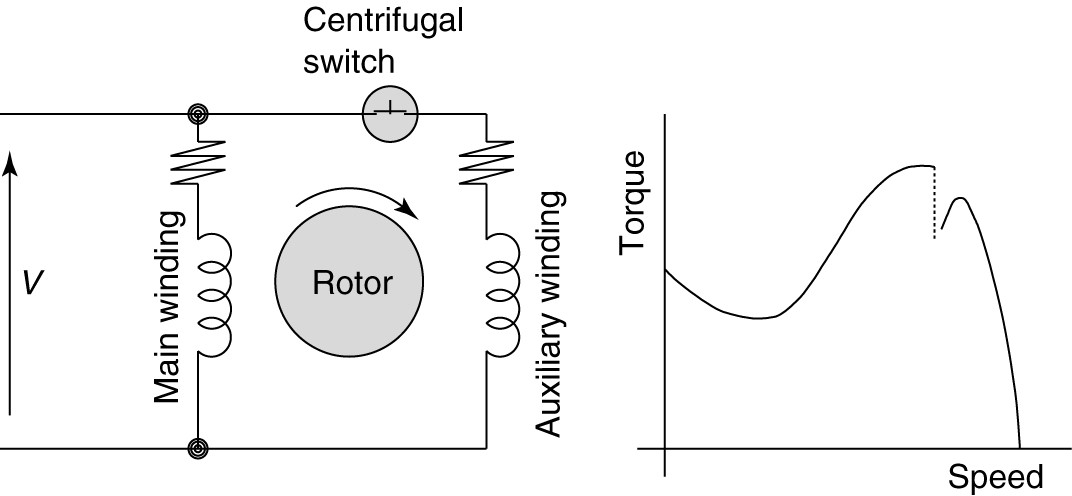
The split-phase induction motor is one of the common single-phase AC motors. It has economic benefits and the requirement of this power system in most of the applications are homes, shops, industry, offices, etc. One of the advantages of this type of single-phase motor is its ability to regenerate power automatically on descending grades. In this article, we find the best answer to the question of what is split-phase induction motors and discuss an overview of split-phase induction motor construction, working, characteristics, types, advantages, disadvantages, and their applications. Follow this new blog in Linquip to find out more about this motor.
On the Linquip platform, you can find all the information you need about induction motors equipment and devices. Our experts are available to answer any questions you may have about the split phase induction motor. To get started, read Linquip’s article titled, “What is Split Phase Induction Motor?“. You need to register as a Linquip Expert in order to access all of the Linquip benefits.
Have you ever considered Guest Posting on the Linquip platform? There is an option for guests to submit their own posts on Linquip.
Construction
To answer the question of what is split-phase induction motors, first, let us see what are the different parts of this motor. The split-phase induction motor basically consists of a stator, a rotor, a centrifugal switch located inside the motor, two end shields housing the bearings that support the rotor shaft. In addition to the main winding or running winding, the stator of the split-phase induction motor carries another winding called auxiliary winding or starting winding. A centrifugal switch is connected in series with auxiliary winding. The purpose of this switch is to disconnect the auxiliary winding from the main circuit.
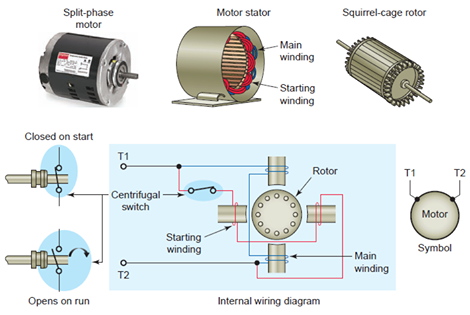
A split-phase motor has no capacitance in the auxiliary circuit. A phase shift to the main current is achieved by using narrow conductors to achieve high resistance to reactance ratio. Increasing the resistance means that the auxiliary winding can only be used during starting, otherwise, it would overheat. A split-phase motor has significantly lower torque at starting due to the reduced phase angle between main and auxiliary winding currents.
Working Principle
In split-phase motor two windings named main winding and starting winding are provided. At the time of starting, both the main and starting windings should be connected across the supply to produce the rotating magnetic field, and when the supply is given to the stator the rotating magnetic field is produced. The rotor is of a squirrel cage type and the revolving magnetic field sweeps part of the stationary rotor, inducing EMF in the rotor.
As the rotor bars are short-circuited, a current flows through them producing a magnetic field. This magnetic field opposes the revolving magnetic field and will combine with the main field to produce a revolving field. Once the rotor starts rotating and attains a speed up to 75 to 80 percent of the synchronous speed, the starting winding can be disconnected from the supply by the centrifugal switch.
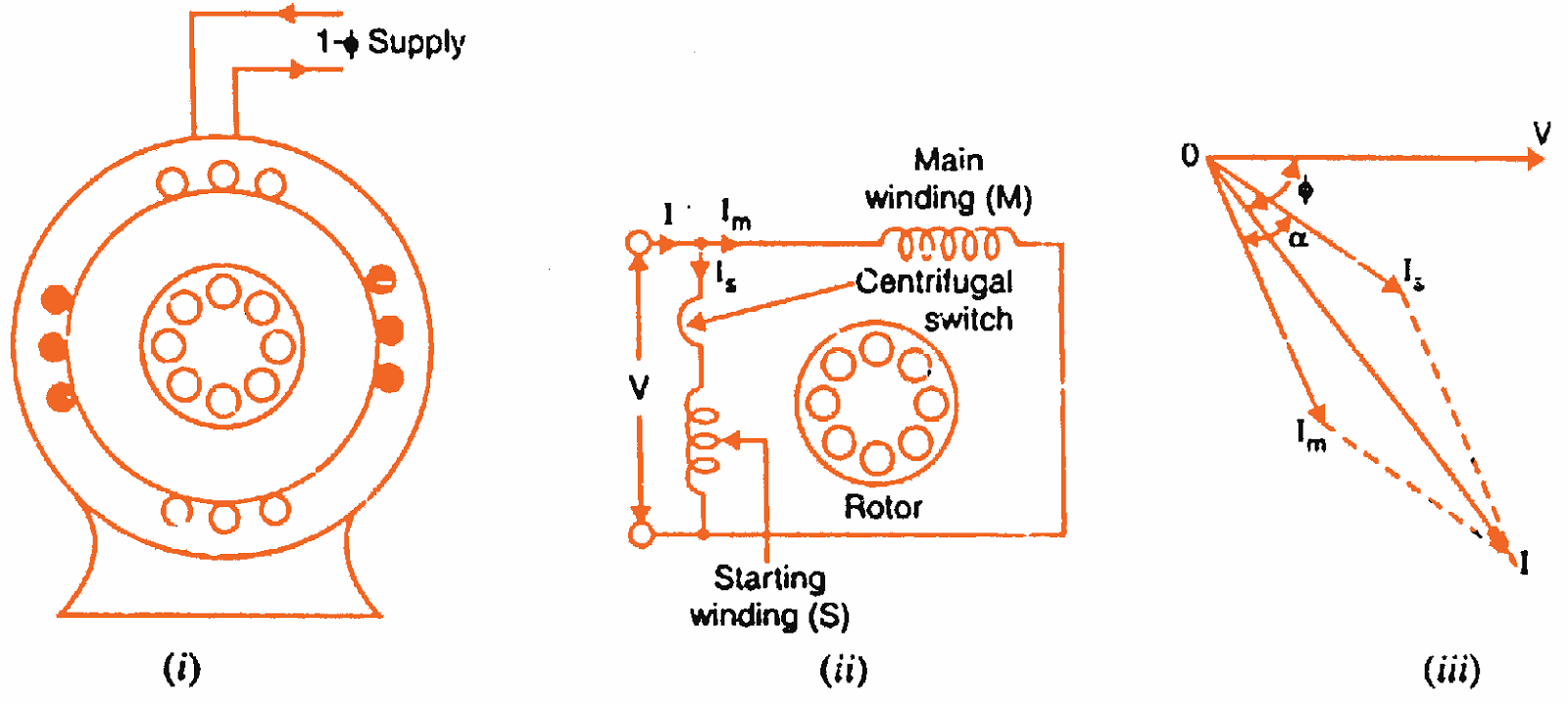
Performance and Characteristics
- The starting torque is about twice the full load torque.
- Speed falls with the increase in load with only about 5% to 7% otherwise it is a constant speed motor.
- The current at the start is about 6 to 8 times.
- Actual speed is less than synchronous speed Ns.
- For the same weight, its rating is about 60 percent that of the polyphase motor. The split-phase induction motor has lower p.f. and lesser efficiency. Its P.f. is about 0.6 and efficiency is also about 60%.
- It is suitable for easily starting loads where the frequency of starting is limited. This type of motor is not used for drives that require more than 1 KW because of the low starting torque.
Types
Different types of split-phase induction motors are as follows.
- Shaded pole motors
- Resistance-start induction-run motors
- Capacitor-start induction-run motors
- Capacitor-start capacitor-run motors
- Permanent capacitor single phase induction motor
Advantages
The advantages of a split-phase induction motor include the following.
- The motor is economical and installed in many domestic appliances.
- It can be changed once it wears out before trying to reverse it.
- These are available in different frame sizes so that they can be placed effortlessly in most of the machines.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of a split-phase induction motor include the following.
- These motors have less starting torque, so not suitable for above 1 KW.
- The disadvantage of this motor is power output and efficiency. As compared to a 3-phase motor, these are unsuccessful while changing the energy from electrical to working.
- These motors rely simply on the different resistance & inductance of the starting winding.
- These motors are used where high starting torque is mandatory like an air compressor.
Application
The applications of this motor include different loads which are used for general purpose. Due to the excellent starting torque and easy direction-reversal characteristics, it finds use in lathe machines, drilling, washing machines, woodworking tools, belted fans, drill presses, oil burners, centrifugal pumps, compressors, air conditioning fans, floor polishers, blowers dryers, mixer grinder, heating blowers with belt-driven and conveyors with tiny belt-driven, and various other low starting torque applications.
This motor is used where the distribution of the three phases is not required.
This motor does not give lots of starting torque, thus the load should be quite small, and where mechanical gain can be used to assist the motor to begin.
So, there you have every single fact to the question of what is split-phase induction motors. If you enjoyed this article in Linquip, let us know by leaving a reply in the comment section. Is there any question we can help you through? Feel free to sign up on our website to get the most professional advice from our experts!
Download Split Phase Induction Motors PDF
If you wish, you can download a PDF version of this article to keep on your computer for future reference.
Read More In Linquip
- What Are Shaded Pole Induction Motors? Ultimate Guide
- Types of Induction Motor: A Concise and Useful Guild
- What is Capacitor Start Induction Motor: A Complete Guide
- Single-Phase Induction Motor : All You Need to Know About It
- Working Principle of Induction Motor: Full Guide
- Efficiency of Induction Motor: Calculation & Equation
- What Is Split Phase Induction Motors? Ultimate Guide
- Synchronous Motors: Definition, Working Principle, Types, and Applications
- Why Is Synchronous Motor Not Self-starting?
- The Beginner’s Guide To Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors
- Types of Induction Motor: A Concise and Useful Guild
- All About DC Motor Types and Their Applications