Alternators are among the vital components of a vehicle. So, it’s important for you to completely understand what an alternator does and what the symptoms of a bad alternator. are. In this article from Linquip, we want to dive deeper into the world of alternators and learn about alternator functions on another level. Continue reading to understand them more.
Alternator Definition
First of all, let us briefly explain the alternator definition for those who are new to this subject or the ones who forgot what it does.
Since alternators provide alternating current (or AC), they are called so. Alternators are the hidden hand behind almost every vehicle’s battery. They provide the necessary electricity to charge up the battery as well as supporting the electrical system of the vehicle. They use mechanical energy and by converting it, provide electricity for your automobile. Alternators are considered as a part of the charging system of a vehicle as well as the battery and the voltage regulator.
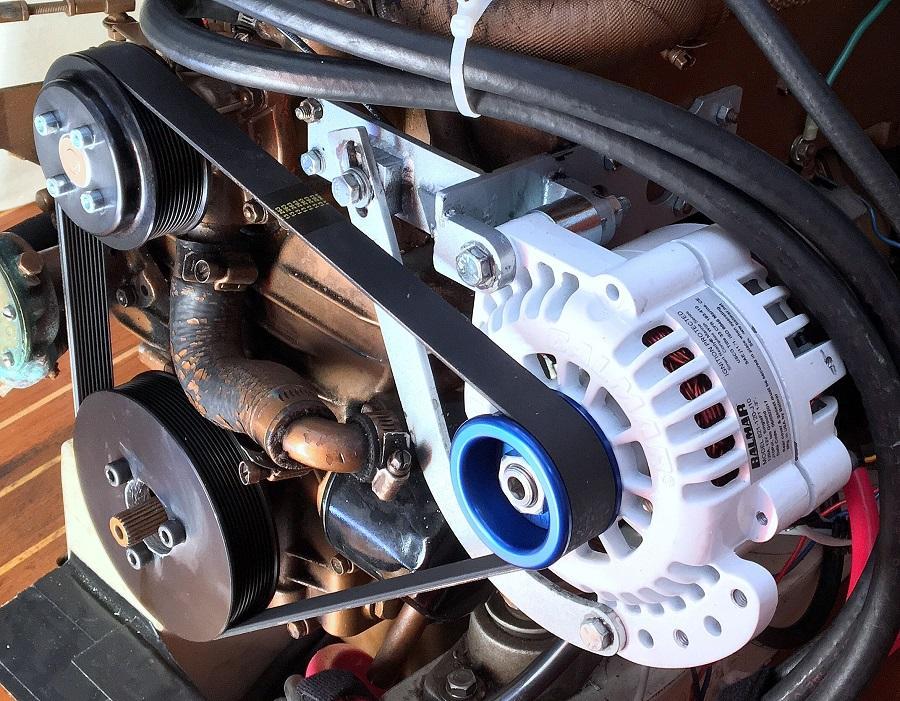
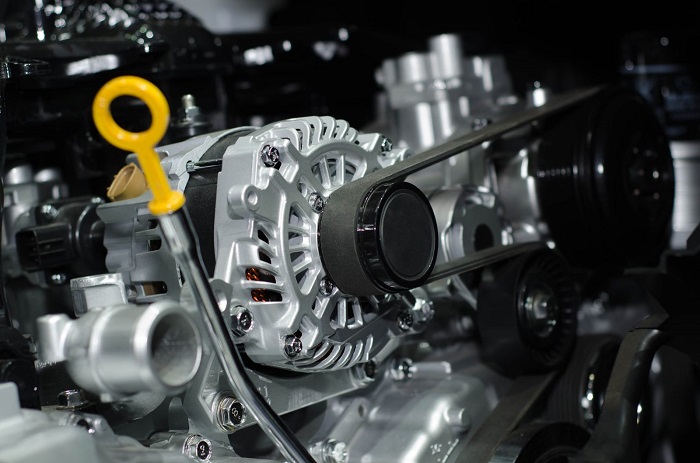
Are you curious to know what an alternator looks like? Take a look at the picture below! This is a kind of alternator that will be mounted under the vehicle’s hood for doing different tasks to make your life easier!
Alternator Application
Knowing the answer to what does an alternator do, enables you to easily understand how it proceeds with each and every task assigned to it. An alternator is used for different purposes, one of them would be the one mentioned above (charging the battery of a vehicle and supporting its electrical system), and other tasks would be powering different electrical components of the vehicle as well as converting mechanical energy into electricity.
What does an alternator do and how it works?
Up to this point, you know the alternator definition and application. But how does an alternator work?
Different parts have been designed inside an alternator to carry the process and provide the desired outcome. It all starts with housing the hold all the components together. Inside the housing, there’s a rotor, stator, bearing, diode, voltage regulator, fans, belt, etc. Each and every one of them has a specific job inside the alternator. For example, the regulator helps in regulating the voltage to make sure that the electrical systems of the car receive the desired voltage. Fans are responsible for the airflow, and so on. Let’s expand their function furthermore to know exactly what does an alternator do and how its components are related to each other.
Alternators are responsible for providing constant power for a vehicle’s battery. They should continuously generate DC when the vehicle is running and charge the battery when the car is moving. It ensures that the car can fully operate throughout the journey. Different signs show when alternator repair is needed such as noise, etc. When an alternator fails, the depletion of the vehicle’s battery begins and eventually, your car will stop working when the battery runs out. You should know that it’s not actually the battery that powers the electrics in a vehicle, rather, it’s the alternator providing the power source for the battery to help start the car via electric starter motor. And when it’s up and running, it is the alternator itself that powers the electrical system of the car and charge the battery by generating the necessary energy.
Many years ago, people called an alternator a generator! It’s good to know that they both convert mechanical energy. But when comparing alternator vs generator, you should know that the output energy of an alternator is AC, while a generator provides DC. Plus, they are different in size! Alternators are much smaller than them! And their interior design differs as well. Alternators produce a rotating magnetic field, while generators produce a stationary one.
How it works is that a drive belt (or a serpentine belt) is responsible for driving the alternator that’s bolted to a specific point on the car’s engine. This bolt turns the rotor via prime mover. This movement generates a magnetic flux. Up to twenty magnetic poles in each rotor are connected to the center prime mover, alternating North and South with the help of different brushes near the poles. They do so via sleep rings around the prime mover, sending a direct current to the poles. An external source of power or attached generators, provide the necessary power for this unit to run.
An assembly of copper coils in a stator makes the proper function of the unit possible. The engine rotates the pulley, resulting in the spin of the rotor past the copper coils that are surrounding a static iron core (this makes up the Stator of the alternator.) Magnetic flux generation produced with the rotor movement creates the alternating current in an alternator. At this stage, the produced AC is not useful for the vehicle. Instead, this current is directed to a rectifier which is made up of a diode, converting the provided AC power to the demanded DC. They can either direct or block the current.
This rectifier is at the end of the alternator and after converting the output, this current can charge up the battery or supply the necessary electricity for the electrical systems of the vehicle. Several terminals at the back of the alternator are connected to the car’s battery, enabling the flow of the produced DC into the battery. Another part that works with the help of these alternators is the ECU that’s in charge of the voltage regulation. That is the case for newer cars, but old cars use a simple voltage regulator for that matter. In the end, the vents at both ends of an alternator help with the airflow. Ventilation and cooling help the alternator to function correctly. The excess heat is driven away through the vents. The fans at both ends that are powered by the drive belt, too, can cool down the alternator.
Some things to remember
- A private car has the average output current of around 50 to 70 Amps, while the older ones have around 30 Amps.
- Alternators can work up to 15 years with the right maintenance and proper care.
- Alternators have low maintenance needs.
- Different signs such as dimming of the headlights, dead battery, unnecessary illumination of the check engine light, problems with electrical systems, etc. can all show that there’s probably something wrong with your alternator and you should fix it right away or else, you won’t be able to use your car at all!
- Test the health of your alternator with a multi-meter to test the battery and its output.
- The warning light that’s in the shape of a battery or the charge icon in your car shows that your alternator needs to be checked.
- Noises from the alternator can also be a sign of a bad alternator and you need an expert to help you identify the problem.
- Keep your alternator away from any water splashes when you wash your car. Any water drops, detergent drops, coolant, or oil leak can easily damage the alternator.
Now that you know the complete structure of an alternator and learned what an alternator does, how about sharing your thoughts and comments on the subject with us? Comment below and let us know what you think! And if you have any questions about alternators, sign up on Linquip right now and we’ll help you in the blink of an eye!
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Alternator Construction and Design
- Signs of a Bad Alternator
- Alternator vs Generator: Your go-to guide to learn their difference
- Alternator Function: The Complete and Easy to Understand Guide to How Alternators Work
- Alternator Slip Rings : discover the basic purpose and other detailed forms
- Types of Alternator : Features, Advantages, and Vast Usage
- What does an Alternator do?