Capacitors are among the crucial parts of many electrical devices. In this article from Linquip, we want to explain in detail the answer to “what is a capacitor” and “what are capacitors used for”. By the end of this article, you will be able to fully understand the structure of a capacitor and how they work inside an electrical device.
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor is considered to be a device for storing electrical energy inside an electric field. This passive electronic component contains two terminals to help store energy. The two conductors inside a capacitor are insulated from each other and are in close proximity. The capacitor’s effect is called capacitance and capacitors are capable of adding capacitance to the circuit. Capacitors belong to a group called “passive components”; these components also include resistors and inductors. All these three elements are used inside electronic equipment.
What are Capacitors Used For? (Different capacitor applications)
A part of knowing “what is a capacitor?” is to know its different applications. Capacitors, also known as condensers, have many different applications. Many devices benefit from using capacitors. One of the important applications of capacitors is their ability to divert spurious electric signals by becoming a filter to differentiate between these signals and the ones that are safe and are not damaging sensitive and important circuits and components during electric surges.
You can also use such parts in digital circuits to make sure that the stored information in computer memories is safe when there’s a temporary power failure. They have been used for early digital computers to work as dynamic memory because of their ability to store energy. Nowadays, capacitors are still used in modern DRAMs inside computers.
The use of capacitors in electronic circuits is because of their ability to block direct current (also known as DC) and in the meantime, they allow the alternating current (Also known as AC) to flow. They are also used in electric power transmission systems for stabilizing power flow as well as the flow of voltage. Another use of capacitors is to smooth the output of power supplies in analog filter networks. As for their application for resonant circuits, they are responsible for tuning radios into particular frequencies.
Capacitor Structure
You need to know the structure of a capacitor when it comes to finding the answer to “What is a capacitor?” Many capacitors have at least two conductors designed in their structure, usually made from metallic plates or surfaces. These electrical conductors are separated by a medium that is usually a dielectric one. The conductor itself can be in the form of a thin film, a foil, or even an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric increases the charge capacity of the capacitor. These dielectrics are usually made of mica, plastic film, glass, paper, air, ceramic, or even oxide layers.
What does a capacitor do and how it works?
Capacitors are used for storing electrical energy. Capacitors, in their ideal form, don’t dissipate energy which is in the contrast with resistors’ functionality. But the real-life situations are a bit different and capacitors dissipate a small amount of energy while in the use. When a voltage (electric potential difference) is applied throughout the capacitor’s terminals, the dielectric will be surrounded by an electric field. This process enables the capacitor to collect a net negative charge on one plate and the negative form on the other. The source circuit of the capacitor experiences a charge flow but the dielectric receives no current flow.
Different types of capacitors
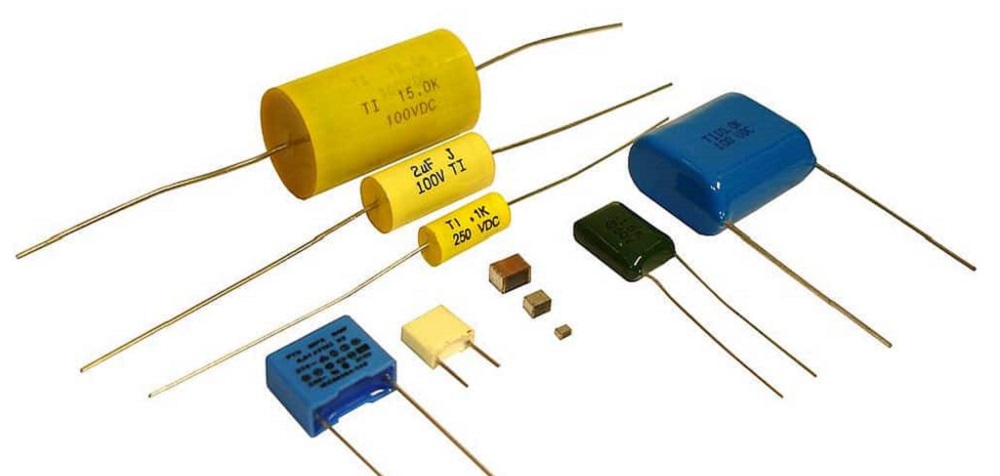
Capacitors have many different types such as ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, film capacitors, etc. If you want to truly know “what is a capacitor?” you should know about different types of capacitors as well.
Categorizing capacitors into different types is based on their form, length, style, girth, material, etc. But the most common element inside them all is that they all have at least two terminals (known as plates) which are electrical conductors that are separated by a dielectric (which is an insulating layer). A major difference between large and small capacitors is in their application. Though in the end, they all follow the same purpose, small capacitors are mostly used to couple signals between different stages of amplifiers in electronic devices. Large capacitors, on the other hand, are usually responsible for energy storage or power factor correction.
Based on the required application, different capacitors have been designed. Below, we’ll introduce the most popular ones:
-
Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are made of different alternating layers of metal and ceramic. The ceramic layer doubles as the dielectric and the metal one act as the required electrodes. To achieve the desired characteristics of the ceramic capacitor, producers use ferroelectric or paraelectric materials. These materials are also modified by mixed oxides to reach the final characteristics.
-
Film capacitors (Plastic film capacitors)
Film capacitors are another type of capacitor you need to know about when you want to find the answer to “what is a capacitor”. Film capacitors (also known as plastic film capacitors) are among the non-polarized ones that use insulating plastic film as their dielectric. It’s interesting to know that metalized film capacitors are capable of having self-healing properties.
These metalized film capacitors have electrodes that may be made of metalized aluminum or zinc, which would be applied on either side or just one side of the plastic film. One of the great advantages of using film capacitors is in their internal construction. They are capable of having direct contact with the electrodes that are located on both ends of the winding; therefore, the current paths become very short.
-
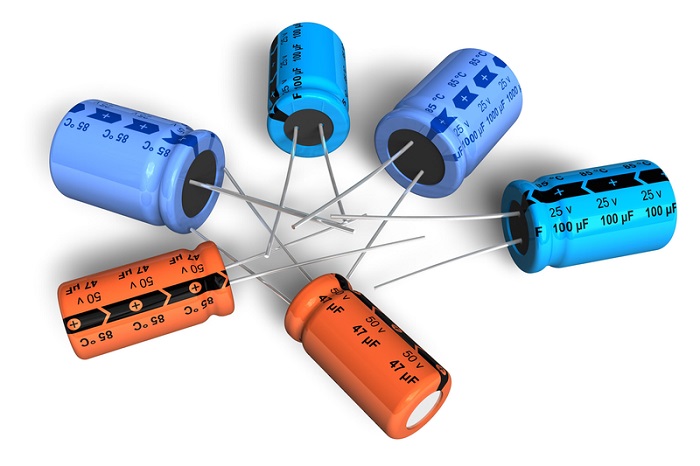
Electrolytic capacitors
This capacitor type contains a metallic anode. This unit is covered with an oxidized layer. The purpose of this layer is to act as the dielectric. A solid electrolyte or non-solid one has also been designed in this capacitor type as its second electrode. This capacitor type is polarized and includes three types: Aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors. The anode in this capacitor type has been highly roughened for increasing the surface area. This type of capacitor has high capacitance per unit volume when it comes to comparing electrolytic capacitors, film capacitors, and ceramic capacitors.
Now you know all there is to know about “what is a capacitor?” their structure, application, and their important role in our lives. What do you think about these systems and their application? Comment below and share your thoughts with us. You can also signup on Linquip to talk to one of our experts and get the answer to all your questions about capacitors.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- What is a Non-Polarized Capacitor? Types & Function
- Difference between Capacitor and Inductor- Capacitor vs. Inductor
- Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a nutshell 2022
- What is a Paper Capacitor?
- What is Paper Capacitor Used for?
- What is Mica Capacitor Used for?
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor? Usage & Application
- What is Film Capacitor & What is it used for?
- 7 Types of Capacitors and Their Uses
- What is Ceramic Capacitor Used for?
- What are Mica Capacitors? Comprehensive Overview
- What is Electrolytic Capacitor?
- What is Film Capacitor? Different Types & Working
- What is Ceramic Capacitor? A Basic Description
- Types of Capacitors: All You Need to Know
- Difference Between Heat Exchanger and Condenser
- Difference Between Condenser and Evaporator