What is Air Valve? Working Principles & Types – An air-operated valve, also known as a pneumatic valve, is a sort of power-operated pipe valve that works in the same way as a solenoid by using air pressure. As the air pressure rises, the compressed air pushes against the piston or diaphragm walls, causing the valve to open. The application determines whether the valve opens or shuts.
These valves are used for a variety of purposes in pneumatic systems, however, they are most commonly utilized for one of two purposes. When a certain pressure is achieved, the first activates a section of the system. The second avoids harm by maintaining a consistent pressure or flow rate inside a system or releasing pressure when it rises too high.
In this post, we will describe the basics of air valves along with their working principle and various types.
⇒ View a List of Air Release Valves for Sale and Their Suppliers ⇐
What is An Air Valve?
Every irrigation system relies on pipes to transport water from the source to the objective. Due to the fluctuating water supply, pockets of trapped air are typical throughout these pipelines during this procedure. Water pipes can get blocked with trapped air, reducing their performance and shortening the lifespan of the system.
As a result, air valves are used. The air release valves assist in the removal of trapped air, allowing water to flow freely through the pipelines and the irrigation system to work effectively. The air release valve opens as the internal pressure inside the water pipe rises, releasing the air.
Air Release Valves, also known as Air Relief Valves, are used to release trapped air at high-pressure points in a pipeline. An air release valve’s internal lever mechanism causes the float force to be greater than the internal pressure, letting it open against internal pressure. When air pockets form in the valve, the orifice is opened by increased force. Air release valves are required to keep the pipeline operating efficiently and prevent it from water hammering.
You are encouraged to visit the Linquip platform, in which you can find numerous air release valve Companies and Manufacturers, along with Service Providers.
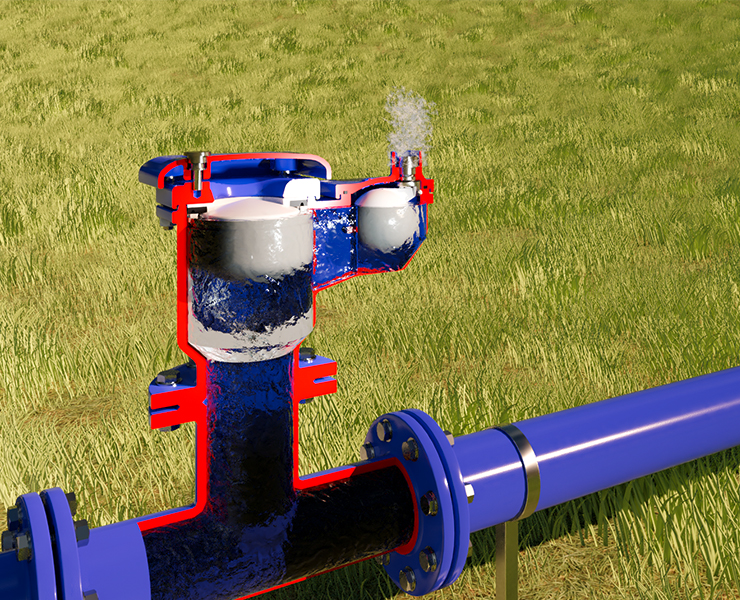

Working Principle of an Air Release Valve
Pneumatic valves are components that regulate the pressure, quantity, and pace of air moving through a pneumatic system by managing the material at the source and then regulating the passage according to the requirements in pipes and tubes. Pneumatic systems rely on compressed air to deliver power and are utilized in a variety of industrial applications such as diesel engines and pneumatically controlled power equipment.
Pneumatic valves are opened and closed using actuation components in a variety of methods, including manually, pneumatically, and electrically. The valve’s control mechanism is based on air, whereas the media that flow through the valve are water, oil, or any other fluid. So, this valve controls the flow of fluid in the valve, but the fluid being regulated is not air. The air is just a control medium that is fed through a pneumatic actuator to shut or regulate the flow.
These valves lower pressure in a regulated manner with the use of actuators and positioners. The controllers detect pressure changes and adjust the signal for air supply to the pneumatic positioner. The pneumatic positioner provides air to the diaphragm, which causes the valve to open, while the spring provides the opposite force which causes the valve to close.
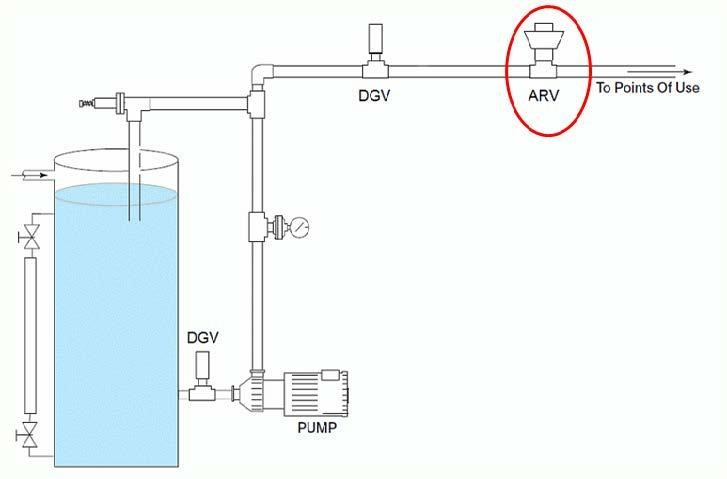
An Air Release Valve’s Components
The pieces of the air release valve are as follows:
Body of the Valve
The inner floats and top mechanism are contained within a compact ductile iron body. The body is constructed with no float guides in the intake, allowing you to install butterfly valves directly under the air valve without losing performance. Each valve body has a bottom 316SS grade tamper-proof drain valve that allows the valve to be drained and tested safely and rapidly.
Assemblies of Inner Floats
Inner floats are composed of polypropylene bar stock, which ensures that their shape and mass do not alter over time. The valve body’s four guide ribs guarantee that the floats are all directed straight to the body, preventing them from becoming offset to one side.
Types of Air Valves
2-way, 3-way, and 4-way air-operated valves are available.
2-Way Valves
2-way valves can be operated in one of two ways: generally closed or normally open. These valves feature two ports that aid in the regulation of air flow in a system. The majority of these valves have a basic on-off operation.
3-Way Valves
3-way valves are available in two configurations: typically closed and normally open, as well as a universal function in which gas may be routed via a third opening to transfer the valve into the normally closed or normally open position. To operate a single-acting cylinder or pilot another valve, 3-way valves pressurize and exhaust one exit port. A pair of three-way valves can be used to operate a double-acting cylinder, obviating the need for a four-way valve. The 3-way valve’s principal function is to save/store compressed air in high-cyclic applications.
4-Way Valves
For systems that demand more air pressure, 4-way valves are employed. In a pneumatic system, four-way valves are the most often utilized components for directional control. The 4-way valve can have four or five ports, each with its own set of functions. The most typical function of these devices is to control the motion of a cylinder, motor or another power source.
From another point of view, automatic air valves, air and vacuum valves, and combination air valves are the three types of air valves used in water systems.
Automatic Air Valves
Automatic air valves discharge little amounts of air from a pressurized pipe on a regular basis. Small orifice air valves and pressure air valves are other names for automatic air valves.
Air and Vacuum Valves
Large amounts of air are discharged from non-pressurized pipelines using air and vacuum valves, which are often employed while filling a line. When lines are emptied, and the pressure decreases abruptly, air and vacuum valves allow significant amounts of air to be admitted. Kinetic air valves, big orifice air valves, vacuum breakers, low-pressure air valves, air relief valves, and single-action air valves are all names for air and vacuum valves.
Combination Air Valves
Automatic air valves, as well as air and vacuum valves, are combined in combination with air valves. The air and vacuum functions discharge and admit huge quantities of air during the filling or draining of pipes, and the automated air release function releases collected air from the system while it is under pressure. Double orifice air valves, double acting air valves, and dual orifice air valves are all terms used to describe combination air valves.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Air Valves
Advantages
Air release valves preserve the pipeline system and keep it running smoothly. These valves make venting huge amounts of air during filling or starting a breeze. They might also let air back in during the emptying process. The significance of this is that under negative pressure, some materials may collapse. When air release valves are placed, they work automatically.
Disadvantages
When a pipeline is loaded or emptied too quickly, the air release valve cannot always handle the air flow needs. The valve must be the correct size for the application.
Applications of Air Valves
Pump failure, corrosion, and flow restriction can all result from a pipe filled with trapped air. It might also lead to an increase in energy usage. Air release valves allow you to manage the flow of air within a pipe, expel surplus air, and keep the system running smoothly. The valves are inserted in pipes where air collects naturally.
In water pipes and sewer force mains, air release valves are widespread. If they’re installed appropriately, they’ll be visible at the system’s high points and peaks. They might be combined with a vacuum/air combination valve or placed somewhat downstream. Air release valves are suitable for any closed-loop system or pressured pipe that might entrap air. Air release valves feature tiny orifices in comparison to other types of air valves. As a result, they’re best suited to applications with lower exhaust air volumes.

Air Valve Size and Placement
Air valves are dimensioned for a distinct installation, with flow, location, and air valve performance all taken into account. As a result, the air valve’s DN does not match the DN of the pipe on which it is mounted. Advanced calculation tools include analyses such as fill rate analysis, drainage analysis, burst analysis, water column separation analysis, and energy-saving analysis to determine the size and position of air valves for a given project.
An air valve’s principal role is to remove undesired air pockets from a pipeline, but it can only do so if it’s fitted appropriately. The right placement of the air valve can considerably increase water flow performance. As a result, air valves should be put at the spots along the pipeline where sub-atmospheric pressure is most likely to occur. In general, an air valve should be positioned at the pipeline’s peak, and it must always be mounted vertically.
The position of an air valve must be studied before installation to ensure that it is protected from freezing, pollution, and floods. For maintenance, operation, and inspection, the air valve should be freely accessible.

To obtain more information on how to size air valves, watch this comprehensive webinar.
FAQs about Air Valves
1. What Are Air Release Valves and How Do They Work?
The automatic air release valve allows collected air to be released when the system is under pressure. When air is present in a water system, it reduces the effective cross-sectional flow area, resulting in lower flow and higher head loss.
2. What Are the Functions of Air Release Valves?
When air builds up at the system’s high points, it causes a line obstruction. Head loss and pumping cycles increase as a result of line constraints, which increases energy consumption. When a fluid is driven into a confined conduit, its velocity rises. As the velocity rises, it’s possible that the air pocket will break apart and be dragged downstream. A water hammer or high-pressure surge is the outcome.
Pressure surges and water hammers can cause catastrophic damage to pumps, valves, and pipelines. This is the most important consequence if the air is allowed to build at the system’s highest point. If the air pocket is not transported away by the fluid’s velocity, it will continue to develop, ending in total obstruction of the flow. Air release valves promote smooth and efficient operation by continually expelling surplus air from the system.
3. Where should air valves be placed?
These valves should be installed where air is most likely to gather since they are designed to discharge air from the pipe system. Install them vertically with the intake down at high places in the system. Remember to install a shut-off valve beneath the valve in case it has to be serviced.
4. When should air release valves be installed?
To effectively vent and pull air into the system, air release valves and air vacuum valves should be fitted every 800m on lengthy pipe lengths as a rule of thumb. Due to the force of the flow, vacuums can occur downstream from valves that are rapidly cut off.
5. How does air get into water pipes?
Water system maintenance is the most common cause of air in the water lines. When the water supply is turned off for a length of time, air might enter the system. (Turning on the faucets for a few seconds typically cures the problem.) Air may enter your system as a result of maintenance work on the water main.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- What is an Air Release Valve? Working Principle & Function
- A Comprehensive Guide To Different Types Of Air Valves
- What is Automatic Expansion Valve: A Basic Guide
- Strainer Valve: a basic guide to know it better
- What is Solenoid Valve and How Does It Work? 2022 Guideline
- What Is Actuated Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What is Balancing Valve? Working Principles,Types & Function
- What is Industrial Valves? Working Principles & Application
- What is Drain Valve? Working Principle, Types & Applications
- What are Coaxial Valves? Working Principles and Type
- What is Isolation Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What is Block Valve? Working Principle & Types
- Backwater Valves: Working Principles & Types



