Types of Bolt Heads – Bolt heads can be made in a variety of forms, but the most common are socket caps, square, hex, and slotted hex washers. The earliest bolts used were square head bolts. A square depression is placed on the head after a shaft that can resist rotation when a torque is applied.
On the Linquip website, among the many options available to you, you will find all the information you need to know about the Bolt Heads, as well as information regarding this marketplace. You can count on Linquip to provide you with as much general and reliable information about this topic, whether you’re a professional or a customer looking for a proper company. We recommend you review a list of all Bolt Heads Products available in Linquip. You can also be encouraged to visit Bolt Heads for Sale and find the most suitable device based on your applications and demands.
Various Types of Bolt Heads
There are many different head shapes for both screws and bolts. The design of these heads allows them to easily grasp the instruments needed to tighten them.
Bolt heads come in a variety of shapes, with square, hex, slotted hex washer, and socket cap being the most popular.
The square head bolts were the first to be used. Square heads are composed of a shaft that can resist rotation when a torque is applied, followed by a square depression on the head.
Hex heads have grown increasingly prevalent, however square heads are still in use. To create torque, hexagonal heads are used with a wrench or a spanner.
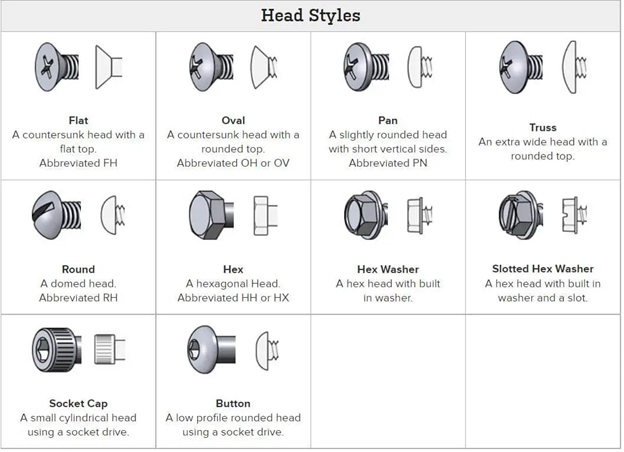
There are also many more head forms in use, including:
- Bolt with a flat top known as a flat bolt head. When using a flat head, it should be countersunk into the material. As the head lies flush with the surface of the material it is being used with, flat heads are frequently utilized when a low-profile fastener is needed.
- A countersunk head with a rounded head top is an oval bolt head. A form of bolt head having an oval head rather than a hexagonal, square, or round head is known as an oval bolt head. Due to the fact that the bolt’s head is flush with the surface of the material it is being used with, it can also be utilized in situations where a low-profile fastener is preferred.
- Pan bolt head: A head that has a short, vertical side and a somewhat rounded top. In ornamental applications, a rounded head with a flat top is frequently utilized. Pan’s heads are similar to round heads in that they are frequently used as ornaments, but they are rounder and have a flatter top.
- The extra-wide, rounded-top head of a truss bolt. A type of bolt called a truss bolt is used to attach trusses in building and engineering applications. It has a flat, triangular head. To preserve the structural integrity of the truss in these applications, a strong clamping force is required, which is made possible by the flat, triangular form of the head.
- A dome’s head is a round bolt’s head. A round head is frequently employed as an ornamental accent. Although round bolt heads are less typical than some of the other varieties, they might be employed in situations that call for a more aesthetic appearance.
- A hexagonal head is found on a bolt. a hexagonal head that a wrench or socket may be used to tighten or loosen. Hex heads are widely utilized in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, the automobile industry, and construction. They are simple to grasp with a wrench or socket, and their design enables the application of high torque.
- Bolt head with a circular washer at the bottom and a hexagonal head. A kind of bolt with a hexagonal head and an integrated washer is known as a hex washer bolt. The washer, which is normally found behind the bolt’s head, is intended to more uniformly distribute the bolt’s weight across the surface of the material it is being used with.
- The bolt head with a slotted hex washer and a built-in washer is hexagonal in shape. Instead of a wrench or socket, the slot enables the bolt to be tightened or loosened using a screwdriver. The hexagonal head of the bolt enables high torque to be applied, and the built-in washer helps to distribute the bolt’s load more uniformly across the surface of the material it is being used with.
- Bolt head with a socket cap: A tiny, cylindrical head that requires a socket driver. a head with a hexagonal recess and a cylindrical shape that may be adjusted with a socket Hex heads and socket heads may both be tightened or loosened using a socket, although socket heads have a cylindrical form as opposed to hex heads’ hexagonal shape. They are frequently utilized in situations where a low-profile fastener is required and strong torque is needed.
- A low-profile, rounded head with a socket driver is a button bolt head. In applications where a low-profile fastener is desirable, a tiny, flat head with a low profile is frequently employed. Flat heads and button heads are similar, but button heads have a smaller head and a lower profile.
While screws and bolts have a lot in common, there are also some key distinctions.
The Benefit of Bolts and Nuts
The usage of nuts and bolts has the benefit over other types of fasteners in that they may be dismantled as required, whereas other fasteners like rivets are intended for permanent placement. The washer increases the surface area across which the attachment force is exerted when bolts are utilized with nuts and washers. Hex nuts are the most popular form of nut to use with a bolt among the many other varieties available. Other varieties of nuts are:
- Locknuts
- Flange nuts
- Hex nuts with slots
- Cap nuts
- Thumb nuts
- Coupling nuts
- Panel nuts
- Square nuts
- Nuts for surface mount
A variety of materials, including wood, sheet metal, steel, iron, and polymers, can be joined together by nuts and bolts. They can also be used to lock the nut firmly in place in other situations, such as when using slotted hex nuts with a matching bolt and cotter pin.
Bolts and nuts can be used with a variety of common hand and power tools, such as socket sets, open-end wrenches, box wrenches, and powered drivers.

Options for Nuts and Bolts in Grades and Materials
Depending on the intended use, numerous types of materials are available for bolts and nuts. Typically, fastener goods like bolts, screws, and other sorts are given a grade. The fastener must fulfill the grade’s minimum acceptable criteria for mechanical attributes or performance. Bolts with higher grades often have better mechanical strength properties.
Grade Markings on Bolts
On the bolt head, grade identification markings are made and utilized to indicate the bolt’s grade. There are grade identification tables that define these marks and outline the minimal permissible values of proof, tensile, and yield strength needed to satisfy a certain grade of bolt for frequently used ASTM and SAE steel grades. The common material choices and heat treatments applied to the completed product are also mentioned.
For ASTM bolts, for instance, SAE grades range from Grade 1 to Grade 8.2. The minimum proof strength, minimum tensile strength, and minimum yield strength for SAE Grade 1 bolt are 33, 60, and 36, respectively (all in 103 psi). SAE Grade 8.2 bolts would have minimum proof strength of 120, the minimum tensile strength of 150, and minimum yield strength of 130 at the top end of the grade scale (measured in 103 psi).
Both ASTM grades and metric fasteners have a similar grading system. The mechanical characteristics and grade standards for metric bolts are specified in ISO 898.
Options for Common Materials
A variety of materials are available for the fabrication of ASTM/SAE grade bolts. These steel materials are the most prevalent:
- Steel with low carbon
- Mid-carbon steel
- Low-carbon steel with martensite
- Weathering steel
- Alloy steel
- Medium carbon alloy steel
There are more material options for bolts outside the standard steels. Stainless steel, metal alloys like brass and bronze, and polymers like nylon or PEEK are some of the alternatives (PolyEther Ether Ketone). While polymer choices are employed when intrinsic strength is less important but a stable material with chemical resistance is required, stainless steel offers great corrosion resistance and strength.

Options For Material Treatment And Finishes
To give material stability and protection from corrosion and rust brought on by environmental factors or exposure to corrosive chemicals, both the use of heat treatments and the application of various finishes can be utilized. Quenching and tempering are two treatment techniques in addition to cold drawing.
Some common finishes are:
- Anodizing
- Armor coating
- Black oxide
- Blue phosphate
- Chrome plating
- Hot-dipped galvanized
- Yellow passivated
- Zinc coating
FAQs about Types of Bolt Heads
- What are the heads of a bolt?
These are made to fit the tool that will be used to tighten them. Instead than allowing the bolt to move, certain bolt heads lock the bolt into place, requiring a tool only for the nut end. Bolts frequently have hex, slotted hex washer, and socket cap heads. The original bolts featured forge-formed square heads.
- What are the three types of bolts?
Anchor Bolts are among the most prevalent types of bolts. Blinking Bolts Bolts for carriages.
- What are bolts with round heads called?
For wood connectors, button heads or round head bolts are frequently utilized. Bolts with a round head resemble carriage bolts but lack the square neck that surrounds the head. Round head bolts are seldom high strength and almost usually offered in a basic ASTM A307 specification since they are frequently used with wood.
- Are there different types of bolts?
Bolts and hardware nuts come in a variety of varieties. The majority of bolt types—if not all—have machine threads. In order to secure or bind things together, threaded bolt screws into nuts. Eye bolts, wheel bolts, and machine bolts are examples of bolt types, whereas cap nuts, expansion nuts, and u-nuts are examples of nut kinds.
- What is the most common type of bolt head?
Bolt heads come in a variety of shapes, with square, hex, slotted hex washer, and socket cap being the most popular. The square head bolts were the first to be used. Square heads are composed of a shaft that can resist rotation when a torque is applied, followed by a square depression on the head.
Conclusion
You may acquire all the details you want about the Bolt Heads and details about this market on the Linquip website, one of the numerous possibilities available to you. Whether you’re a professional or a client seeking for a reputable business, you can rely on Linquip to give you as much basic and trustworthy information on this subject. We advise you to look through the whole range of Bolt Heads Experts and take advice from our professionals. If you need any services required for your product, you can count on Linquip and visit Bolt Heads Services.
Download PDF for Types of Bolt Heads
You can download the PDF format of this post from the link provided here.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More On Linquip
- Different 5 Types of Fasteners: A Practical Guide
- Different Types Of Screw Heads: A Practical Guide
- Different 15 Types of Hand Saws: Clear Guide
- 12 Types of Industrial Sewing Machine + Advantages
- The 6 Best Industrial Sewing Machine
- 12 Types of Electric Saws: Clear Guide
- Types of Drill Bits for Metal: Comprehensive Guide
- Different Types of Socket Wrench: Clear Guide
- 42 Types of Wrenches + Guide for Choosing a Wrench
- Different Types of Socket Wrench: Clear Guide
- 13 Types of Adjustable Wrench: Clear Guide
- All 24 Types of Drill Bits + Video: Clear Guide
- 3 Types of Crimping Tools + Name & Their Uses
- 33 Types of Pliers & Their Names: A Comprehensive Explanation
- 53 Differents Tools for Construction Workers



