Types of circuit breakers are used for a variety of applications. Circuit breakers are classified through different methods, such as arc extinction, or rated voltages. To learn about different types of circuit breakers check out this article at Linquip.
What is a Circuit Breaker and How Does It Work?
A circuit breaker is a mechanical device that disturbs the flow of a high current and performs a switch function. It is specifically intended to lock or open an electrical circuit and thus avoid harm to the electrical system.
The circuit breaker comprises primarily fixed and moving contacts. These contacts meet each other and hold the current while the circuit is closed in normal conditions. The current-carrying contacts, known as the electrodes, are engaged under spring pressure while the circuit breaker is closed. The arms of the circuit breaker may be extended or closed for system switching and servicing during the usual operating condition. The circuit breaker is opened by just one pressure on a button. Whenever there is a malfunction on some part of the device, the trip coil of the breaker gets energy and some process divides the moving contacts and thereby opens the circuit.
Types of Circuit Breaker
As mentioned above, the classification of circuit breakers is based on many methods. One method is that circuit breakers are classed based on their mechanism. Therefore, we can find them in these categories: Voltage, Interruption Mechanism, Installation Location, and Features or Design.
However, the most famous method is arc extinction. This method in types of circuit breakers is below to help you understand each classification.
Types of circuit breakers according to arc extinction medium
sf6 circuit breaker
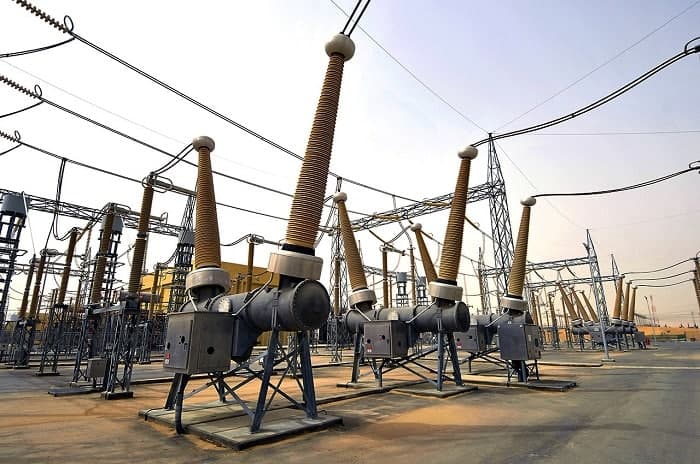
sf6 circuit breaker is the first CB we introduce here for types of the circuit breaker. This circuit breaker uses Sulphur hexafluoride, which is why is known as SF6 CB. The SF6 circuit breaker is an advanced and widely used CB. SF6 has very good insulating properties and high electronegative efficiency. Free electrons arise because of ionization as an arc happens. These free electrons interfere with SF6 gas molecules. SF6 molecules are vulnerable to free-electron absorption. SF6 has an outstanding capability for heat transfer. The arc creates high temperatures and the SF6 will reduce the temperature. SF6 is an arc quenching medium 100 times more effective than air. This circuit interrupter is used for the 33 kV to 800 kV voltage range. The downside to this type of circuit breaker is that it has 23,900 times the global warming potential to CO2.
oil circuit breaker
This type of circuit breaker uses oil as a dielectric medium. This oil is known as mineral oil or transformer oil. This kind of circuit breaker is the very oldest kind of circuit breaker and is seldom seen in today’s system network. The oil is a strong dielectric and is the best liquid insulator. The fixed contact and moving contact are immersed in the insulating medium of mineral oil. The arc will initialize amongst contacts as the circuit breaker is switched ON and OFF. The oil vaporizes and gets decomposed into hydrogen gas. This gas is created as a bubble and these bubbles are made around the arc and keep the arc from being limited when the current hits a zero-period crossing. The oil type of circuit breaker has two kinds: Bulk oil circuit breaker and Minimum oil circuit breaker.
air circuit breaker
An air circuit breaker, as another type of circuit breaker, uses air as a means of arcing and is called an air circuit breaker or an air blast circuit breaker. This CB is not used for high voltage. It is used at low to medium voltage. This CB is better than oil CB because this CB is safer. Oil explosion is very dangerous and is likely to occur. The air circuit breaker used in developing countries was CB rather than oil. Compared to other CB, the operating principle of air CB is distinct. For arc interruption, it produces an arc voltage. You can find two types of air circuit breakers Plain air circuit breakers and Airblast Circuit Breakers.
Vacuum circuit breaker
To continue talking about types of circuit breakers, we introduce a vacuum circuit breaker. Within this type, the circuit breaker is a dielectric medium in which a vacuum is often used. This is not completely a mature CB technology. The performance of CB depends on the material used for the contacts. Copper/chrome is commonly used to perform well. The vacuum has great dielectric characteristics. The dielectric power of the vacuum is 8 times higher than that of air and 4 times that of SF6 gas. The creation of an arc is caused by the ionization of metal ions as the breaker works. Electrons and ions are created during the arc by metallic vapor. The arc is then easily extinguished. The voltage range is 22 kV to 66 kV and vacuum CB is used for the distribution system. Generally, this CB is used in rural areas.
The second type of circuit breaker
Single-Pole Circuit Breakers
Single-pole circuit breakers are the most common type of circuit breaker in today’s homes. They are referred to as single-pole because, in the case of a short or electric overload, they are equipped to track the current of a single wire. Single-pole breakers are designed to handle 15 to 30 amps and provide the circuit with 120 volts.
Double-Pole Circuit Breakers
The second CB among other types of circuit breakers that falls into this class is the Double-pole circuit breaker that simultaneously controls the flow of electricity through two wires. The two interlinked side-by-side switches make them easy to be distinguished as a single breaker. If one or both wires are low or overloaded, this kind of breaker can switch. This type of circuit breaker can be used to produce anything between 15 amps to 200 amps, either 240 volts or 120/240 volts on the electrical circuit. Double-pole breakers are needed by circuits supplying power to equipment needing significant electricity, such as washing machines and dryers.
GFCI Circuit Breakers
Ground fault circuit interrupter circuit breakers (GFCI) are designed to avoid line-to-ground errors. This is because there is an unsafe electrical path between a grounded element and an electrical current. GFCI breakers often have protection against an electrical short or overloaded current. Any electrical codes for house areas that may become watered, including toilets, laundry rooms, and outside areas, include these breakers.
AFCI Circuit Breakers
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter Circuit Breakers (AFCI) are designed for use in electrical wiring where arcing is observed. The result is to damage an electric cord or make the coating too thin and pose a significant fire risk. Standard single-pole and double-pole circuit breakers do not always detect electric arcs, because extreme heat is the only way to do so. As part of the electric code of newer houses, AFCI circuit breakers are needed.
Types of circuit breakers according to rated voltages
We have another categorization for types of the circuit breaker. In this categorization, the circuit breakers below a rated voltage of 1000V are known as the low voltage circuit breakers, and above 1000V are called the high voltage circuit breakers.
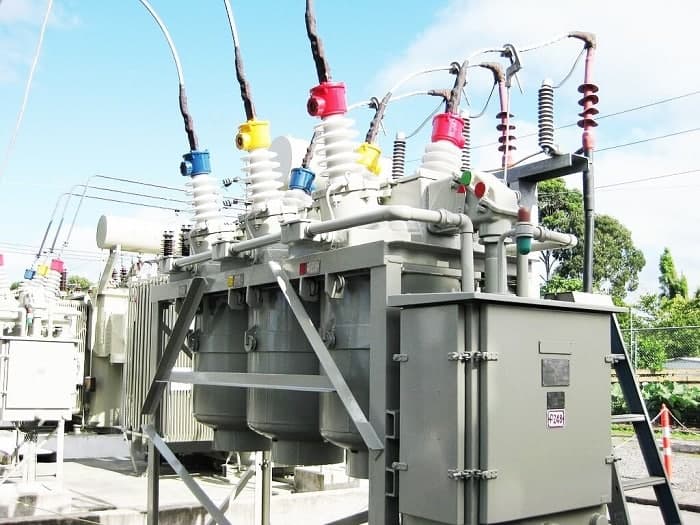
Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers
This can be used in buildings, companies, and manufacturing as one of the most commonly used circuit breakers on the market. Low-voltage circuit breakers have been built to be serviced quickly. Sometimes they are disassembled for maintenance without the customer needing to disassemble the switchgear. Some assemblies are automated so that an operator can open them and shut them off remotely. These circuit breakers can be used also for direct current applications. As the internal electrical arc of direct current doesn’t stop and resume, a separate form of the breaker must be used inside the device. When a home or company does not have a power requirement above 2500 amps, its operations are secured and controlled by a low-voltage circuit breaker.
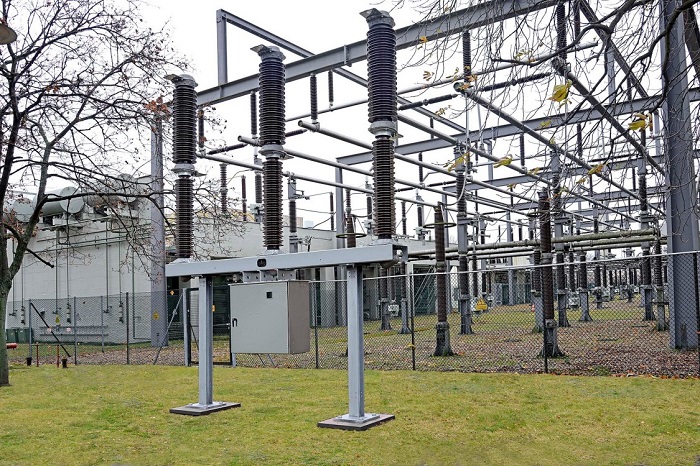
High-Voltage Circuit Breakers
These breakers use solenoids operated by protective relays and current transformers. They also have complex safety nets, which can be used in many ways to avoid overcurrent incidents. The breakers use several different forms to break the arc: bulk oil, minimum oil, air blast, vacuum, sulfur hexafluoride, and carbon dioxide. However, oil and carbon dioxide are excluded in favor of the environmentally friendlier sulfur hexafluoride solution.
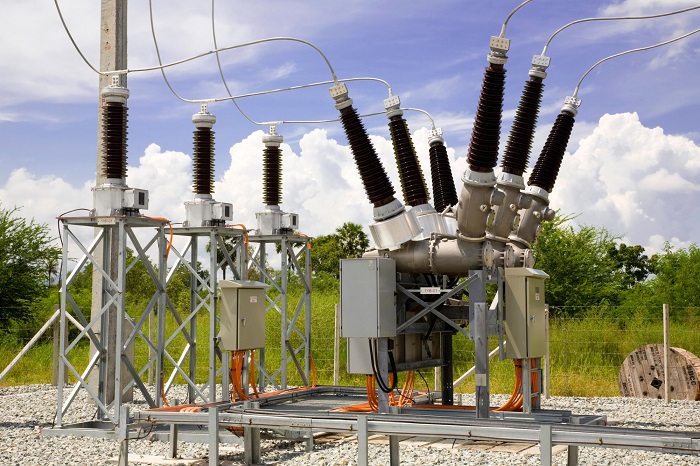
And Medium-Voltage Circuit Breakers
Types of circuit breakers do not end. There is another circuit kind within this classification. Medium-Voltage Circuit Breakers, that treat voltages ranging from 1.000 to 72.000 Volts and are installed for indoor and outdoor applications. Indoor systems have used air for a long time to break the arc, but gradually under 40,500 volts, they are switching to vacuum breakers. Current transformers detect the current moving through the circuits and trip circuits using an electrically controlled switch. Protective relays track dangerous anomalies in the existing current.
Let us just mention some other types of the circuit breaker.
Types of Circuit Breakers Based on Type of External Design:
Circuit breakers are classified into two kinds based on their physical construction:
Dead Tank Type: The switching equipment is positioned in the vessel at the base potential, surrounded by the shielding medium and interrupters. These types of the circuit breakers are largely used in the United States.
Live Tank Type: The switching equipment is positioned at the highest potential in the vessel and is surrounded by the shielding medium and interrupters. These types of the circuit breaker are typically used in European and Asian countries.
Right up here, we mention different types of circuit breakers like high-voltage, low-voltage, air, oil, etc. If you want to explore more details and more information about types of a circuit breakers, register at Linquip. Then contact us; we will provide you with the best answers.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Types of Electric Circuits: All Classification with Application
- Difference between Series and Parallel Circuits | What are they Completely?
- A good look at Vacuum Circuit Breakers
- Difference Between Isolator and Circuit Breaker: Ultimate Guide
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker: Everything You Need to Know
- How does a Circuit Breaker Work?
- The 8 Best Circuit Breaker Locators
- The ultimate guide to knowing everything about all types of MCB