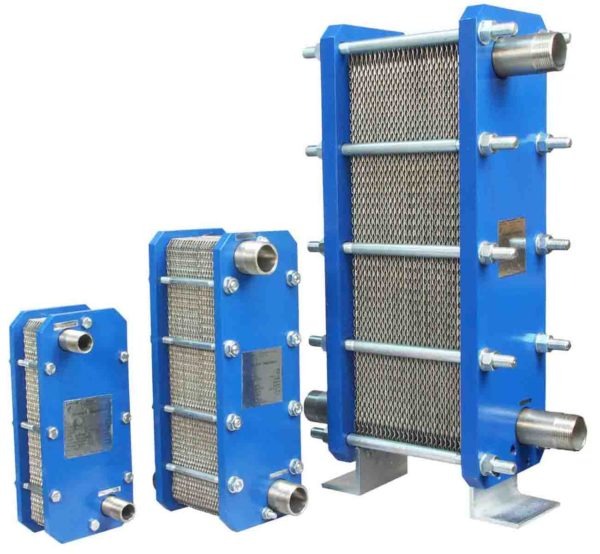
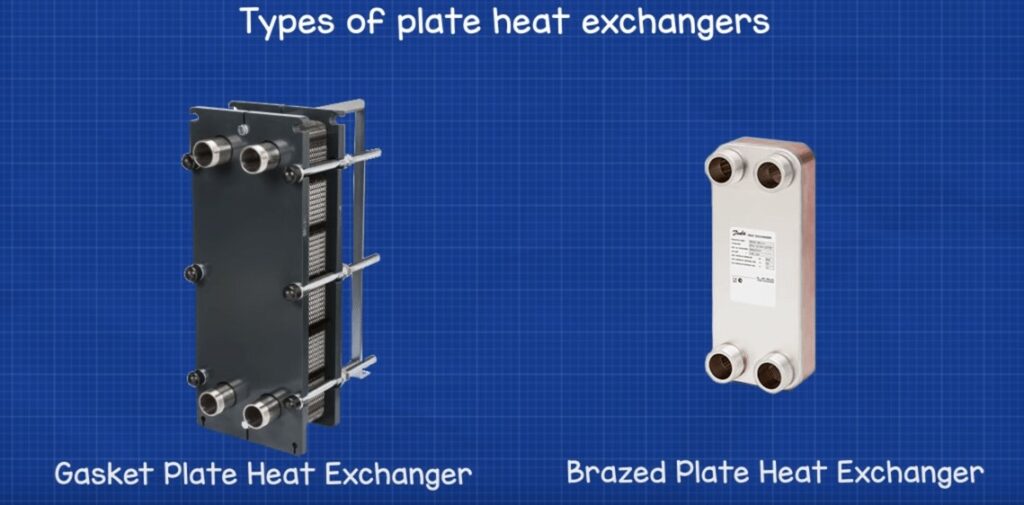
While simple in construction, plate heat exchanger is intricate in its design and operation. Looking at the different types of plate heat exchanger from gasket type, brazed plate type, welded type, and microplate type as well as their applications, this article will focus on this one of the most popular versions of the heat exchanger. So, follow us in Linquip.
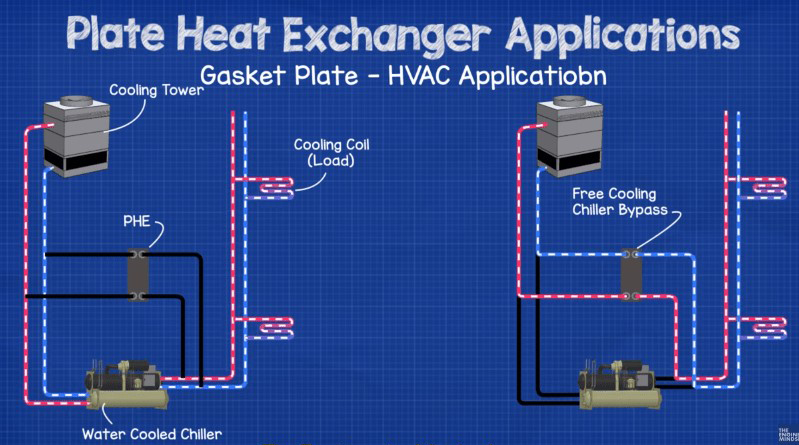
plate heat exchanger applications
Different types of plate heat exchanger have many potential applications. This includes pasteurizers, beverage processing, connectors between chillers, boilers, and cooling towers, and other process engineering applications. plate heat exchanger is a modular system that offer excellent heat transfer while being a fraction of the size of most conventional designs. It also supplies water and most other fluids instantly while keeping the appropriate fixed-point temperature within 1 or 2 degrees for your particular use.
In addition, it is standard practice to use a plate heat exchanger as a central heating system split to shield a costly piece of equipment such as a commercial-sized boiler. Plate heat exchanger is used in these systems to divide the central heating system into two circuits, one devoted to the boiler and the other to the radiators and related devices. The general concept behind the Central Heating System Break is to divide the heating into two circuits so that any deposits floating in an old heating system do not disrupt or shorten the life of the costly boiler.
Types of plate heat exchanger
There are four main types of plate heat exchanger:
- Multiple sheets of thin metal are arranged to form channels in gasket-style heat exchangers. Through inserting or removing internal plates, gasket plate heat exchangers may increase or decrease their heating or cooling capability. They can also be disassembled for washing and repair purposes. The plates are generally made of stainless steel, sometimes platinum, the endplates are typically made of mild steel, and the gaskets are typically made of rubber. Gasket plate heat exchangers can be used in a variety of heavy-duty HVAC, automotive, and process engineering applications. They have an extraordinarily high thermal efficiency despite their small size. These types of plate heat exchanger use high-quality gaskets and a well-designed seal to keep plates together and prevent leaks. Plates may be quickly removed for washing, extension, or replacement, significantly lowering maintenance costs.
- Welded plate heat exchangers are similar to gasket plate heat exchangers, except the plates are welded together instead of bolted together. These types of plate heat exchanger are highly robust and are suitable for moving fluids that are hot or corrosive. Since the plates are welded together, mechanical plate washing is not an alternative, as it is with plate and frame heat exchangers.
- Semi-welded plate heat exchangers combine welded and gasket plates. They are made up of two-plate pairs that are welded together and then gasketed on other pairs since one fluid path is welded and the other fluid path is gasketed. This produces a plate heat exchanger that is easy to service on one hand while still being capable of transferring more intense fluids on the other. Since these types of plate heat exchanger have a relatively low chance of fluid loss, semi-welded heat exchangers are ideal for moving heavy materials.
- Brazed plate heat exchangers are usually found in smaller applications, but in recent years, this has begun to change, with larger units being manufactured and used in industry. These types of plate heat exchanger are used in a wide range of automotive and refrigeration applications. They are highly corrosion-resistant due to the stainless-steel plate composition and copper brazing. Brazed Plate heat exchangers are economical because they are efficient and lightweight. These heat exchangers often use thin plates to isolate the fluids, but the plates are brazed together to form a full seal. The seal is formed by the brazing and positioning of the plates, which determines which channel each fluid will flow into. A unit composed entirely of surfaces that specifically move forward heat transfer and can endure both high temperature and high-pressure conditions.
plate heat exchanger advantages and disadvantages
Any types of plate heat exchanger have their pros and cons. Here we present some of the very important advantages and disadvantages of plate heat exchanger:
Plate heat exchanger is Easy to Remove and Clean. Simply cut the tie bolts and slip the movable frame on. If required, the plate pack may be inspected, pressure washed or withdrawn for refurbishment.
Plate heat exchanger is Expandable. The plate heat exchanger has the advantage of being expandable, which allows for an improvement in heat transfer capabilities. If the heat transfer specifications adjust, you can easily install plates rather than purchasing a whole new frame unit, saving you time and money.
It has High Efficiency. Because of the pressed plate patterns and short spaces, there is a lot of noise at a low fluid velocity. Heat transfer coefficients are very high when combined with counter-directional flow.
Find it with a Compact Size. Because of the high performance, less heat transfer area is needed, resulting in a much smaller heat exchanger than would be required for the same effectiveness of other heat exchanger models. A plate heat exchanger usually takes up 20-40% less space than a shield and tube heat exchanger.
One Single Unit but Multiple Duties. The plate heat exchanger may be constructed in parts that are divided by basic divider plates or more complex divider frames with additional connections. This enables the heating, regeneration, and cooling of a fluid in a single heat exchanger, as well as the heating or cooling of several fluids from the same cooling or heating source.
Less Fouling. The pattern of the plates, the many touchpoints, and the small distance between the plates all contribute to extremely high turbulence. This, along with the flat plate surface, significantly prevents fouling as compared to other forms of heat exchangers.
Not Much Cost. High heat transfer coefficients imply a smaller heat transfer region and, in some cases, fewer heat exchangers. This, as well as reduced space needs, lower flow speeds, and smaller pumps imply.
The concept of plate heat exchanger advantages and disadvantages is not done. Despite the above advantages, plate heat exchangers are not the right option for all applications. In cases where there is an extreme temperature difference between two fluids, it is usually more cost-effective to use a Shell & Tube heat exchanger. Due to the vast amount of turbulence produced by the small flow channels in a plate heat exchanger, there may be a high-pressure loss. Applications requiring a low-pressure loss may often want to consider a Shell & Tube heat exchanger.
Summary
In a nutshell, the plate heat exchanger is one way of exchanging heat between two fluids, and it is particularly useful for heat transfer between two liquids. It is made up of layered corrugated plates stacked one on top of the other. There are openings between the various plate layers through which a cold and a warm medium migrate. This article presented an understanding of different types of plate heat exchanger. Moreover, you found out about the applications as well as the advantages and disadvantages. For more information, consult our experts. Feel free to register at Linquip and get more about types of plate heat exchanger.