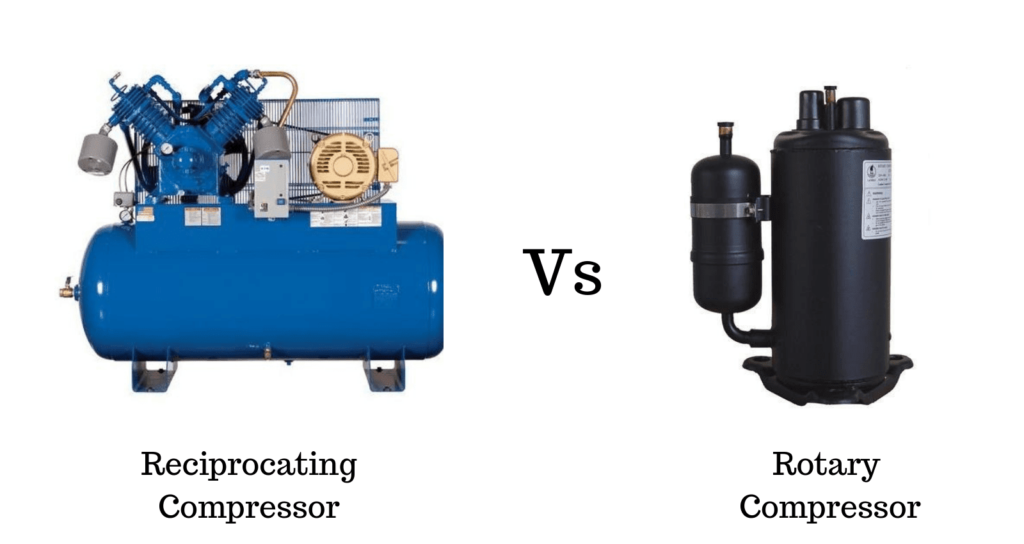
The positive displacement air compressor is the most common type of air compressor in use today and it is classified into two types: rotary and reciprocating compressors. These types of compressors are both components of gas transfer systems. They have the same purpose to bring gas into the system, exhale exhaust, then repeat the process. They both do this by changing the pressure at certain points to force gas in and exhaust out. Although they have things in common, they differ in several factors. In this article, we discuss the differences between rotary & reciprocating compressors. Follow this new blog in Linquip to find out more.
Rotary Compressor
The rotary compressor is a type of positive displacement compressor producing compressed fluid/refrigerant by the rotary movements of blades or the movement of eccentric roller connected to the motor shaft. There are mainly two types of rotary compressor
- Stationary blade type rotary compressor
- Rotating blade type rotary compressor
The rotary compressor, generally finds use in large industrial applications, high-power air tools like jackhammers and impact wrenches, pneumatic pumps, sandblasting operations. It is used where continuous fluid flow is required, such as automated manufacturing, food packaging plants.
Reciprocating Compressor
Reciprocating compressors are the other type of positive displacement compressors in which the compressing and displacing element is a piston having a reciprocating motion within a cylinder. There are two types of reciprocating compressors:
- High speed (separable)
- Low speed (integral)
Reciprocating compressors are used to compress natural gas (gas transmission pipeline applications), supply high-pressure gas for oil well drilling for gas lift, as well as in various industrial or chemical applications involving air and refrigerant compression, for example in refrigeration plants.
Rotary compressor VS. Reciprocating compressor
There is a description of the differences between rotary & reciprocating compressors by considering several factors. Various factors, like those mentioned further, are taken into account while selecting a compressor for a particular application. The following factors show the main differences.
Operation Speed
- The speed of the rotary compressor is high.
- The speed of the reciprocating compressor is low.
Size
- The size of the rotary compressors is smaller than the reciprocating compressor for the same discharge.
- The size of the reciprocating compressor is bulky and larger than the rotary compressor for the same discharge.
Efficiency
- The efficiency of the rotary compressor is nearly 100%.
- The efficiency of the reciprocating compressor is less than 100%.
Compressed Efficiency
- The rotary compressor has higher efficiency with a compression ratio of less than 2.
- The reciprocating compressor has higher efficiency with a compression ratio of less than 2.
Compression Operation
- In the rotary compressor, the compression takes place due to the rotary motion of the blade.
- In the reciprocating compressor, compression takes place with the help of piston and cylinder arrangement and also the reciprocating motion of the piston.
Mechanical Efficiency
- The rotary compressor has higher mechanical efficiency due to fewer sliding parts.
- The reciprocating compressor has lower mechanical efficiency due to several sliding parts.
Efficiency Calculation
- In the rotary compressor, Isentropic efficiency is used for all sorts of calculations.
- In the reciprocating compressor, Isothermal efficiency is used for all sorts of calculations.
Initial Cost
- The rotary compressor has a lower initial cost.
- The reciprocating compressor has a higher initial cost.
Maintenance
- The rotary compressor requires lower maintenance due to fewer sliding parts.
- The reciprocating compressor requires higher maintenance due to the reciprocating engine.
Suitability
- The rotary compressor is suitable for the large volumes discharges of air at low and medium pressure.
- The reciprocating compressor is suitable for the low discharge of air at medium and high pressure.
Flexibility
- No flexibility in capacity and pressure range in the rotary compressor.
- The reciprocating compressor has greater flexibility in capacity and pressure range.
Space Requirement for Installation
- The installation space requirement is less in a rotary compressor.
- The installation space requirement is more in a reciprocating compressor.
Pressure Ratio
- The discharge pressure of air in the rotary compressors is low. The pressure ratio per stage will be in the order of 3 to 5.
- The discharge pressure of the air in the reciprocating compressor is high. The pressure ratio per stage will be in the order of 4 to 7.
Maximum Free Air Discharge Rate
- The maximum free air discharge rate in the rotary compressor is as high as 3000 m3 per minute.
- The maximum free air discharge rate in the reciprocating compressor is as low as 300 m3 per minute.
Coupled to Prime Mover
- The rotary compressor can be directly coupled to the prime mover.
- Due to the low speed of rotation, the reciprocating compressor can’t be directly coupled to prime mover but it requires a reduction of speed.
Lubrication System
- Generally, the rotary compressor has simple lubrication compare to the reciprocating compressor.
- The reciprocating compressor contains a complicated lubrication system.
Handled Volume
- A large measure of air handled can be handled in the rotary compressor and it is about 500 m3/s.
- The quantity of air handled in the reciprocating compressor is low and is limited to 50 m3/s.
Cycle of Operation
- The rotary compressor executes one step of the Rankine cycle.
- The reciprocating compressor executes the whole Brayton cycle.
Air Supply
- The air supply in the rotary compressor is steady and continuous.
- The air supply in the reciprocating compressor is intermittent.
Balancing
- In the rotary compressor, balancing is not a problem. It contains less vibration due to rotary mass.
- In the reciprocating compressor, balancing is a major problem due to cyclic vibration.
Maximum Delivery Pressure
- The maximum delivery pressure for the rotary compressor is 10 bar by multistage up 40 bar.
- The maximum delivery pressure for the reciprocating is as high as 1000 bar.
Cleanliness of Delivered Air
- The delivered air in the rotary compressor is cleaner because it does not come in contact with the lubricating oil.
- The delivered air in the reciprocating compressor is less clean because it comes in contact with the lubricating oil.
Working Fluid
- Air or some other gases are working fluid in the rotary compressor.
- Pressurized steam is the working fluid in the reciprocating compressor.
Few more points about the differences between rotary & reciprocating compressors to keep in mind:
- Rotary compressors are lighter weight and provide more capacity in a smaller package than reciprocating compressors.
- The reciprocating compressors use pistons while rotary compressors use rollers.
- Rotary compressors last longer than reciprocating air compressors and maintain the same performance throughout their long life.
So, now you know everything you needed to know about the differences between rotary and reciprocating compressors. Do you think there are other more differences than what we mentioned above? Share your thoughts with Linquip in the comment section. And feel free to sign up on our website if you want our experts to answer your most complicated questions regarding this field.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip








This article is the most comprehensive analysis of compressors that I have seen in performance analysis. Others will be a lot less. This comparison is more comprehensive.
Thank you very much
We would like to know your opinion about other articles as well
Thank you for this very detailed and informative blog highlighting the differences between rotary and reciprocating compressors, which is very useful for our industry. Reciprocal compressors, often referred to as piston-type air compressors, and rotary air compressors are the two most widely used types of air compressors now on the market. In order to choose the right type of air compressor, it is crucial for purchasers to understand the distinctions between these two types. Keep posting more these detailed and very well researched content!