Why Do We Use AC Instead of DC? Exploring the Advantages of Alternating Current
Generators are one of the most critical appliances in the present-day world. Electric failures can happen due to a variety of reasons such as natural disasters, load shedding, system failures, and infrastructure breakdown. Without generators, your world will go dark on such occasions. Without knowing the detail and use of each type of generator, you can end up spending your hard-earned money on the wrong machine. In this article from Linquip, we will discuss different types of generators and their applications and dive deeper into knowing each one of them on another level. As you probably know, Some generators are more popular than other competitors on the market. Here, we will introduce the most popular ones. Are you ready to expand your knowledge? Read on to find out more.
In Linquip, you will find everything you need to know about generators, from the basics to the most advanced units. In case you need help with a generator, our experts are available to assist you. For a basic understanding of these industrial devices, please take a look at Linquip’s article “Generator: Working Principles, Function & Diagram.”
Do you have any experience with the use of generators? Browse Linquip’s selection of Generator Products to find the generator that will meet your needs. Is there a particular type of generator that you are looking for? We provide free access to all available Generator Devices for Sale at Linquip. When you are looking for generator prices, you can also submit an inquiry/request for quotes through Linquip to all Generator Suppliers and Companies for free.
What is a Generator?
Generators provide electrical power by converting mechanical energy and are used in an external circuit. Different mechanical energy sources such as wind turbines, steam turbines, water turbines, gas turbines, and internal combustion engines are used to provide the source for this conversion. There are different types of generators, each of them tailored to specific needs.
Different Types of Generators
Whether you need a temporary electricity fix or want backup power for your factory, there is always a generator suitable for your specific purpose on the market.
Here are List of some different types of generators:
- Gasoline
- Diesel Fuel
- Biodiesel
- Emulsified Diesel
- Propane Gas
- Natural Gas
- Solar Generators
- Portable generators
- Inverter generator
- Standby generators
- Induction generators

Also, there are two fundamental types of generators known as AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) generators. While the technique of producing electricity is the same in both types, AC and DC power become different in terms of their applications – how loads receive electric power. For instance, generators for home use deliver AC power whereas cars use generator engines that produce DC power.
Characterizing generators may be done in several ways which are:
-
- By the energy source used as input
- By the application or industry in which the generator is employed
Generators by Energy Source
Common input energy sources for generators are either a fossil fuel that is combusted in an engine to produce rotary motion within the generator or a natural energy source that is captured and turned into motion.
Fossil-Fuel Energy Source Generators
Generators that are based on a fossil fuel energy source include:
-
Gasoline
Of all the options on the list, gasoline generators are among the most common, primarily because gasoline is readily available and these generators are on the low end of the cost scale. However, gasoline is usually unavailable during power outages, because it requires electricity to pump. Gasoline generators are available in small sizes, ideal for portable models, but the fuel is highly flammable. You can use them for various purposes such as residential or commercial uses. But if you want to use them for your house or office, keep in mind that they are loud and produce disturbing noises that might annoy you in the long run.
Gasoline lasts less than one year when stored, and gas prices are comparatively higher than diesel, propane, and natural gas. Gasoline generators produce relatively high emissions, do not typically last as long as some other models, and do not tend to start well in colder temperatures.
-
Diesel Fuel
Diesel is the least flammable of all the fuel sources and is almost as readily available as gasoline. These engines have long lifespans and perform more efficiently while lasting longer under heavy, rigorous use, so long as they are properly maintained. This type of generator is affordable to operate and starts relatively easily in cold environments. So, you can easily use them in cold weather too!
However, diesel fuel is only good for up to 24 months in storage, and storing large quantities can be expensive. Like gas, it is often impossible to pump diesel during power outages. Because diesel engine emissions are quite high, some areas limit the number of hours these engines can be operated per day due to environmental concerns. Besides, it is advised not to use them in wet environments because if the moisture gets into the fuel, it will damage the engine.
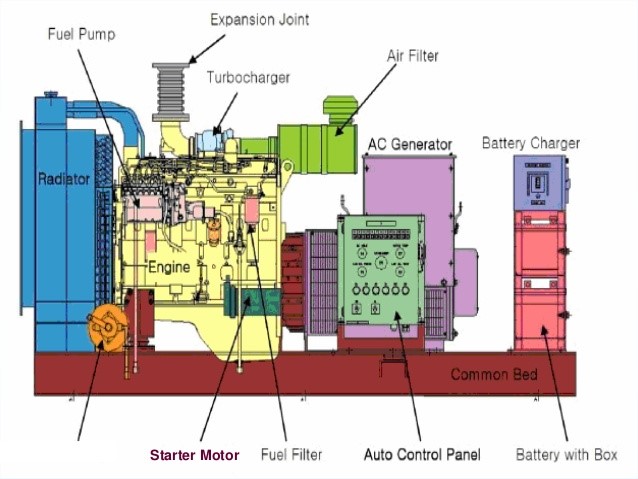
-
Biodiesel
Biodiesel fuel is made from a mixture of diesel and another biological source, such as vegetable oil or animal fat. The pros and cons of biodiesel are similar to those of ordinary diesel fuel, only with more environmental benefits. Biodiesel uses less of the non-renewable energy source of fossil fuels and burns with lower emissions and less waste. This makes it an environmentally friendly option compared to regular diesel. All diesel fuels are less flammable than the other liquids and gasses on this list, but these engines are also noisy.
Like diesel, biodiesel lasts two years or less in storage and is sometimes unavailable during a power outage because it cannot be pumped.
-
Emulsified Diesel
Emulsified diesel is a mixture of diesel fuel and water blended with a mixing agent. It shares the pros and cons of diesel and biodiesel fuels. As with biodiesel, emulsified diesel produces fewer emissions than ordinary diesel and consumes fewer fossil fuels. It too has a shelf life of two years or less, and maintaining the proper ratio of water to diesel is challenging, especially in hectic work environments.
Natural Energy Source Generators
Other types of generators that take advantage of a natural energy source include:
-
Propane Gas
Propane boasts a longer shelf life than gasoline or diesel fuels and burns cleaner. It is easily stored in any quantity and is readily available even during power outages. Propane produces relatively low emissions and is not subject to wet stacking common in diesel generators. This type of generator is generally affordable and lasts a long time. Propane also starts easily in cold temperatures and offers quiet operation.
On the con side, propane is kept under pressure and is highly flammable, even explosive. Propane generators are more expensive to buy and operate, burning about three times the amount of fuel as comparable diesel engines. -
Natural Gas
Natural gas is readily available in almost every location and the new shale reserves opened up by fracking techniques mean a virtually limitless supply. Because natural gas lines are run to the site of operation, these generators never run out of fuel or need to be refilled. This also means that the generators are not portable.
Natural gas generators burn cleanly with very little waste, and the gas is readily available even in the absence of a power supply. These units are also affordable in comparison to other choices. Natural gas also starts well in cold conditions and runs relatively quietly. Another advantage of using them is that they run quietly which makes them perfect for residential uses.
Although they are inexpensive, they have high installation costs since they should be connected to the running gas lines. Besides, these generators do not typically last as long as diesel generators. -
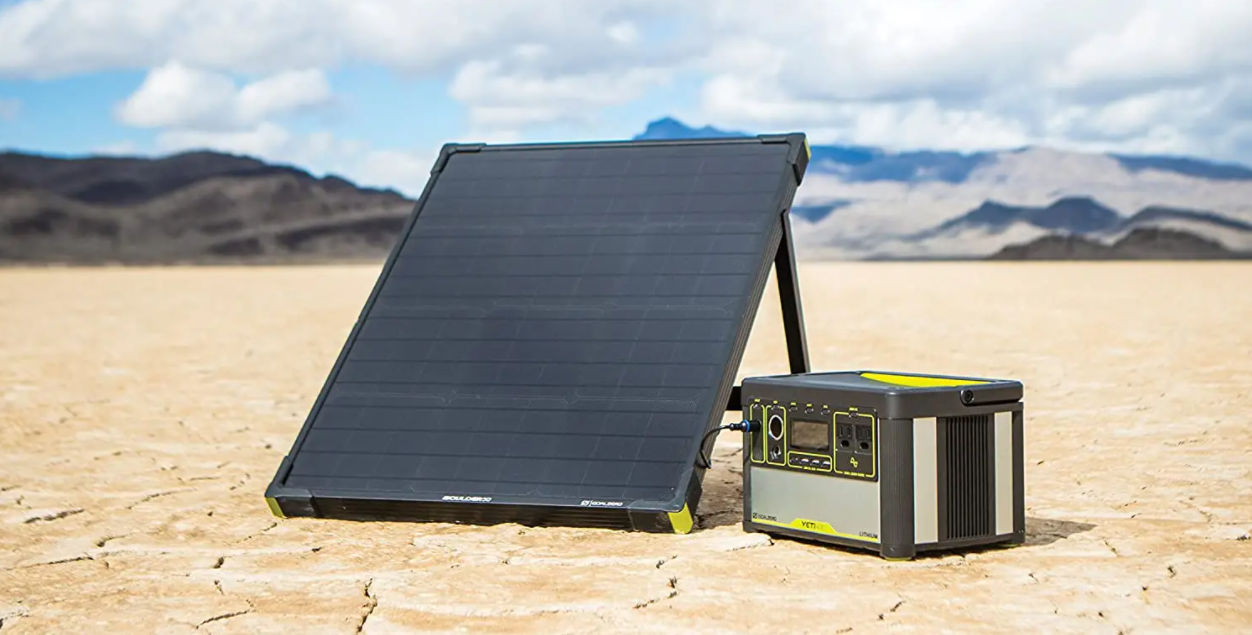
Solar Generators
Solar generators use the sun’s radiating energy as their fuel source. They use solar panels for capturing the sun’s energy and charge the battery in the generator. This charge is used for producing electricity which is the final goal of the generator. It also contains an inverter for changing the power to alternating current since many appliances use AC. These types of generators are great for minimal electrical requirements. Plus, they do not produce disturbing noises. One of the drawbacks of them is that they are not cheap at all! Plus, they run very slow when charging their batteries.
-
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is tremendously abundant, non-toxic, clean, cheap, and produces more energy per pound than any other fuel source.
Though not as readily available as some other types of generators, hydrogen generators are portable and useful for many environments, including laboratories. When equipped with proper safety features, hydrogen generators are also safe and portable.
Generators by Application
Generators based on their application include:
- Portable generators
- Inverter generator
- Standby generators
- Induction generators
-
Portable generators
This generator type uses gas or diesel as its fuel source. Just like standby generators, they use a combustion engine to produce electricity. They are great if you need temporary electrical power and remote construction sites for power tools and lights. They can be wired into the sub-panel for residential uses to power a refrigerator, television, etc. or you can use them by plugging your electrical appliances into the power socket of the portable generator.
Portable generators are very useful in a variety of applications. They come in varying power configurations suitable for different types of uses. They are handy during natural disasters or calamities when grid power breaks down. They are more suitable for residential purposes and smaller commercial establishments such as retail outlets and shops, at construction sites for powering smaller tools, camping, outdoor weddings, outdoor events, and, powering agricultural equipment such as bore wells or drip irrigation systems.
If you are looking for different types of generators for electricity generation for your house or office, this type may be the right choice for you. They not only provide temporary electricity but are also cheap and work very well. But keep in mind that you cannot install them inside a house or a garage! Plus, they need protection against diverse weather conditions. -
Inverter generator
Inverter generators produce AC power and by using a rectifier that converts the AC power into DC power and then inverts it to AC to provide steady current to appliances. These are very useful for appliances such as air-conditioners, refrigerators, automobiles, boats, and recreational vehicles which need particular values of voltage and frequency, which inverter generators are capable of providing. They are also light in weight and compact, therefore highly suitable for such applications.

-
Standby generators
Standby Generators are among the most popular types of generators that are also known by the name of “backup generators”! They are considered to be an emergency power system that may use gas or diesel as their fuel source. They work up to 48 hours because of their large external tank. When there is a power outbreak, an automatic transfer switch on these generators is activated for powering a device.
Their automatic operation as well as using an internal combustion engine, not to mention their ability to deliver permanent power protection, make them a common choice on the market. After only a few seconds of the power loss, they start operating to supply the necessary electricity for you. That makes them a perfect choice for medical support equipment. This type of generator is also very useful for residential apartments, hotels, restaurants, hospitals, and commercial establishments connected to grid power. But it comes at a price! They are extremely expensive and need regular maintenance. -
Induction generators
These comprise two types including externally excited generators and self-excited generators.
Externally excited generators find uses in regenerative braking applications needed in hoists, cranes, elevators, and electric locomotives.
Self-excited generators find uses in windmills where wind as a non-traditional source of energy gets converted into electric power.
So, there you have a detailed description of different types of generators and their applications. Do you know any other popular types? Then comment below and share your thoughts and comments with us. To receive the latest information about generators and ask your questions, feel free to sign up on Linquip where our experts will help you find what you are looking for.
Download Types of Generators PDF
For your convenience, the PDF version of this document can also be downloaded to your computer. Below is a link to download it.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Parts of Generator: a Simple, Yet Useful Guide
- More Details about Siemens Generators
- More Information about Siemens Generators Services
- Read More Information about Siemens Generator Installation Services
- Read More Details about Siemens Generator Maintenance Services
- More Information about General Electric (GE) Generators
- More Information about GE Generator Services
- More Details about GE Generator Installation Services
- More Details about GE Generator Maintenance Service
- What are Alstom Generators? (Clear Guide)
- Generator Maintenance: The Most Essential Tips to Know
- Best Portable Generators: Everything You Need to Know
- The Best Diesel Generator
- The 10 Best Solar Generator
- Concise Guide to Generator Transfer Switch Installation Cost
- Generator Efficiency
- What Is a Generator? A Comprehensive Explanation of Working Principles, Types, and Components
- The 5 Best Gasoline Generator
- Parts of DC Generator: Explanation of Parts, Working, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages
- Best Dual Fuel Generator
- Electric Generator Maintenance, Repair, and Services
- Gasoline Generator Repair and Maintenance
- How Much Does It Cost to Install a 22kW Generac Generator?
- How Long Can A Standby Generator Run Continuously?
- What is the Difference Between a Whole House and Standby Generator?
- The Difference Between Prime & Standby Generators
- Can I install a Standby Generator Myself? (An All-In-One Guide)
- Portable vs. Standby Generator (Best Choose for Home)
- DC Generator Repair, Maintenance & Testing (Full Guide)
- Pros and Cons of Inverter Generators
- The 5 Best Propane Generators
- The 9 Best RV Generators (Clear Guide)
- The 10 Best Ozone Generators (Ultimate Guide)
- How to Connect a Generator to Your Home? (Best Guide)
- The 3 Best Portable Power Station Generators +Pros & Cons
- How To Store Your Generator Safely? (Clear Guide)
- How To Quiet A Generator? (Comprehensive Guide)
- How Do I Choose The Right Generator For My Needs?
- How to Calculate The Fuel Consumption of the Generator?
- How Do I Maintain The Battery of My Generator?
- How Long Can a Generator Run Continuously?
- How to Use a Portable Generator During a Power Outage?
- Why Do We Use AC Instead of DC? Exploring the Advantages of Alternating Current
- Main Benefits of Generators for Disaster Response
- How To Clean Up Generator Power? (Clear Guide)
- What Are The Benefits of Generators?
- Do Generators Work In A Flood? (What to Do If Your Generator Is Flooded?)
- Can A Home With Solar Panels Use A Generator?
- Converting Your Generator To Propane: Step By Step (Clear Guide)







It’s good to know that standby generators are popular. That tells me they work. So I am okay with getting one of those.
Thanks for your comment
Good luck