired outcome.
Rheostat Application
Rheostats are widely used. One common rheostat used is in power control devices. They can be used to control the intensity of light in light dimmers, ovens and heaters, and so on. Keep in mind that some devices use switching electronics instead of rheostats. That’s why rheostats are nowadays often used for other purposes such as calibration and tuning in circuits.
As we already discussed, the most common use of rheostat is the use of the rheostat function to control the current. You can easily limit the current with the help of a rheostat to help prevent high current faults.
Different rheostat types are designed to suit different needs. Now based on the types of rheostats, we will explain the working process and applications:
-
Linear Rheostat
The sliding terminal glides over the linear resistive path of the rheostat to change the aforementioned length. Although this unit has two fixed terminals, only one of the fixed terminals in this rheostat type is connected to the slider.
Linear rheostats are commonly used in laboratory applications.
-
Rotary Rheostat
Rotary rheostats’ resistive path is rotary. The wiper in this type is mounted on a shaft and the movement of this shaft will change the length and therefore, the resistance.
The rotary rheostat function is usually used in power applications but its working principle is the same as all linear rheostats and the preset type.
-
Preset Rheostat
Preset rheostats are used in a printed circuit board. This type is also called a trimmer which is a small rheostat with two terminals. Sometimes a three-terminal potentiometer trimmer can also work as a two-terminal rheostat to serve the same purpose. Since the structure and purpose of a potentiometer and a rheostat are the same, potentiometers can be wired as rheostats to achieve this purpose. By wiring the potentiometer in a way that a fixed terminal and the moving terminal work as one like a single moving terminal, you’ll end up with two terminals, making the whole unit operate as rheostats. Preset rheostats are used for calibration purposes inside a circuit.
Now you know all there is to know about the rheostat function and how it works, plus its different types and application. What do you think about this variable resistor and its different types? Share your thoughts with us in the comment section! If you have any questions about rheostats, feel free to sign up on Linquip. Our experts are here to help answer your questions in a flash and eliminate the need for you to search any further for the answers.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- 13 Parts of CNC Machine + Function & PDF: A Clear Guide
- What is a Polarized Capacitor? Function and Applications
- What is Capacitive Circuit? Formula & Function
- What is Inductor? Usage & Function | Linquip
- What is a Non-Polarized Capacitor? Types & Function
- What is the Difference Between Potentiometer and Rheostat?
- What is Rheostat? All You Need to Know About Rheostats and Their Working Principles