Different types of submersible pumps can be applied in applications such as wells. A submersible pump (also known as sub pump or electric submersible pump (ESP)) is a machine that is designed to be immersed in a well, tank, and container. The whole assembly, including the pump and the sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body, is submerged in the fluid. The main strength of this pump is that it prevents cavitation in the pump components. Dissimilar to jet pumps, a submersible pump pushes fluid to the surface, which produces a vacuum relying on the atmospheric pressure. Therefore, submersible pumps have higher efficiencies than jet pumps.
In 1928, the first submersible pump was successfully installed in an oil field by an Armenian oil delivery system engineer, Armais Arutunoff. Pleuger Pumps (today Pleuger Industries) pioneered the submersible turbine pump design in 1929.
Basics of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps are machines positioning vertically. In this type of pump, fluids are accelerated by the impeller and lose their kinetic energy due to the conversion into pressure energy in the diffuser. This is the operating principle of radial and mixed flow pumps. The motor of the submersible pump is enclosed within chambers filled with oil separate from the pushed fluid.
Fluid enters the pump through the impeller eye and is driven by the pump stages. Other components include the radial bearings located along the shaft, giving radial support to the shaft. The optional thrust bearing absorbs a portion of the axial forces created in the pump. However, most of these forces are taken up by the thrust bearing of the protector.
Besides, there are screw-type submersible pumps in which a steel screw is a functional element. The screw enables the pump to operate in water with a high sand concentration and other mechanical impurities.
The following figure shows the installation structure of a submersible pump.
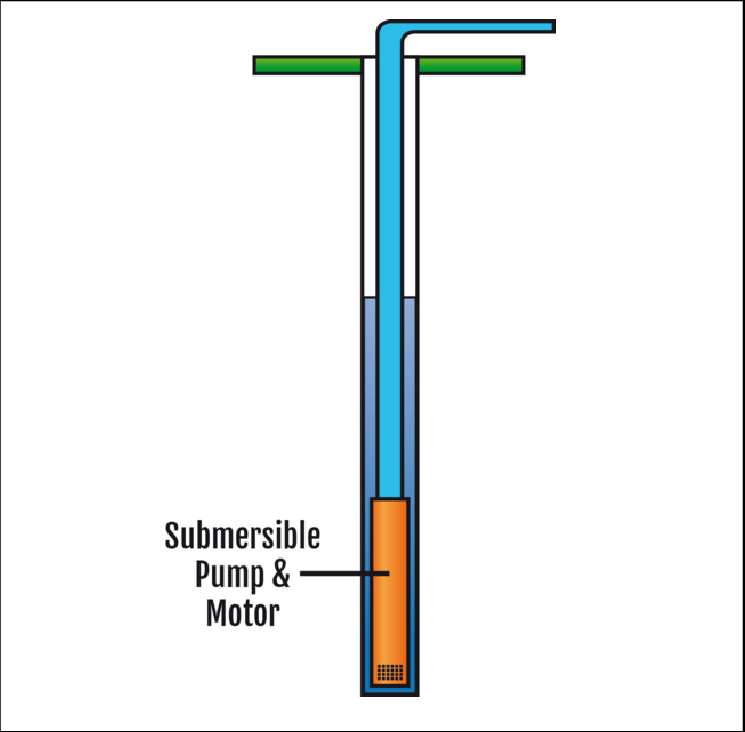
Submersible pumps are used for many purposes. In their simplest form, these pumps transfer water from the floor or bottom of a tank. Single-stage pumps are utilized for drainage, sewage pumping, slurry pumping, and general industrial pumping. Also, they are common in pond filters.
However, multiple-stage submersible pumps are most typically used for residential, municipal, commercial, and industrial extraction (abstraction) of water wells and oil wells.
Other applications of submersible pumps include sewage treatment plants, firefighting, seawater handling, water well and deep well drilling, seawater handling, offshore drilling rigs, mine dewatering, irrigation systems, and artificial lifts.
In the following figure, you can see different components of an electrical submersible pump.
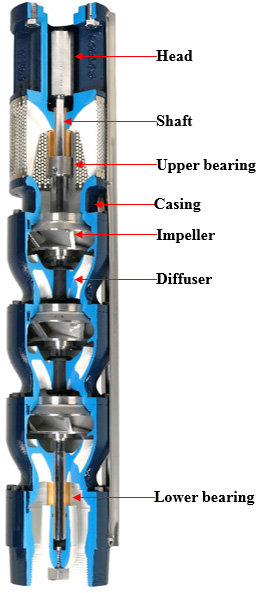
Specifications of Submersible Pumps
When choosing between the available submersible pump types, four main specifications are important to consider:
Maximum Discharge Flow
This parameter shows the maximum flow generated by the pump. This value depends on the pressure head the pump must apply.
Maximum Discharge Pressure
This is the maximum pressure the pump generates.
Horsepower (hp)
This value expresses the amount of mechanical energy consumption. One horsepower is equivalent to 745.7 watts and is defined as the work done at the rate of 550 foot-pounds per second.
Discharge Size
This is the size of the discharge or outlet connection of the pump.
Operating Range of Submersible Pumps
Submersible pumps usually operate in the following ranges:
- Flow rates from 20 to 28000 l/min
- Total head (pressure) between 0.4 and 6 Bar
- Horsepower ranging from 1 to 250 hp
Types of Submersible Pumps
Different types of submersible pumps are used in wells, tanks, and so on. The main classes of these pumps are discussed below.
Bladder Pumps
In cases where high integrity samples with low flow rates are required, and peristaltic pumping cannot be an option, the bladder pump systems offer an effective alternative to customers. Applying a submersible stainless steel pump and coupled controller/compressor at the well surface, the bladder pump system uses controlled air pressure to direct water samples to the surface. In addition, using a disposable polyethylene bladder within the submersible pump guarantees that air and water do not mix. Thus a sample of high integrity is ensured.
Grinder Pumps
Sewage grinder pumps are created to operate with raw sewage and solid waste materials. Grinder pumps soften the solids using their cutting blades before pumping the waste. Although on a larger scale for sewage waste, a grinder pump operates similar to a household garbage disposal. It grinds solids and other hard waste material up into fine slurry and then transfers it into the sewer system.
This type of pump is manufactured to be utilized in residential and commercial applications and high-pressure sewage systems such as long-distance pumping, high lifts, or pressurized municipal sewer lines. For direct pumping into a septic tank, the use of a sewage grinder pump is not recommended.
Deep Well Pumps
The deep well pumps are submersible pumps with extensive use. These pumps can also be utilized for municipal applications. The body of these pumps can be connected to the motor for working underwater. It is simple to be fixed and repaired. When these pumps start working, they must be completely immersed in the water. Light acidic and freshwater can frequently be pumped using these pumps.
Dry Pit Submersible Pumps
Dry pit submersible pumps are initially designed for applications where the pump unit is immersed in liquid. These submersible pumps are now used in dry well stations in which the wet well and the dry pump chamber are separated. Dry pit submersible pumps have replaced the old centrifugal pumps.
Stainless Steel Pumps
Seemingly, stainless steel pumps have better performance than cast iron pumps. They are entirely coated with stainless steel, and thus, they have excellent acidic resistance. The whole body of the pump can be immersed in the water while running.
Bottom Suction Pumps
Bottom suction pumps are widely used for lake, pool, river, and mining dewatering. They are engineered with a guide sleeve beneath the pump. These pumps utilize the water from the base and effectively ensure the high-quality cooling feature of the electric motor. These pumps are expedition and emergency pumps. The installation of bottom suction pumps is considered to be easy compared to other types of pumps.
Water Cooler Pumps
Water cooler submersible pumps are typically applied in water supply for the industrial, farmland, residential fields, and so on. The motor of a water cooler submersible pump can be fixed for working under the water. For cooling the hot motor, it can be filled with fresh water. These pumps are suitable in cases where high-quality water is used.
Oil-Filled Pumps
Despite the water-filled submersible pump being internally filled with water to cool the motor, the motor of the oil-filled submersible pump is cooled with the oil. Oil-filled pumps use oil-filled immersion motors. These types of pumps are widely used in different areas, including water lifting in wells as well as the water supply for agricultural lands, residential regions, industrial drainage systems, and mountain areas. Oil must be filled for heated motors cooling.
These machines can be employed in cool areas since oil cannot be frozen. The fitting and refurbishing of these pumps are very simple. These pumps transfer the clean water such as the lakes, pools, or rivers.
Although these pumps have longer service life than water-filled submersible pumps, these pumps may have an environmental impact due to oil pollution. Moreover, under the same flow conditions, they are more expensive than water-filled submersible pumps.

Borehole Pumps
Borehole pumps are centrifugal pumps operated by a submersible motor. Because they typically draw into the fluid directly without a suction line, they need to be constantly submerged in the fluid.
These pumps are engineered as single- or multistage pumps coupled to the submersible motor. Depending on the application, the motor can be located above or under the pump.
Submersible borehole pumps are employed in tank farms and as cavern pumps. Borehole pumps are more cost-effective than deep-well pumps, particularly for deep installations due to their simpler designs.

Utility Pumps
Utility submersible pumps are multi-functional pumps. Their applications range from everyday use around you to specific ones. The vertical head the water can be moved using these pumps may be zero up to around 25’.
Utility pumps can be considered the most versatile water pumps. They work excellent with the common home tasks such as emptying the clogged sinks, draining excess rainwater from stairs and window wells or aquariums and water beds and removing standing water from the yard or flooded basement and construction sites.
Solids Handling Submersible Pumps
These submersible pumps are able to transport solid material through the pump without any obstruction or interference from entry to discharge. Spherical material with a diameter of 2 inches to 13 inches or more can move through these submersible pumps.
Booster Pumps
Booster pumps raise the low flow of the water in systems or industrial facilities and transfer the water from a lake, pond, or storage tank for domestic or commercial use. For example, a household that does not receive adequate pressure from the city water source needs a pump to increase the low pressure of the water flow. A hotel requires a large commercial booster pump to bring water to the top floors.
A booster pump is also applied to re-pressurize water from a storage tank and transfer it throughout a home. For example, In a rain harvesting system, water accumulates in a storage tank. To use it for flushing toilets or washing laundry, the water needs to be transferred from the tank into the house.
Condensate Pumps
A condensate pump is a centrifugal pump used in condensers to transfer the condensed steam as water (called condensate) in a vacuum (near vapor pressure). In an open circuit, the condensate pump moves the condensate into a tank (feed water tank). However, it sends the condensate into the boiler feed pump through a low-pressure feed heater in a closed circuit.
Macerator Pump
A macerator pump is connected to a toilet that grinds up solid waste utilizing a high-speed rotational blade. It then pumps the waste into the sewerage system.
Macerators are created to pump out the waste materials and wastewater from toilets without relying on a regular drainage system. Usually, they are used in bathrooms that are far from the main drainage systems.

Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Different Types of Hydraulic Pumps: a Complete Guide
- Different Types of Pumps: Ultimate Guide
- Types of Centrifugal Pumps: All Classification & Working Principles
- A Cheat Sheet For The Types of Pump Couplings
- 3 Types of Positive Displacement Pump + Name & PDF
- 20 Parts of Submersible Pump + PDF
- Submersible Pump: Working Principles, Function & Diagram
- Top Dosing Pump Manufacturers and Suppliers
- Top Water Pump Manufacturers and Suppliers
- The 7 Best RV Water Pump (Clear Guide + Review)
- The 10 Best Electric Air Pump (Clear Guide)
- The Best HVAC Vacuum Pump (Clear Guide)
- 9 Different Types of Rotary Pumps + PDF
- The 5 Best Well Pump (Clear Guide)
- The 10 Best Condensate Pumps of 2022: A Complete Guide
- 13 Parts of Concrete Pump with Name & PDF
- 5 Types of Concrete Pumps + PDF
- Delving Deep into Submersible Well Pumps: How Do They Work?
- 12 Types of Water Pressure Pumps with Applications & Characteristics



