Types of Dynamic Pumps – Different types of dynamic pumps may be found on the market and you can find any type of them on Linquip. This post will help you understand the primary functions of each type of pump. The type of pump and its selection are mostly determined by your needs. The type of fluid you want to pump, the distance you want to move the fluid, and the volume you require in a given length of time are all part of the application. However, determining which sort of pump you require might be challenging. The design as well as the locations can be used to identify the pump.
⇒ View a Comprehensive List of Dynamic Pumps for Sale and Their Suppliers ⇐
What Is a Dynamic Pump?
A dynamic pump is a form of velocity pump that uses increased flow velocity to impart kinetic energy to the fluid. When the velocity of the flow is lowered prior to or as it departs the pump into the discharge pipe, this increase in energy is transformed into a gain in potential energy (pressure).
Because it uses kinetic energy to pump the fluid, a dynamic pump is also known as a kinetic pump. The fluid is typically pumped by centrifugal force in this pump. Dynamic pumps are utilized in situations where a constant flow rate is required. An impeller, diffuser/volute casing, and housing are all included in these pumps. The First Law of Thermodynamics, or more particularly Bernoulli’s principle, explains this conversion of kinetic energy to pressure. For water supply, dynamic pumps are employed, whereas positive displacement pumps are used for foam.

The primary distinction between a dynamic and a positive displacement (PD) pump is the way they function. A spinning impeller is used in dynamic pumps to create a cavity, whereas a reciprocating element (such as a piston or plunger) is used in positive displacement pumps to create a cavity. Positive displacement pumps feature more rotatory components than dynamic pumps. They are less heavy than PD pumps. The most prevalent types of dynamic pumps are centrifugal and submersible pumps.
Dynamic pumps can be further segmented based on the method used to accomplish velocity increases. Pumps of this type have a variety of characteristics:
- Increase in kinetic energy due to the conversion of more energy (increase in velocity)
- Increased velocity (kinetic energy) is converted to a rise in pressure head
- Continuous energy
The way dynamic and positive-displacement pumps work under closed valve circumstances is a practical distinction. Because positive-displacement pumps physically displace fluid, shutting a valve downstream of one causes a continuous pressure build-up that can cause the pipeline or pump to break mechanically. Dynamic pumps are distinct in that they may be safely operated with closed valves (for short periods).
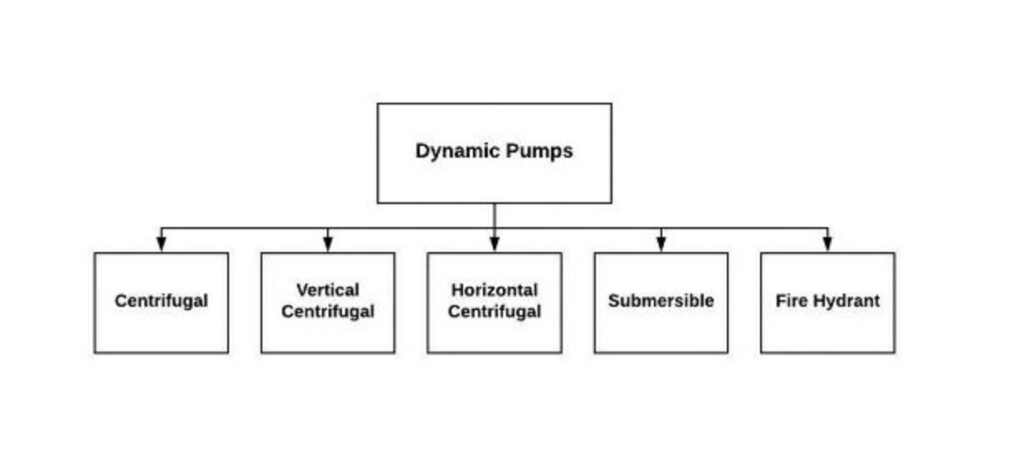
What are the Main Types of Dynamic Pumps?
- Axial Pump
- Centrifugal Pumps
- Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
- Horizontal Centrifugal Pumps
- Submersible Pumps
- Fire Hydrant Systems
Submersible, Axial, Centrifugal, Horizontal centrifugal, Vertical centrifugal, and Fire hydrant systems are some of the types of dynamic pumps that are mentioned here.
Axial Pump
One of the most well-known varieties of the dynamic pump is the axial pump. These pumps are designed to pump incompressible liquids at high flow rates over a short delivery head. As a consequence, only the axial pump’s flow-related activity transmits energy. The liquid pumps are parallel to the shaft of the pump in an axial pump. Water enters radially and exits axially in these pumps.
Centrifugal Pumps
A centrifugal pump is a dynamic pump that converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy by using centrifugal force. The pump’s two key components, the volute casing, and impeller are responsible for energy conversion. The main function of the volute casing is to collect the liquid that exits the impeller and convert it into pressure energy.
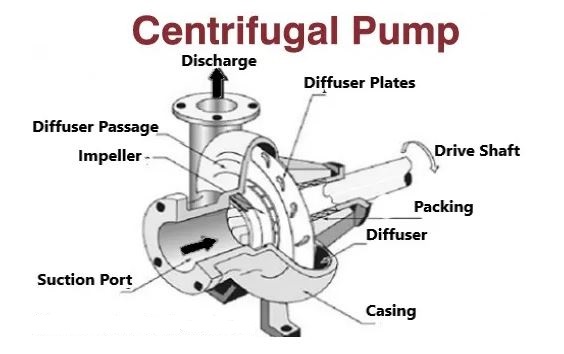
Pumps of this sort are the most frequent in use across the world. The operation is straightforward, well-explained, and thoroughly tested. This pump is sturdy, efficient, and very inexpensive to construct. The fluid pressure will rise from the pump’s input to its exit whenever the pump is in operation. The liquid will be pushed throughout the system by the change in pressure.
By passing mechanical power from the electrical motor to the liquid through the spinning impeller, this type of pump increases force. The liquid flow enters the impeller’s core and leaves via its blades. The centrifugal force increases the fluid’s velocity and allows kinetic energy to be converted to force.
The most typical application for these dynamic pumps is to pump liquids from low to high head. Pharmaceutical, chemical, septic tanks, petroleum, mining, municipal, power plants, agricultural, and other areas employ dynamic pumps.
Vertical Centrifugal Pumps
A cantilever pump is another name for a vertical centrifugal pump. They have a special shaft and bearing mount that allows the volute to swing in the sump while the bearings are mounted outside of it. Because the bearings are exterior to the pit, these pumps have a unique shaft and maintenance design that allows the volume to fall into the pit. This type of pump does not employ a filling container to cover the shaft, instead opting for a throttle bushing.
For shaft sealing, these pumps do not require a stuffing box and instead rely on throttle bushing. This pump requires very little room to install. If you need to place a pump in a small space, this is the ideal alternative. High-pressure and hot fluids are appropriate for them. The most typical application for this type of pump is a parts washer.
Horizontal Centrifugal Pumps
A horizontal centrifugal pump’s shaft is normally mounted horizontally between overhung or bearings. This pump is simple to set up and maintain, with easy access to internal components. To deliver the needed pump pressure, you must choose the proper shaft design. Horizontal pumps are appropriate for low-suction applications, whereas high-suction applications necessitate a bearing shaft. There are at least two impellers in these pumps, but there may be more. Pumping services make use of these pumps. Every stage is, at its core, a divide pump.
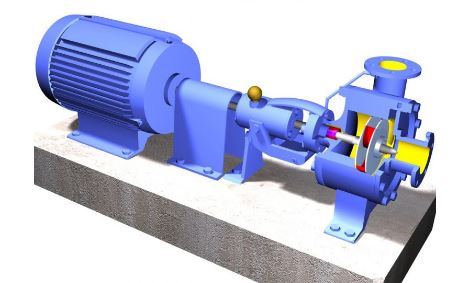
The stages are all housed in the same shelter and connected by the same shaft. A minimum of eight stages can be put on a single horizontal shaft; otherwise, extra stages can be mounted. Every step improves the head by roughly the same amount. In rare circumstances, the initial impeller of multi-stage pumps can have single or double suction. This type of centrifugal pump has been provided and serviced by a variety of pumps.
When the facility is concerned about the amount of space occupied, horizontal centrifugal pumps take up more room. These pumps, on the other hand, operate at a lower temperature and pressure than vertical pumps.
Submersible Pumps
A submersible pump is a mechanical device that pushes water toward the surface rather than drawing it away. It contains a hermetically sealed engine that helps to push the fluid toward the surface.
Slurry pumping, sewage pumping, general industrial pumping, septic tank pumping, and drainage are all frequent applications for dynamic pumps. Stormwater, sewage, and septic pumps are all terms used to describe these pumps. Building services, household, commercial, industrial, municipal, rural, and rainwater recycling applications are the most common uses for these pumps.
Stormwater, sewage, subsoil water, greywater, black water, trade waste, rainfall, chemicals, bore water, and foodstuffs are all good candidates for these pumps. These pipes are used in a variety of impellers, including closed, contra-block, multi-stage, vortex, cutter, single-channel, and grinder pumps. There is a wide range of options available for various uses, including high flow, low flow, low head, and otherwise high head.
Fire Hydrant Systems
A hydrant system is a firefighting water supply that provides appropriate pressure and flows through a network of nozzles, pipelines, and hydrants throughout a structure. Hydrant boosters, fire pumps, and fire water pumps are all terms used to describe fire hydrant pump systems. These are high-pressure water pumps designed to increase the capability of construction firefighting by raising the force inside the hydrant service when the mains are insufficient. Irrigation and water transport are two of the most common uses for this system.
In the case of an emergency, this pump has a series of pipes connected directly to the main water supply to send water to each hydrant outlet. A fire hose can be connected to several discharge valves on each hydrant pump. This fire hydrant system aids firemen in their efforts to put out fires. The hydrant system improves firefighters’ capacity to control flames on the job site where it is installed.
Advantages of Main Types of Dynamic Pumps
- The size of these pumps is tiny.
- For installation, they require a little amount of space.
- They are less expensive.
- In comparison to a positive displacement pump, dynamic pumps are easier to maintain.
- They can handle fluids with low to medium viscosity.
- They’re suited for applications with a low to medium headcount.
Disadvantages of Main Types of Dynamic Pumps
- Shaft misalignment is a concern with these pumps.
- They’re having problems with impeller damage.
- In a short amount of time, wear a ring of this pump damage.
- They have issues with seal ring damage.
- Overshooting causes the bearings of these pumps to wear out fast.
Applications of Main Types of Dynamic Pumps
- For water supply, dynamic pumps are utilized.
- Pumping crude oil is a common use for these pumps.
- They’re in the chemical business.
- They are used in both business and domestic settings.
- Pumps like this are used in the food sector.
- These pumps are commonly utilized in the fire-fighting industry.
- They are used in the manufacturing of cellulose, petrochemicals, hydrocarbons, paint, and beverages.
Dynamic Pump Vs Positive Displacement Pump
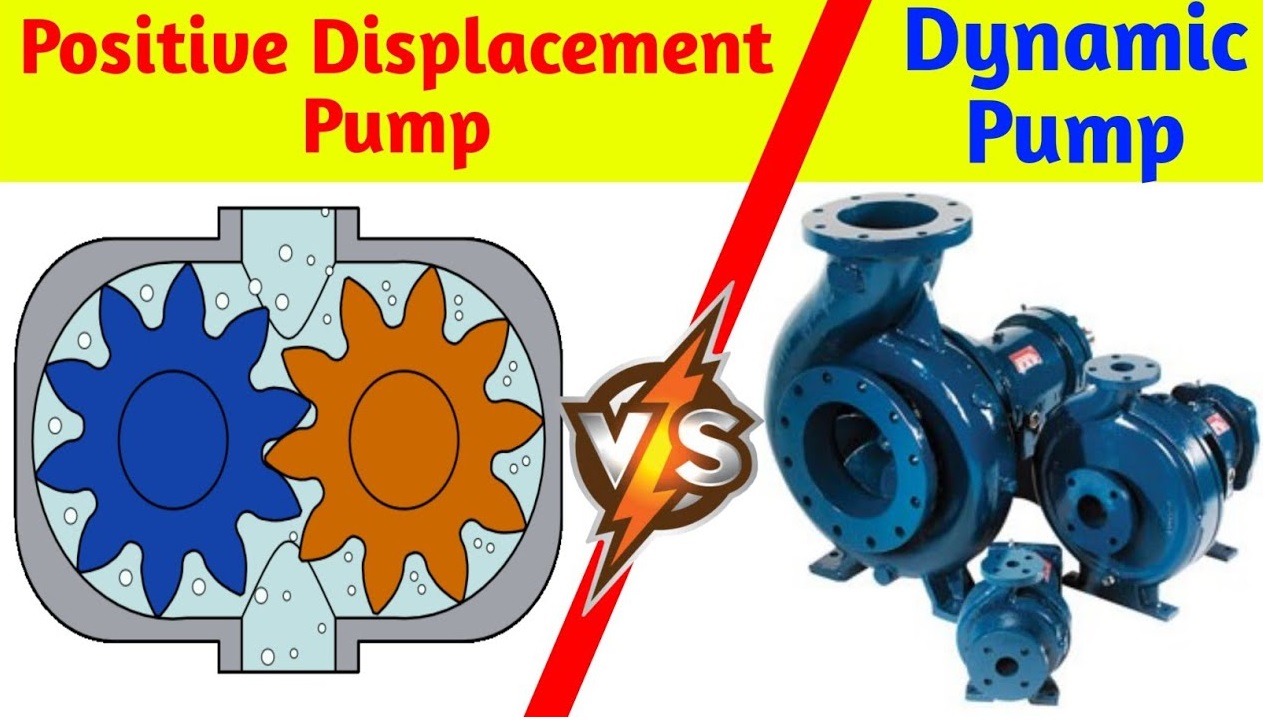
The following are the primary differences between a dynamic and a positive displacement pump:
Features of Dynamic Pump
- A dynamic pump uses kinetic energy to move fluid from one location to another.
- The fluid is pumped using an impeller and diffuser.
- The flow rate fluctuates in response to pressure changes.
- Pump performance degrades when the viscosity of the fluid rises owing to internal friction losses in the pump.
- At a given pressure, the dynamic pump has maximum efficiency. The pump efficiency changes when the pressure is changed.
- It has a cavity problem.
- Initial priming of the dynamic pumps is required.
- A dynamic pump’s required power is higher than a PD pump.
- It is inexpensive.
The following are some examples of dynamic pumps:
- Multistage Pump
- Axial Pump
- Centrifugal Pump
- Septic Tank Pump
- Submersible Pump
Features of Positive Displacement Pump
- The fluid is transferred via a positive displacement pump, which traps it in a closed cylinder.
- The fluid is pumped by a reciprocating or rotating portion (such as a piston, diaphragm, or screws).
- The flow rate is unaffected by pressure changes.
- The positive displacement pump’s performance is unaffected by viscosity variations since the internal clearance readily manages them.
- The performance of the positive displacement pump is unaffected by pressure.
- There are no cavities in it.
- The self-priming positive displacement pumps are self-contained.
- It necessitates a lower driving standard.
- It is a colossal force.
The following are some examples of positive displacement pumps:
- Plunger Pump
- Rotary Pump
- Reciprocating Pump
- Diaphragm Pump
- Screw Pump
Summary
This concludes the discussion of pump classifications such as centrifugal and positive displacement. These are used to aid in the circulation of liquid fluids in a number of buildings. Pumps used in residential and commercial buildings may manage water. Fire pumps provide a hurried water supply for automated sprinklers and firemen, while booster pumps provide clean water to apartments on higher levels. For more information about different types of dynamic pumps, contact Linquip Experienced Experts to meet all your requirements.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- What is Dynamic Pump & How Does it Works?
- A Cheat Sheet For The Types of Pump Couplings
- Different Types of Pumps: Ultimate Guide in 2022
- Different Types of Hydraulic Pumps: a Complete Guide
- Types of vane pumps: review the types, select the best
- 5 Types of Vacuum Pump and Applications + PDF
- Types of Piston Pumps
- Types of Water Pumps and Their Principles
- 3 Types of Well Pumps + Applications
- 3 Types of Oil Pumps + Working Principle & PDF
- 5 Main Types of Fuel Pump & How They Works?
- What is Deep Well Pump & How Does it Works?
- 3 Types of Positive Displacement Pump + Name & PDF
- 6 Parts of Pool Pump + Diagram & PDF
- 7 Parts of Screw Pump: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Types of Screw Pumps: How Each Type Gives Benefits?
- What is Head of a Pump? A Complete Guide
- The 5 Best Air Source Heat pump in 2022 (Clear Guide)
- 7 Best RV Water Pump In 2022 (Clear Guide & Review)
- The 10 Best Electric Air Pump in 2022 (Clear Guide)
- The Best HVAC Vacuum Pump in 2022 (Clear Guide)
- The 5 Best Well Pump in 2022 (Clear Guide)
- The 10 Best Condensate Pumps of 2022: A Complete Guide
- 13 Parts of Concrete Pump with Name & PDF
- 5 Types of Concrete Pumps + PDF
- 6 Type of Sump Pump and Which Are Better to Buy?
- Types of Pump Casings (In Centrifugal Pumps & Others) + Pros & Cons
- 7 Parts of Screw Pump: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Types of Centrifugal Pumps: All Classification & Working Principles