What Are Resistors for LED Circuits? – When an electric current flows through an LED (Light Emitting Diode), the LED begins to emit light. A voltage source connected in series with a resistor and an LED is the simplest circuit for powering an LED. A ballast resistor is a common name for this type of resistor. The ballast resistor is used to control the current flowing through the LED and avoid allowing it to become too high and damage it. There is no need for a resistor if the voltage source and the voltage drop of the LED are equal. Additionally, integrated packages of LEDs with the proper resistance for LED operation are available.
On the Linquip website, among the many options available to you, you will find all the information you need to know about the Resistors for LED Circuits, as well as information regarding this marketplace. You can count on Linquip to provide you with as much general and reliable information about this topic, whether you’re a professional or a customer looking for a proper company. We recommend you review a list of all Resistors for LED Circuits available in Linquip.
We would be delighted to provide you with more information on how we can help you generate revenue within your industry. Don’t hesitate to contact us if you have any questions! With Linquip’s Solutions for Each Company Level, you will be able to upgrade the capabilities of your organization in order to gain a competitive edge by taking advantage of a wide range of options to enhance your organization’s performance. If you are looking for the simplest or the most sophisticated marketing and advertising package for your business, we can help you ensure that your company gets as many customers as possible to grow your business.
What Are Resistors for LED Circuits?
When an electric current flows through a Light Emitting Diode (LED), the diode releases photons, creating light. An LED may be powered by a voltage source, a resistor, and a sequence of electrons, which is the simplest possible circuit. A ballast resistor is a common name for this type of component. Because too much current can destroy an LED, a ballast resistor is typically employed to set a safe maximum throughput. You won’t need a resistor for an LED if the voltage coming from the source is the same as the voltage it will drop to. LEDs can also be purchased in an integrated package that includes the necessary resistor for LED operation.
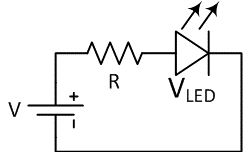
Ohm’s law and Kirchhoff’s rules of circuits make it simple to determine the ballast resistor’s value. By subtracting the LED’s rated voltage from the input voltage and dividing by the LED’s required current, we can get the optimal voltage and current settings:
R=(V-VLED)/I
V is the input voltage, VLED is the LED’s operating voltage, and I is its current. In this manner, the appropriate resistance for LED functioning may be located.
A DVD player or computer screen might benefit from this ballast resistor and LED circuit in the form of a power-on indicator. Ballast resistors are often employed in consumer electronics, although their low efficiency belies their prevalence. In order to improve energy efficiency, more complicated circuits are occasionally used.
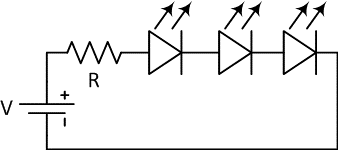
Multiple LEDs in a Series Circuit
Multiple LEDs are often linked in series to share a common power supply. This allows a number of resistors to share a single current source. LEDs used in a series configuration must all be of the same kind to provide a consistent current flow. Please take note that the power consumption of this circuit when a single LED is lit is the same as that of numerous LEDs lit in series. The voltage source needs to be able to produce a voltage that is higher than the total voltage drop between the LEDs and the resistor. As a rule, the total LED voltage should be at least 50 percent greater than the voltage source. Instead of employing a high voltage source and a big current, a lower voltage source and a higher number of LEDs can be used to compensate for the reduced brightness of each individual LED. And because the LEDs aren’t working as hard, they’ll last longer and generate less heat.
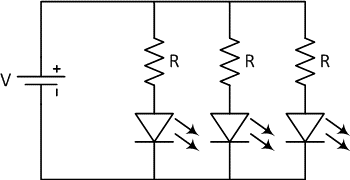
Multiple LEDs in a Parallel Circuit
Connecting LEDs in parallel is doable, but it often leads to more issues than using a series circuit. If the LEDs’ forward voltages don’t line up, just the one with the lowest voltage will light up, and it might overheat and burn out. LEDs with identical specs may nonetheless exhibit poor I-V characteristic matching owing to manufacturing inconsistencies. This results in a different current being sent via the LEDs. LEDs in parallel often include a ballast resistor for each branch to reduce the current disparity.
What Makes An Led Light Up?
A light emitting diode, or LED, is a type of electronic component. One may think of it as a P-N junction with a lead on either side. If forward biased, the resistance of an ideal diode is zero, and if reverse biased, it is infinite. However, with actual diodes, some voltage must be applied across the diode for it to conduct. The materials and design of the diode influence its voltage and other properties. Excess electrons on one side of the junction start combining with holes on the other when the forward bias voltage is high enough. This results in the electrons entering a lower energy state and discharging their stored potential. Photons are the form of energy emitted by LEDs. The wavelength of the light produced by an LED is established by the materials it is constructed from. Gallium arsenide was used to create the first LEDs, which shone a red light. These days, LEDs can be fabricated from many different materials and produced to provide many different color temperatures. LEDs have different operating voltages, ranging from around 1.6 V for red LEDs to roughly 4.4 V for ultraviolet ones. As applying too much voltage across the diode might result in greater current than the LED can safely manage, it is crucial to have an accurate understanding of the voltage requirements.
Modern LEDs may be found in both low- and high-power varieties. LEDs, on the whole, are more energy efficient than incandescent bulbs of the same brightness and produce far less heat. Plus, they’re more durable than standard bulbs. Many different kinds of lighting and light detecting devices employ LEDs.
Using LEDs as Photodiodes
A photodiode is a device that may be used with an LED. Photodiodes are a type of semiconductor that exhibit the inverse behavior of light-emitting diodes. A photodiode, in contrast to a light-emitting diode (LED), conducts electricity when exposed to light of the right wavelength. When an LED is hit with light below its optimal operating wavelength, it will show this trait. This paves the way for LEDs to be included into a wide variety of circuits, including light sensors and fiber optic communication networks.
Do Leds Require Resistors All The Time?
A resistor is not always necessary when connecting an LED to a power supply. In particular, when the forward voltage drop of the LED is the same as the voltage source utilized to power the LED.
There is no need for a current limiting resistor in this application. If the forward voltage drop of the LED is 3 volts and the power source is 3 volts, then there is no need for a resistor to be connected between the two.
Download PDF for What Are Resistors for LED Circuits?
You can download the PDF format of this post from the link provided here.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Variable Resistor∶ Learn The Basics, Get The Most out of It!
- A Quick Guide to Resistor Color Code
- Everything You Need to Know About Variable Resistor Function
- Variable Resistor Symbol։ Everything You Need to Know
- Types of Resistor: Classification, Application, and Finally Clarification
- What is Shunt Resistor? + Function & Applications
- Best LED Lighting for Warehouse & Gurage
- Best LED Fixtures for Warehouse and Garage
- Difference between Series and Parallel Circuits | What are they Completely?
- Mastering Resistance Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide for Electrical Enthusiasts
- What are the Differences Between Series and Parallel Circuits?
- Difference Between Linear and Nonlinear Circuits
- Types of Electric Circuits: All Classification with Application