Hydraulic pumps are an essential part of some of the major machinery and equipment that are used to complete vast and complicated tasks. If you have ever worked with construction, manufacturing, or industrial equipment, chances are high that you were using some kind of hydraulic pump. It may seem like such a basic question to ask, but unfortunately, many who even work in this industry do not know what is hydraulic pump. In this article, we will give a plain answer to this question and explain the way hydraulic pumps operate. Keep reading this new blog in Linquip for more information on these pumps.
⇒ View a List of Hydraulic Pump for Sale and Their Suppliers ⇐
What is a Hydraulic Pump?
A hydraulic pump is a mechanical source of power that converts mechanical power into hydraulic energy (hydrostatic energy i.e. flow, pressure). When a hydraulic pump operates, it performs two functions. First, its mechanical action creates a vacuum at the pump inlet which allows atmospheric pressure to force liquid from the reservoir into the inlet line to the pump. Second, its mechanical action delivers this liquid to the pump outlet and forces it into the hydraulic system.
A pump produces liquid movement or flow: it does not generate pressure. It produces the flow necessary for the development of pressure which is a function of resistance to fluid flow in the system. For example, the pressure of the fluid at the pump outlet is zero for a pump not connected to a system. Further, for a pump delivering into a system, the pressure will rise only to the level necessary to overcome the resistance of the load.
Hydraulic pumps components
- Pump Housing/Casing
- Impeller Blades
- Pump Shaft
- Bearing Assembly
- Sealings
Hydraulic pumps are used for energizing fluids to flow from a lower potential to higher. It has several mechanical moving components that receive energy from any other source. Most of the hydraulic pumps have rotating parts that operate using the electrical source. The basic components used in hydraulic pumps are described as follows.
- Pump Housing/Casing: This is the exterior part of the hydraulic pump to protect the inner components. Smaller pumps use aluminum as the construction material and others use cast iron.
- Impeller Blades: The impeller blades will rotate inside the pump housing. The rotation of impeller blades will rotate the surrounding fluids and thus the fluid flow at a higher potential. Also, they play an important role in lubricating and cooling the system.
- Pump Shaft: The pump shaft is used to mount the impeller. Steel or stainless steel is used for constructing the shaft and the size will depend on the impeller.
- Bearing Assembly: Assistance for continuous impeller rotation is the function of pump bearings. Most of the centrifugal pump uses standard ball-type anti-friction bearings.
- Sealings: Most of the pumps fail due to the damage of bearing assemblies. Seals will eliminate the risk of failure to a greater extent by protecting the bearing assemblies from contaminants and coolants.
Hydraulic pump Working Principle
Hydraulic pumps will carry oil or any other fluids from the reservoir/tank to other parts of the system. The working of the hydraulic pump is based on the displacement principle (Any object, wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object).
Both the inlet and outlet of the hydraulic pump contains different check valves. The check valve located at the inlet will push the fluid from the tank/reservoir into the pump and the one located at the outlet will pump fluid to other parts of the system.
The vacuum created will push the fluid into the pump inlet. Electric, motor or a gas engine are used as the prime mover to rotate the shaft. The impeller blades are located on the shaft and the surrounding fluids will rotate with the movement of the shaft.
A vacuum is created inside the cylinder when the piston is pulled. The vacuum created will close the outlet check valve and open the inlet check valve. Then, fluid from the tank or reservoir enters the pump and partially fills the cylinder. When the piston is pushed, the fluid molecules will come closer and the inlet check valve will close. This will open the outlet check valve and fluid flows through it.
Different hydraulic pump types
- Reciprocating pumps
- Rotary pumps
- Gear pumps
External gear pumps
Lobe pumps
Internal gear pumps
Gerotor pumps
- Gear pumps
-
- Screw pumps
- piston pumps
Axial piston pumps
Radial piston pumps
-
- Vane pumps
Hydraulic pumps are manufactured depending on different functional and hydraulic system requirements, such as operating medium, required range of pressure, type of drive, etc. A large range of design principles and configurations exists behind hydraulic pumps. Consequently, not every pump can fully meet all sets of requirements to an optimum degree. The most common hydraulic pump types are mentioned above.
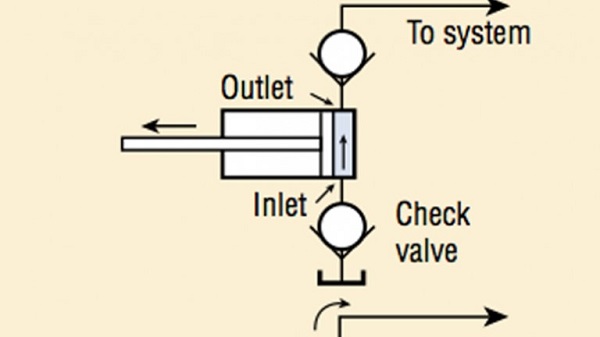
Hydraulic pump Diagram
As mentioned above, the hydraulic pump generates a flow with enough power that overcomes the pressure produced by the load at the outlet of the pump. A vacuum is created at the outlet of the pump when the pump is operated. The vacuum forces the liquid into the inlet of the pump and delivers it to the pump outlet with mechanical actions and finally forces the liquid into the hydraulic system.
A simple hydraulic pump diagram is shown in the figure below.
Hydraulic pumps application
Hydraulic pumps are still widely used in industrial environments. Injection molding machines, presses (shear, stamping or bending, etc), material handling, lifts, conveyors, mixers, forklifts, pallet jacks, foundries, steel mills, slitters, etc. The more severe the application, the more likely it will be powered by a hydraulic pump.
Besides, hydraulic pumps are used on every conceivable mobile or industrial hydraulic machine. They are used on excavators, cranes, loaders, tractors, vacuum trucks, forestry equipment, graders, dump trucks, mining machinery, etc. Mobile applications use hydraulic pumps more prolifically than do industrial machines because electric actuators are generally not used for mobile machinery.
So, now that you know the answer to the question ‘what is hydraulic pump?’, let us know what you think by leaving a reply in the comment section. We will be glad to have your viewpoint on the article. Is there any question we can help you through? Feel free to sign up on Linquip to get the most professional advice from our experts.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- How Does a Hydraulic Pump Work? A Definitive Guide
- What is Head of a Pump? A Complete Guide
- What Is Pump Cavitation
- Different Types of Hydraulic Pumps: a Complete Guide
- What Are Air Source Heat Pumps? A Complete Guide
- Pump Curve: All You Should Know About Definition and Read One
- Working Principles of Hydraulic Pump
- What is Sump Pump and How Does It Work?
- 10 Parts of Hydraulic Pump + PDF & Function