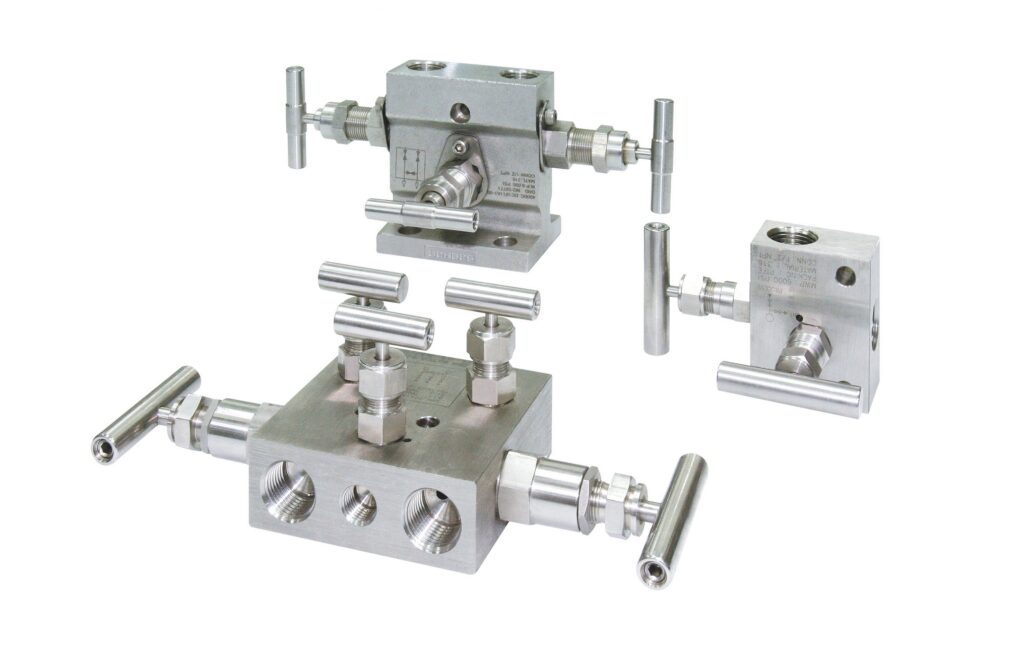
What is Manifold Valve? A valve manifold is an essential component of pressure and differential pressure transducers. The inclusion of a valve manifold in the tool allows it to be calibrated or replaced without shutting down the facility. In this post, we at Linquip talk about the principles, styles, and types of manifold valves.
It is possible for you to find a substantial amount of information on Linquip’s website that may prove helpful to you in learning about valve manifolds before you make a purchase decision. This will make it easier for you to select the best product that suits your needs. Any time you require information on valves or their respective equipment, whether you are looking for information on services or products, Linquip will be the best choice for you. We at Linquip are available to assist you with any questions you may have about these pieces of equipment. We strongly recommend that you read Linquip’s article titled “Valve manifolds,” as it contains useful information for you.
You can take full advantage of the Linquip platform with the help of a Linquip Expert account. Therefore, we highly recommend that you register as one with us. As a registered member of Linquip, you will have the opportunity to demonstrate your expertise in industrial equipment to potential clients in a way that is tailored to their specific needs. You may want to consider contributing a guest post to the Linquip website as a guest author. In the Linquip platform, you can add your own content directly to the site. Your writing will be published by using the Guest Posting feature.
⇒ View a List of Valve Manifolds for Sale and Their Suppliers ⇐
What Is a Valve Manifold?
If you’ve ever wondered what a valve manifold is or how it works, Linquip can provide some insight in our most recent blog. We’ll go through the design and functions of ordinary valve manifolds, as well as their benefits and some of the important aspects of manifold valve products.
Understanding Valve Manifolds
You must first have a fundamental knowledge of what a valve manifold is. A manifold is a hydraulic system component that joins one or more block/isolate valves. Ball, needle, bleed, and vent valves are examples of hydraulic system valves. The function of a block and bleed manifold is to keep fluids from upstream from coming into touch with downstream components. This is accomplished by separating the fluid flow in the system.
Suppliers at Linquip provide a wide choice of manifold valves. All of their valves, which range from 2-way to 5-way and mono-flange manifolds, provide better efficiency and dependability. To complete your manifold package, they may also supply a selection of manifold accessories, such as connectors and adaptors. To explore more about manifolds, visit here.
Types of Manifold Valves
2-way valve manifolds, 3-way valve manifolds, and 5-way valve manifolds are the three varieties of valve manifolds.
2-Way Valve Manifold
Only a 2-way valve tube is utilized for pressure sensors. One block valve and one drain or test valve make up a conventional 2-way valve manifold.
The pressure transmitter must be calibrated.
Open the drain valve after closing the block valve. Then, to test the pressure, attach the drain valve to the pressure generator.

3-Way Valve Manifold
A differential pressure transmitter uses a 3-way valve manifold. Two block valves and one equalization valve make up a conventional 3-way valve manifold.
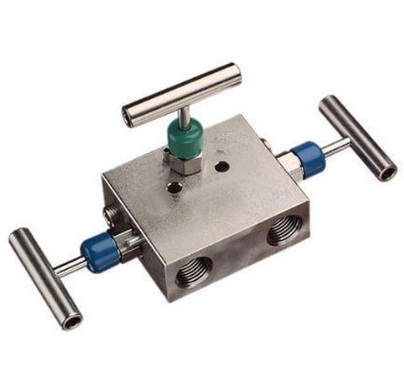
Close the block valve and open the equalizing valve to verify the differential pressure transmitter’s zero.
Due to the lack of a test connection, the 3-valve manifold is rarely utilized in the oil and gas industry, particularly on offshore sites.
A blocked test connection was added to some 3-valve manifolds by some firms.
5-Way Valve Manifold
A differential pressure transducer is also connected to the 5-way valve manifold. Two block valves, one equalization valve, and two vent or test valves make up a conventional 5-way valve manifold.
Close the block valve and open the equalizing valve to test the transmitter’s zero.
Connect the test valve to a pressure generator once the pressure has been equalized to calibrate the transmitter for 3 or 5-point calibration.
The most typical valve manifold for a differential pressure transmitter is this 5-way valve manifold.

Manifold Valve Function
A manifold is a hydraulic system component that joins one or more block/isolate valves. Ball, needle, bleed, and vent valves are examples of hydraulic system valves. The function of a block and bleed manifold is to keep fluids from upstream from coming into touch with downstream components. This is accomplished by separating the fluid flow in the system.
The following are some essential characteristics of typical manifolds:
- Anti-rotational thrust brush for consistent packing compression, pressure-tight sealing, and minimizing cold flow channels
- Bonnet/body washer that ensures total atmospheric leakage and allows on-site bonnet retrofitting with a 100% re-sealing guarantee
- T bar for ease of operation
- Dual cap
- Gland adjuster lock nut
- Adjust the gland packing adjustment to compensate for gland wear.
- Valve bonnet arrangement with replacement bonnet sealing washer
- Anti-blowout spindle with high-quality micro mirror stem finishing for positive gland sealing, suitable for low torque operation.
- Gland packing for optimum sealing with the least amount of air adjustment
- The spindle tip provides a bubble-tight shutoff, ensuring leakage-free performance and downstream functional safety for the user.
Make-Up of an Instrumentation Manifold Valve
Body Type
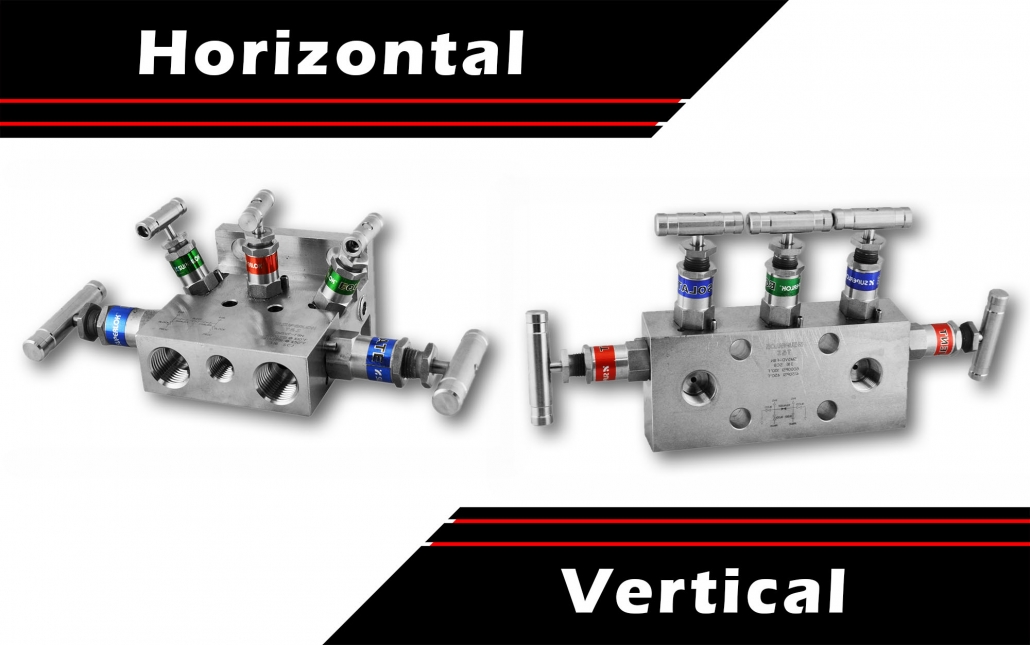
The horizontal style manifold and the vertical type manifold are the two basic styles available. The orientation of the valve’s main body is determined by these styles. The multiple body and valve orientations of instrumentation manifolds are shown in this figure.
Mounting Style
Furthermore, there are two different styles of manifold installation to take into account. The two forms of mounting are distant mounting and direct mounting. The direct mount style, as the name implies, involves mounting the manifold directly to pressure instruments. Flange and threaded connectors are commonly used in direct mount valves. Remote mounting manifolds, on the other hand, allow installation away from the instruments using just threaded connections.
Number of Valves / Layout
Manifolds provide a range of block and isolate valves, as well as apertures for threaded or flanged pipe connections, all on a single body. The number of block and isolate valves is determined by the operation of the manifold.
2-way, 3-way, and 5-way manifold designs with color-coded functions and pressure ratings up to 6,000 PSI are available from Suppliers. The drain, vent, and test functions are colored red, the isolate/block is blue, and the equalization valves are green.
When to Use a Manifold
In processing applications, manifolds keep a system or line flowing. When configuring your process line, instrumentation manifolds are essential. Other valve types with the same threaded connections, such as needle valves and check valves, can simply attach to them. In fact, they can connect to two or more valves in a system, making them the go-to solution for connecting in tight locations.
Furthermore, pressure instruments have usually used manifolds when another piece of equipment has to be calibrated without requiring a system shutdown. Isolation/shutoff valves, also known as manifolds, are used with pressure equipment such as transmitters and differential pressure transmitters.
What is differential pressure, and why is it important to know? The difference between two applied pressures is called differential pressure, and it’s “frequently the basis of other measures like flow, level, density, viscosity, and even temperature.” Differential pressure readings reveal if there is a possible problem in the process line, and they are vital to detect since changes might have substantial implications.
Transmitters, sensors, gauges, and transducers are examples of differential pressure instruments. By far the most frequent instrument used with manifolds is the Differential Pressure Transmitter. “Sense the difference in pressure between two ports and provide an output signal concerning a calibrated pressure range,” says a DP transmitter.
To prevent over-range and isolate the transmitter from the process line for maintenance and calibration, system designers utilize 3-valve or 5-valve manifolds in combination with the DP transmitter.
Manifolds are frequently used with DP transmitters because their isolation function allows the transmitter to be isolated from the process instrumentation line, allowing the system to remain idle rather than shut down.
Advantages Of Using a Valve Manifold
Valve manifolds have various applications, ranging from small mobile devices to large industrial complexes. Obviously, each mounting option has its own set of advantages. You’re already ahead of the game if you opt to employ a manifold with your processing system! In general, there are various benefits to employing a manifold with your system to consider. Here are some other advantages of valve manifolds:
- Shorter flow pathways reduce pressure loss and heat, increasing energy efficiency.
- Because of the small form, installation expenses and fluid connections are reduced.
- Oil leaks and maintenance are reduced since there are fewer connections to strain, wear, and loosen.
- To fit into tight locations, small and compact versions with cartridge valve designs are available.
- The overall arrangement has been improved, with fewer hoses and fluid connections.
Here are a few other advantages to consider when choosing a direct mount manifold.
Benefits of the Direct Mount Manifold
- Less expensive maintenance
- Less expensive installation
- Fewer leak points
- Integrated valves
- The system is still hard piped
Remote mount manifolds have the benefit of protecting instruments from a temperature above their limits by lowering and/or raising process temperature since they are attached indirectly into lines rather than directly onto instruments.
Benefits of the Remote Mount Manifold
More advantages of employing a remote mount manifold may be found here.
- Easier maintenance
- The piping is mounted to the transmitter
- Easier installation
- Uses standard instrument manifolds
- Fewer leak points
- Uses tubing and tube fittings
Download What is Manifold Valve? PDF
The article can be downloaded as a PDF file by clicking the link provided below.
Summary
A manifold is a multi-faceted product with several purposes, making it a vital component for pressure instrument use. Check out the choices on our Linquip Manifold Valves Manufacturers Page, or Contact Us and we’ll help you select the right manifold for your operation.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- What is Air Valve? Working Principles & Types (Clear Guide)
- What is Solenoid Valve and How Does It Work? 2022 Guideline
- What is Automatic Expansion Valve: A Basic Guide
- Strainer Valve: a basic guide to know it better
- What Is Actuated Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What Is Linear Valve? With Example, Working Principles & Types
- Valve Manifolds: Working Principles, Function & Diagram
- What is Balancing Valve? Working Principles,Types & Function
- What is Drain Valve? Working Principle, Types & Applications
- What are Coaxial Valves? Working Principles and Type
- What is Isolation Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What is Block Valve? Working Principle & Types
- The 10 Best Shower Valves (2022 Reviews)



