The sound that is produced at a higher level than the human hearing range is named ultrasound. The ultrasonic transducer is one kind of sound-contributed sensor. While ultrasound begins typically at 20 kHz, most ultrasonic transducers begin at 200 kHz according to their application. Ultrasound, which is naturally like audible sound, has far lower wavelengths and is more desirable to identify small faults. These shorter wavelengths are special because they make ultrasound and ultrasonic transducers very useful to measure materials and nondestructive testing. These transducers are the main elements in sensors for flow, level measurement, and distance, as well as in biomedical, power, and other applications of ultrasound.
What is Ultrasonic Transducer?
The ultrasonic transducer is an intensely remarkable and important section of any ultrasonic test. Choosing the appropriate transducer for a specific application is a considerable matter. Factors containing instrument situations and settings, substance properties, and coupling situations will also influence test results. Ultrasonic Transducers can be chosen by resolution or sensitivity.
Resolution is the capability of a transducer to disconnect signals made by two reflectors when they are close together. Sensitivity is introduced as the capability of an Ultrasonic transducer to identify small flaws in substances. A transducer that is extremely damped helps low the reflected signal permitting the transducer to revise closely spaced faults. Transducer system producers can supply focused transducers for higher sensitivity and resolution and a large option of polarized ceramic materials and single crystals to change the transducer process. For more information on the structure of ultrasonic transducers, visit here.
Ultrasonic transducers launch the electrical signals to the target, and while the signal hits the object, it returns to the transducer. In this procedure, this transducer gauges the distance of the target, not the quality of the sound. These transducers utilize ultrasonic waves for the evaluation of a few variables. It has a vast range of applications in several fields. The frequency range of ultrasonic waves is above 20 kHz. These are typically utilized in measuring distance usage. The following image demonstrates the ultrasonic transducer.

An ultrasonic transducer is a system that has the ability to produce and receive ultrasonic vibrations. This transducer consists of a wear plate, an active element, and a backing. The active element is a piezoelectric or single-crystal substance that transforms electrical energy into ultrasonic energy. Then, it will recover back ultrasonic energy and transforms it into electrical energy. The electrical energy pulse is produced from a device like a fault detector.
In ultrasonic NDT (Nondestructive Testing), transducers transform an electrical energy pulse from the test device into mechanical energy in the type of sound waves that move within the test piece. Sound waves sent back from the test piece are transformed by the transducer into an electrical energy pulse that can be performed and illustrated by the test system. Actually, the transducer operates as an ultrasonic speaker and microphone, producing and recovering pulses of sound waves at frequencies much more than the level of human hearing.
Ultrasonic Transducers Types
Different types of ultrasonic transducers are accessible depending on key factors such as piezoelectric crystal arrangement, footprint, and frequency. The most efficient types of them are as the following:
- Linear Transducers – In this kind of transducer, the piezoelectric crystal array is linear.
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Transducers – This type of transducer has a small footprint and low frequency. (its main frequency is 2 MHz – 7 MHz)
- Standard Transducers – This model is also introduced as convex transducers. In this type, the piezoelectric crystal is in a curvy shape. For in-depth applications, these are too suitable.
- For nondestructive testing, ultrasonic transducers have various kinds, including Angle beam transducers, Delay line transducers, Immersion transducers, Contact transducers, and Dual element transducers.
Ultrasonic Transducer Components
An ultrasonic transducer is a device that can produce ultrasounds and receive them. It contains three basic components. The performance of each part is presented below.
The Piezoelectric Crystal
The center of the transducer is introduced as the ‘active ingredient’ of the system. It tolerates rarefactions and compressions in order to transform the electrical energy into ultrasonic energy or contrariwise. A fault detector is another instrument utilized to produce the electrical pulse, which then conveys to the transducer.
The Backing
It is a very dense substance, which is also too fundamental. The exclusive target of this is to absorb the energy that emits from the back of the crystal to monitor the vibrations. An excellent accuracy transducer can be constructed by controlling the acoustic impedance of the backing substance of the crystal. If the backing material is transformed, the difference in this acoustic impedance can be modified. This will certainly influence the transducers as the resolution may change much higher.
Wear-plate
A wear plate is set in the transducer to support the piezoelectric crystal in different applications. The environmental problems are that it protects the ultrasonic transducer from usually wear and tear and corrosion. The wear plate generally operates as an acoustic converter between the crystal and water, wedge, or delay line.
Working Principle of an Ultrasonic Transducer
When an electrical signal is performed to an Ultrasonic transducer, it vibrates around the characteristic frequency range and produces a sound wave. These sound waves move, and whenever any obstruction happens, these sound waves will send back the transducer data. Finally, this data transforms into an electrical signal.
Here, the transducer evaluates the time pause between sending the sound wave to gaining the echo signal. The ultrasonic sensor transmits the ultrasonic pulse at 40 kHz, which moves through the air. These transducers are more desirable than infrared sensors because these ultrasonic transducers are not influenced by black materials, dust, smoke, etc.
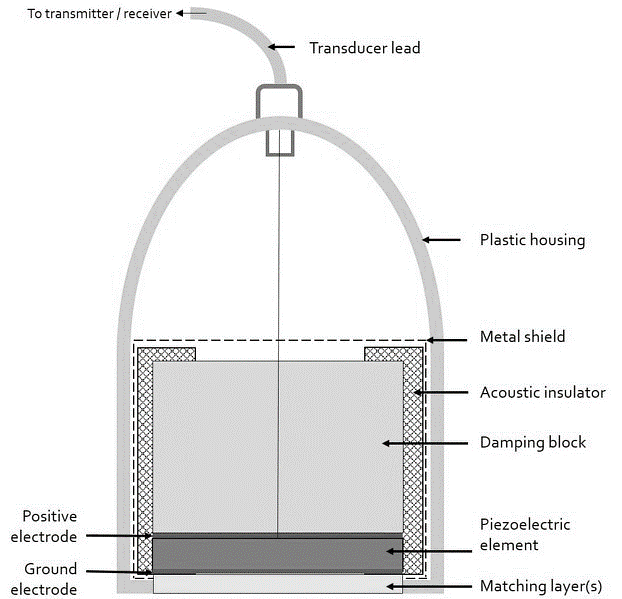
The application of composite devices in which the usual solid ceramic disk or plate is substituted with a micro-machined part has increased in recent years. They are some tiny cylinders of piezoelectric ceramic, which are fixed in an epoxy matrix.
Composite parts can supply increased bandwidth and improved sensitivity in many fault detection applications. When it is stimulated by an electrical pulse, this piezoelectric part produces sound waves, and when it is vibrated by a returning signal produces a voltage. This certain element is preserved from damage by a wear-plate or acoustic lens and is supported by a block of damping substance that silences the transducer after the sound pulse has been made. This ultrasonic subpart is installed in a case with proper electrical couplings. All angle beams, delay lines, common contact, and immersion transducers employ this main model.
The phased arrangement probes utilized in imaging systems easily incorporate a number of individual transducer parts in a single design. Dual element transducers, generally employed in corrosion checking systems, vary in that they have distinct transmitting and receiving parts divided by a sound barrier and an integral delay line to direct and combine the sound energy instead of a wear-plate or lens. The above figure demonstrates the typical construction of an ultrasonic transducer. If you want to explore more about how an Ultrasonic Transducer works, visit here.
Circuit Diagram of Ultrasonic Transducers
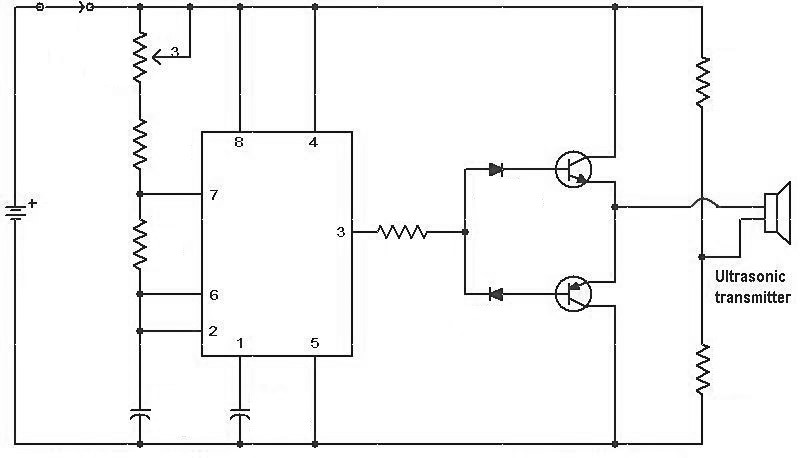
The ultrasonic transducer has two main circuits: a transmitter and a receiver. They are made with 555 timers or CMOS technology (Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor). The transmitter and receiver of this transducer operate on the same frequency.
The transmitter of this transducer sends the ultrasonic waves toward the target, and when the sound waves hit the object, the sound signals are transformed into ultrasonic and electrical signals. The following diagram illustrates the transmitter circuit diagram of the transducer.
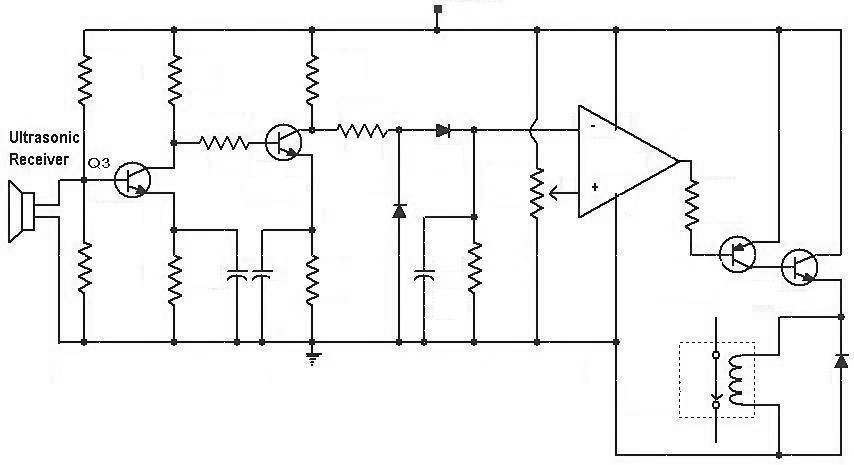
The receiver circuit receives the signals after hitting ultrasonic waves to the target and then transforming them into electrical form. The next diagram demonstrates the receiver circuit diagram of the transducer.
Ultrasonic Transducer Applications
The applications of Ultrasonic Transducers are various. These transducers have many usages in different fields like medical, industrial, etc. These are having more requests because of ultrasonic waves. This helps discover the object and measures the distance of the object to the target. Then it can identify the position of the object and evaluate the state of the target.
Also, these transducers are beneficial in the medical field. They have usages in surgical applications while treating cancer, internal organ testing, heart examinations, diagnostic testing, eyes, and uterus checkups.
Ultrasonic transducers are utilized in the industrial era. They have a few considerable applications. They can measure the distance of particular targets to keep away from the collision, and product line management, control liquid levels, detect wire break, identify people and vehicles for counting, and many more.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Transducers
Ultrasonic transducers have different benefits. They have the ability to measure any kind of material. They can also sense all types of substances. They are not influenced by water, dust, temperature, or any. In any environment, the ultrasonic transducers will operate in an appropriate condition. It would be necessary to say that they can measure high sensing intervals.
However, this type of transducer has some disadvantages as the following.
Ultrasonic transducers are sensitive to high and immediate temperature variation. These unexpected temperature conversions may change the detection ability of an ultrasonic transducer. They will also face some difficulties while identifying the reflections from very small targets, which are too thin and soft. Nevertheless, new studies are undergoing to address these issues.
By and large, this is all about an outline of an ultrasonic transducer. Eventually, we can derive that this device is utilized to measure the distance to the target by employing sound waves. It calculates intervals by sending out a sound wave at a particular frequency and waiting for that sound wave to receive back.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Photoelectric Transducer
- Important Detailed Information About The Types of Transducers
- Piezoelectric Transducer and Its Impressive Applications in Electric Circuits
- What Is a Pressure Transducer? A Simple Descriptive of the Definition, Working Principle, and Considerations
- Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge, Advantages and Applications
- How to Wire Up Piezoelectric Sensor? A Comprehensive Guide




How interesting that you mention what an ultrasound transducer is. I am pregnant with my first child this year. I will find a good portable ultrasound machine for sale close by to help.
Thanks for visiting our website, Tiff! We also encourage you to visit the Linquip website, where you can find thousands of experts, companies, and industrial equipment according to your application and demand.