Transducer vs. Sensor is a controversial subject in electronic systems; however, many people think that Transducers and Sensors have an identical application. The words transducer and sensor are applied interchangeably, and this can make telling the difference difficult; however, they are different instruments with various features. What is the main difference between a transducer and a sensor? Sensors and transducers are both instruments that respond to a variation in a sensible quality. The fundamental difference between a transducer and a sensor is that a transducer measures quality in one form and modifies it to another, while a sensor senses the variations or modifications in the environment and gives the output as the internal format.
Distinguishing Transducer vs. Sensor
What is the importance of distinguishing Transducer vs. Sensor? Sensors and transducers have various other differences besides their names. One of the considerable differences between them is that sensors detect the physical variations that happen in the surroundings while the transducers transform the physical and nonelectrical value to another electrical signal. Other differences between the transducer and sensor are defined further in the comparison data below.
A sensor identifies a chemical, biological, or physical value and transforms the received data through its detection normally into an electrical signal. A transducer is a more widespread instrument for turning energy from a specific form into another form. As a result, it can be said that a sensor is a particular type of transducer that converts one physical or chemical form into a different special form, including electronic data. A transducer can include such a sensor and employ it to achieve data, which it then transforms into readable information.
A transducer is more of a transformer, while a sensor is more of an identifier. Functionally, it means that a sensor accumulates information and reacts to it because the information is useful for it. For example, a thermometer, which detects variations in temperature and immediately presents a measurement output with important information. Visit here to compare sensors and transducers fundamentally.
If the sensor does not generate perfect output in its application, it should be combined with a transducer to supply the meaningful output. For instance, a loudspeaker may contain a sensor that identifies the sound vibrations and converts them to electrical signals, but it requires a transducer to complete the procedure of importing that sound in one part and generating intensified sound in the loudspeaker in the other section. Generally, a sensor detects, and a transducer modifies.
Differential Pressure Sensors: An Ultimate Guide
Comparison data
Comparison data for explanation more about Transducer vs. Sensor:
Definition and Function
Sensors fundamentally detect the physical variations that occur in the surrounding, transform it into a meaningful quantity, and induce the corresponding electrical signals. Otherwise, the transducer is an instrument that converts the energy from one form to another form when actuates.
Applications
Sensors are used in flushing the Infrared toilet lights, controlling the level of pressure in oxygen sources, and monitoring the patients. Transducers are utilized in controlling the engines, monitoring HVAC systems, navigating systems on vehicles, and lifting or positioning bridges or ramps.
Popular Examples
Thermistors, Mercury thermometers, Motion sensors, and Pressure switches are common examples of sensors, while cable extension, microphones, and linear Pressure devices are usual transducers used in industries.
Important Detailed Information About The Types of Transducers
What are the Characteristics of a Sensor?
Sensors are introduced as an instrument that is applied to detect a physical quality, for example, temperature, light, sound, etc., and send the output in a simple format for the user to read easily. Sensors transform them into a useful form. Sensors are too accurate instruments if calibrated perfectly.
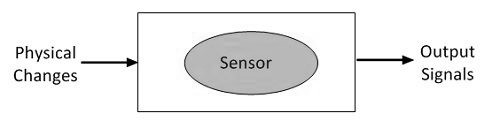
In some textbooks, there is a general definition that “not all transducers can be assumed as sensors, but many sensors are transducers”. For instance, a thermistor is a sensor; it will react to the variation in temperature but does not transform the energy into a different form like what was originally detected. This thermistor is a sensor on its own but, when it is combined with a bigger circuit or diagram, it will be the main part of a transducer.
Another example is the mercury thermometer; the mercury expands easily when the temperature increases to send a reading format for the user. There are no electrical signs or changes. So, it is originally a sensor.
Sensors Application
The sensors used in the electronic industries have different applications, which a few of them are described below:
- Photosensors detect the ultraviolet or infrared light in offices or domestic rooms.
- Motion sensors are employed in the security systems of buildings and the automation door devices.
- Accelerometer sensors are used in the mobile for identifying the rotation of the screen.
What are the Characteristics of a Transducer?
A transducer can identify similar values to a sensor but will turn the physical signal from one format to another. It means that its output and input signals are not the same as each other. Transducers are occasionally introduced as energy converters. They have six different types of measurements; thermal, electrical, chemical, mechanical, magnetic, and radiation.
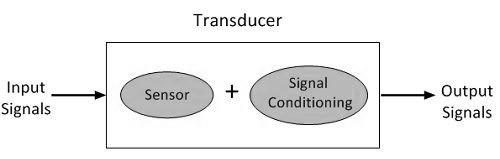
Transducers can also be introduced as input transducers and output transducers. An input transducer receives a format of energy and transforms it into electrical output, while an output transducer gets electricity and transforms it into another format. Light bulbs and motor are good examples of this method. The first one is used to take electricity and convert it to light, and the other converts electricity to motion.
Classification of a transducer
Transducers can be classified based on their transduction form:
- Passive and Active transducers
- Primary and Secondary transducers
- Digital and Analog transducer
- Direct and Inverse transducer
For more information about various types of transducers, click here.
Key Differences Between Sensors and Transducers
Sensors and Transducers have some key differences. The most considerable of them are introduced below:
- The sensor itself is the main part of the sensor circuit, while this sensor and its signal conditioner are the major elements of the transducer diagram.
- The sensor just detects the physical variations across the environment, while the transducer can convert one format of physical quantities into another form of energy like an electrical signal. The barometer, gyroscope, and accelerometer are the common examples of the sensors, whereas the thermocouple is the ordinary example of a transducer.
Here, we can clearly find the main differences between the Transducers and Sensors.
Thermocouple: Sensor or Transducer?
One of the instruments that sometimes bewilders people, which is a sensor or transducer, is the thermocouple. A thermocouple is an equipment that measures temperature with the thermoelectric influence. Its function is to identify the voltage variation between two electrical conductors when the temperature changes.
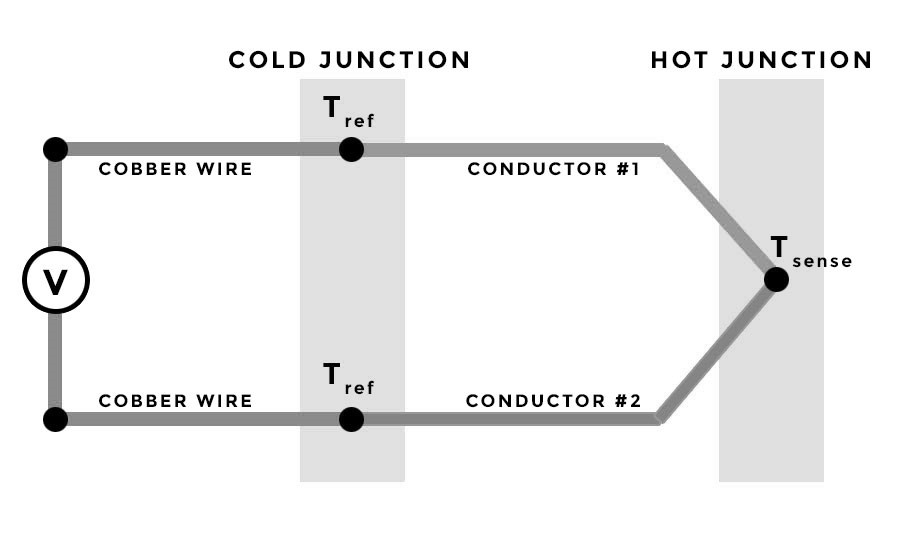
Thermocouples are too useful devices in industrial measuring. People employ them for various temperature measurements, such as diesel engines, kilns, thermostats, and gas turbine exhaust. But the fundamental question is that are they sensors or transducers?
Many people know them as transducers according to the supplying of a meaningful temperature output in one section, but in fact, the reading you obtain from a thermocouple is not the outcome of any transformation. It is actually a demonstration of the voltage made as a result of temperature variation.
As we discussed before, a sensor detects physical values like, in this case, temperature variation and converts it to an electrical output. For thermocouples, this electrical signal is formed as the voltage. Because no other modification happens, the thermocouple is more accurately named a sensor. Nevertheless, these terms are utilized interchangeably in an industrial or engineering environment. It is an appropriate concept to be as particular as possible to stop confusion and reduce the possibility of problems.
Transducer vs. Sensor : Selection Criteria
We should consider the following parameters of the Sensors and Transducers while selecting them:
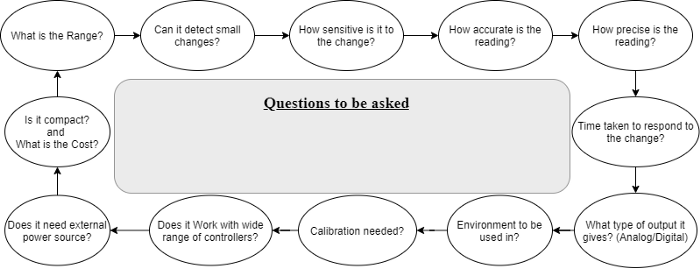
Range
The range is the difference between the minimum and maximum amount, which can be detected by the transducer or sensor.
Resolution
It is the smallest variation which can be identified by the sensor or transducer. So, it should be high for many applications.
Calibration
Sensors and Transducers should be simple to calibrate according to the fact that they require frequent calibration.
Nature of Output
It should be clear that the output of the sensor or transducer is Analog or Digital.
Sensitivity
It is the ratio of unit modification in the input to a variation in output.
Error
Error is defined as the difference among the true value and the measured value.
Accuracy
It is inversely corresponding to Error and should be high.
Precision
Precision is the capability to regenerate the perfect value repeatedly.
Response Time
It is the time duration between the output and input. Therefore, it should be minimum in sensors or transducers.
Signal to Noise Ratio
It is the ratio between the noise at the output and the magnitude of the internal signal.
Environment
The environment is one of the most considerable features because not all instruments can operate in extreme conditions. Sensors and Transducers can be influenced by non-ideal situations (like moisture, temperature, etc.), which may change their output.
Interfacing
It means that instruments should be suitable to combine with a wide range of instruments.
The power source
Some sensors and transducers require the external power source for generating the output to avoid additional errors in their circuits.
Size and Weight
Instruments must be close-packed and weightless.
Comparison for a Selection
In conclusion, let’s see, how we will be applying the above tips in selecting the perfect temperature sensor. We have a brief comparison between LM35 and DHT11 here depend upon the above points.
LM35 is an analog temperature sensor utilized to sense the temperature through an electrical signal changed with the temperature. The range of work is between -55 to 150°C, and the scale factor of this sensor is .01V/°C. So, if the temperature is 30°C, then the output voltage will be 0.3V. It doesn’t need extra calibration and keeps the accuracy of ±0.4°C for building temperature and ±0.8°C, out of the range of 0°C to 100°C.
DHT11 is a digital moisture and temperature sensor. The level of functioning is between 0 to 50°C with the accuracy of ±2°C for temperature sensing. Its accuracy is between 20 to 80%, with a 5% error for moisture detecting, and the sampling rate is 1Hz.
Now we can see that LM35 has a greater range of functioning than DHT11, but when we want to use them in a home application, both of them can be employed. However, we can select LM35 for more accurate results. Otherwise, if we want to control humidity with temperature, then DHT11 is a better option.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Types of Sensors Detectors/Transducers: An Entire Guide
- Resistive Transducer: Working Principle & Example
- Photoelectric Transducer: Application & Working Principles
- What Is a Pressure Transducer? A Simple Descriptive of the Definition, Working Principle, and Considerations
- Important Detailed Information About The Types of Transducers
- Pressure Transducer: Definition, Working Principle, and Types
- Transducer vs. Sensor: Basic Differences & Advantages of Them
- Temperature Transducer: Definition, Working Principle, and Types
- Piezoelectric Transducer and Its Impressive Applications in Electric Circuits
- What are the Main Benefits of an Ultrasonic Transducer?
- All You Need to Know about Transducer
- What is a Fuse Wire & How Does It Work?
- What is Electrical Identification? (2022 Ultimate Guide)
- How to Wire Up Piezoelectric Sensor? A Comprehensive Guide



