In any setting where liquids or gases have to be controlled, solenoid valves ensure accurate and precise operations. These control units feature an electric oil with a plunger, which either opens or closes off a small orifice, restricting or allowing the fluids to flow. Below, we’ve discussed the various types of solenoid valves, their principle of operation, features, and applications. Read on to learn more.
What is a Solenoid Valve?
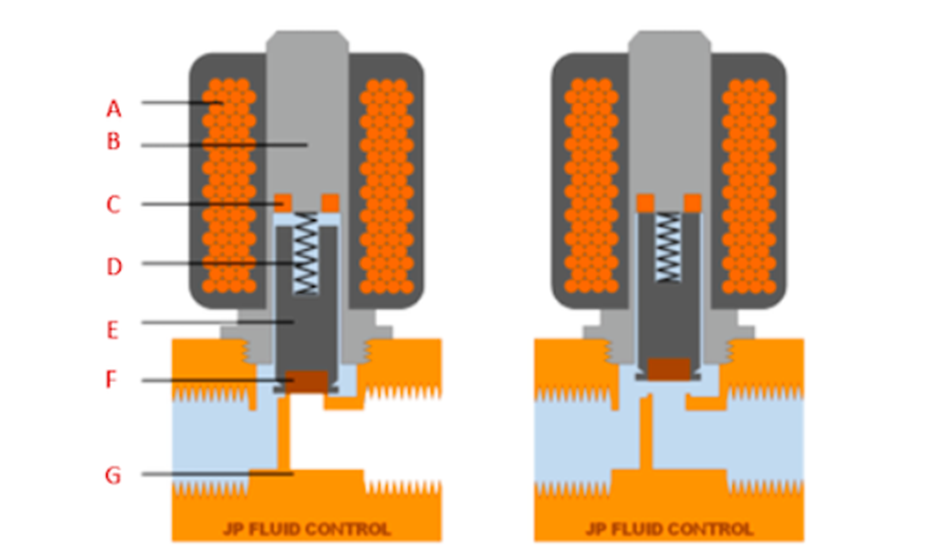
A solenoid valve is an electro-mechanical device used to control the flow of fluids. They consist of two main components, the valve body and a solenoid, which has an inductive coil and a movable ferromagnetic core in its center. Solenoid valves are used to control clean fluids as they are sensitive to dirt. They work to either open, close, dose, or mix a fluid medium with two or more inlets/outlets.
At rest position, solenoid valves are either normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC). When there’s no current in the coil, the NO valve is open while the NC valve is closed. Once the coil is energized, a magnetic field is created, exerting an EMF (electromagnetic force) on the plunger, which overcomes the spring force and causes the plunger to either close the orifice for NO valves or open the orifice for the NC valves.
Solenoid Valves Circuit Functions and Valve Types
The solenoid valve’s circuit function specifies the function of the valve, whether it’s for closing, opening, distributing, or mixing fluids. There are two main circuit functions, represented by the 2-way and 3-way solenoid valves. The 2-way solenoid valves have an inlet and outlet port used to open and close the orifice. A 3-way valve has three ports but with two positions or states (open or close). The latter is used to close, open, mix or distribute a fluid media; hence it can switch between two circuits.
When it comes to the valve types, there are two popular types, the normally closed (NC) and the normally open (NO). The normally open valves are best used for applications requiring the solenoid valve to stay open for extended periods since they are more energy-efficient.
With that said, there’s another solenoid valve type called the bi-stable or latching valve. An instantaneous power source switches this solenoid, and it will stay in the current position without power. The next time another momentary power source is applied, it will change position and remain in that particular position with no power. This valve type is neither NC nor NO as it stays in the most recent position until power is applied. Bi-stable valves use permanent magnets in the place of a spring.
Read More on Linquip
- Types Of Solenoid Valves: Everything You Need To Know
- The Essential Guide To Solenoid Valves Working Principle
- 6 Main Types of Expansion Valves: an Easy to Understand Guide
Solenoid Valves Working Principles
There are three main classifications of solenoid valves based on their working principles. In other words, solenoid valves can either be direct-acting, indirect-acting/ servo/pilot-operated, or semi-direct acting. Below is a detailed overview.
Direct Acting Solenoid Valves
With direct-acting solenoid valves, the maximum flow rate and operating pressure are directly proportional to the solenoid’s magnetic force and orifice diameter. This means that direct-acting solenoid valves are used for small flow rates. Similarly, they require no minimum pressure or pressure difference; hence they can operate from zero bar up to the valve’s maximum allowable operating pressure.
Indirect Acting (Servo/Piloted) Solenoid Valves
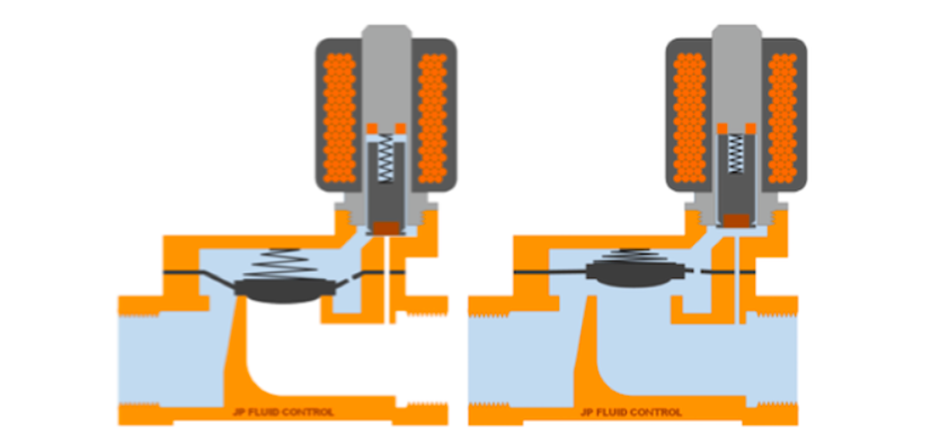
This type uses the pressure difference between the medium over the outlet and inlet ports to close or open the valve. Most solenoid valves in this category require a minimum pressure difference of 0.5 bar. In between the valve’s inlet and outlet port is a rubber membrane called a diaphragm. When there’s enough pressure difference between these two ports (in an NC valve), the diaphragm is lifted, allowing the fluid medium to flow from the inlet to the outlet port. This solenoid valve also has an extra chamber above the diaphragm that serves as an amplifier. This allows a small solenoid to control larger flow rates.
Semi-direct Acting Solenoid Valves
This type of solenoid valve combines the features of direct and indirect-acting solenoid valves. They operate from zero bar and can still handle a relatively high flow rate. These solenoid valves resemble indirect valves only that the plunger is connected directly to a movable membrane/diaphragm with a small orifice/hole and pressure chambers on either side. The semi-direct acting solenoid valves have very powerful coils, and they consume slightly more energy.
Solenoid Valves Special Features
Not all solenoid valves have the same characteristics. Some are designed for unique applications; hence they come with some exceptional capabilities. Here are some of the special features you can find:
- High-pressure solenoid valves designed for pressure requirements of up to 250 bar.
- Latching coil technology designed for lower power consumption and minimal heat development. This is often used for applications requiring low-frequency switching.
- Media separation design allows fluid media to separate inside the valve, commonly used with slightly contaminated fluids.
- Special vacuum valves designed to meet strict leakage rate specifications in vacuum environments.
- Low noise feature achieved by using a damped valve design that helps reduce the noise when the valve is closing.
If you need any of these features in your solenoid valve, be sure to specify them during the selection process. This will help you achieve optimal operational efficiency, safety, and overall satisfactory results.
Choosing the Right Solenoid Valve for Your Applications
When choosing a solenoid valve for your fluid control applications, there are a couple of factors you’ll need to consider. First, understand the scope of work that the solenoid valve will be doing.
Moreover, solenoid valves are used in a wide range of applications including: refrigeration systems to control the flow of refrigerants, in irrigation systems, air conditioning systems, water tanks, car washes, industrial settings, etc.
Once you know your application, you can quickly tell if you need a 2-way or 3-way valve. From there, you can proceed to consider these other aspects:
- Housing material – some materials can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures while others have the minimum chemical and mechanical properties and may be suited for less intensive applications. Depending on the operating environment and the medium the valve will control, you always want to consider the solenoid valves’ housing material keenly. For instance, stainless steel is quite durable and can withstand extreme temperatures and pressure, while brass is best for neutral media.
- Seal material – the temperature and chemical properties of the media will largely determine the type of seal material to pick. Common examples include PTFE (Teflon), EPDM, NBR, and FKM (Viton).
- Response time – this refers to the time the valve takes to go from a closed to an open position and vice versa. Indirect and semi-direct acting valves have slower response times than their direct-acting counterparts.
- Approvals – some fluid control applications require specific solenoid valves that are approved for safety and efficiency. Industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals may need certain approvals such as the UL/UR, CE, and FDA certifications.
The other things to keep in mind include the valve’s operating and maximum pressure, the minimum and maximum operating temperature, and the degree of protection (Ingress protection rating). Additionally, factors such as the solenoids’ voltage version and operation types matter, and you would want to keep them in mind.
Final Thoughts
Now that you know the different types of solenoid valves, their working principles, features, and selection criteria, choosing the right type for your fluid control applications shouldn’t be a problem. If there are other things that you do not understand, feel free to consult knowledgeable.
Read More on Linquip
- Solenoid Valve Manufacturers
- Air release valve Manufacturers
- Pinch Valve Manufacturers
- Plug Valve Manufacturers
- Valve Manufacturers
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers





Very well explained! I can now understand what a Solenoid Gas Valve is and how it works.
Thanks for sharing your experience with us, Iqra! You can also visit our industrial directories, where you can find thousands of various industrial equipment based on your application and demand.