Non-Polarized Capacitor– One of several models of capacitors is a non-polarized capacitor. The capacitor can be classified into two types based on their polarity: non-polarized capacitors and polarized capacitors. And here’s what this article will go over: What is the definition of a non-polarized capacitor? What is the purpose of it? How should non-polarized capacitors be chosen? What makes polarized capacitors different from non-polarized capacitors? Let’s have a look at it.
There is a variety of information available on Linquip’s website about non-polarized capacitor equipment and devices. If you have any questions regarding non-polarized capacitors, you can get help from Linquip’s team of experts. Linquip has a brief detailed article, “What Is Non-Polarized Capacitor?“, that may be of interest to you.
If you wish to access all the advantages offered here, you can also register as a Linquip Expert. Have you ever considered guest posting on Linquip? You can submit your articles as a guest on the Linquip platform.
What is a Non-Polarized Capacitor?
Capacitors with neither positive nor negative polarity are known as non-polarized capacitors. Non-polarized capacitors’ two electrodes can be put into the circuit at random and will not leak. They’re typically found in the coupling, decoupling, compensation, feedback, and oscillation circuits.
There is no polarity in the ideal capacitor. However, in actuality, unique materials and structures are utilized to achieve a big capacity, resulting in the fact that the actual capacitors are moderately polarized. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors and tantalum electrolytic capacitors are examples of polarized capacitors. Electrolytic capacitors have a large capacity in general. Making a large-capacity non-polarized capacitor is difficult since the volume required is enormous. That is why the actual circuit contains so many polarized capacitors. Polarized capacitors can be useful in this circuit because the voltage is only one way and the size is minimal.
To prevent its drawbacks and to take advantage of its benefits, we employ polarized capacitors. This is how we can interpret it: A polarized capacitor is one that can only be utilized in a single voltage direction. Both voltage directions can be utilized with non-polarized capacitors. As a result, non-polarized capacitors outperform polarized capacitors in terms of voltage direction. Non-polarized capacitors can completely replace polarized capacitors as long as the capacity, working voltage, volume, and other specifications are met.
Working Principle of a Non-Polarized Capacitor
Non-polarized capacitors are used in pure AC circuits and can also be used for high-frequency filtering due to their modest capacitance. To demonstrate how the capacitor can be used, consider the following scenario:
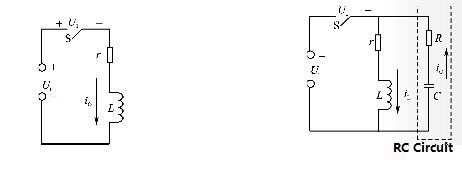
The RC spark suppression circuit is primarily used in this instance. When the antenna receives a radio or television program when the fluorescent lamp is turned on and the fluorescent lamp flashes, you will hear an erratic sound from the radio or television speaker. High-frequency clutter interference created by electric sparks causes many brilliant lines and bright spots on the TV screen.
When inductance-based circuits are severed, a spark is generated between the contacts. The switch S is abruptly switched off, and the current quickly vanishes as shown in the circuit to the left in the following figure. Because the current change is considerable, a large self-inductance is formed at both ends of the coil. This electromotive force may prevent current from changing, and it has the same direction as the applied voltage. When the two are overlaid, the voltage U1 across the switch becomes extremely high, and when the voltage exceeds a particular threshold, the “sharp” voltage breaks down the air and produces an electric spark.
The spark may prompt the contacts to be ablated and oxidized, resulting in failure. As a result, it’s critical to get rid of the spark between the contacts. When the circuit is turned off, as long as the control coil’s current does not drop too low, the voltage at the coil’s two ends will not be too high, and no spark will occur. The RC spark suppression circuit is joined at both ends of the inductor, as shown in the schematic on the right. i1 will charge the capacitor when the switch is abruptly switched off.
Types of Non-Polarized Capacitors
Electronic devices with two conducting surfaces (plates) separated by an insulator are known as capacitors (the dielectric). They have the ability to momentarily store an electric charge. The electrolytic capacitor is the only form of the polarized capacitor (functions differently depending on which way the current flows). Although electrolytic capacitors offer a larger capacitance, non-polarized capacitors are recommended for most applications. They’re less expensive, may be put in any direction, and have a longer lifespan.
Ceramic Capacitors
The most prevalent type of non-polarized capacitor is a ceramic capacitor. They’re a tried-and-true technology that’s also the cheapest type of capacitor. The oldest style (from the 1930s) is disk-shaped, whereas contemporary forms are block-shaped. They operate well in radio frequency circuits, and the latest variants can also be used in microwave applications. They range in size from 10 picofarads to 1 microfarad. They have some dielectric leakage, and their function and temperature stability differ according to the manufacturer.
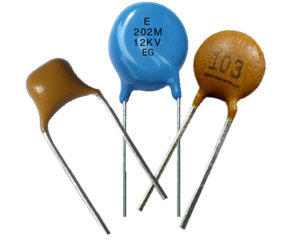
Polyester Capacitors
Mylar capacitors are another name for polyester capacitors. They are low-cost, precise (they have the exact rating that is stated on them), and leak-free. They work in the 0.001 to 50 microfarad range and are utilized when precision and stability aren’t as crucial.

Polystyrene Capacitors
Mylar capacitors are another name for polyester capacitors. They are low-cost, precise (they have the exact rating that is stated on them), and leak-free. They work in the 0.001 to 50 microfarad range and are utilized when precision and stability aren’t as crucial.
Polycarbonate Capacitors
Polycarbonate capacitors are high-priced and of excellent quality, with excellent precision and low leakage. Unfortunately, they have been phased out and are now difficult to come by. In the 100 picofarads to 20 microfarad range, they perform well in severe and high-temperature conditions.
Polypropylene Capacitors
Polypropylene capacitors in the 100 picofarads to 50 microfarad range are pricey and high-performance. They are exceedingly accurate, stable over time, and have very little leakage.

Teflon Capacitors
These capacitors are the most reliable on the market. They are incredibly precise and almost leak-free. They’re usually regarded as the best all-around capacitor on the market. It’s worth noting how they react exactly the same throughout a wide variety of frequency variations. They work in the range of 100 picofarads to 1 microfarad.

Glass Capacitors
Glass capacitors are extremely durable and are the capacitor of choice in extreme conditions. They function in the 10 picofarads to 1,000 picofarad range and are reliable. They are, regrettably, also the most expensive capacitor.

The Difference Between Non-Polarized Capacitors and Polarized Capacitors
The fundamentals of both polarized and non-polarized capacitors are the same: they release and store charges; the voltage on the plate (the electromotive force of charge accumulation here is termed voltage) cannot change abruptly.
Varied mediums, performances, capacities, and structures lead to different environments and usage. With the advancement of science and technology, as well as the discovery of new materials, more great and diverse capacitors will emerge.
The Difference in Dielectric
The majority of polarity capacitors use electrolytes as dielectric, resulting in a higher capacitance than conventional capacitors of the same volume. Furthermore, the capacitance of polarized capacitors made with various electrolyte materials and techniques would vary.
Voltage withstand, on the other hand, is mostly determined by the dielectric material. The usage of polarized and non-polarized capacitors is defined by whether the nature of the dielectric is reversible, and there are numerous non-polarized materials, including the most extensively used metal oxide film and polyester.
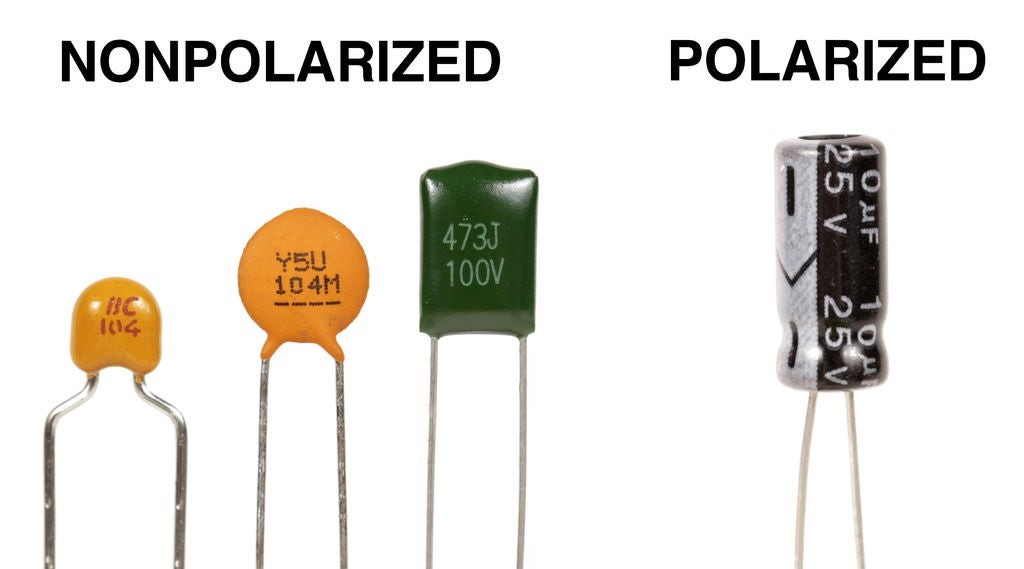
The Difference in Performance
The requirement of usage is performance and demand maximization. I’m afraid that only a power supply can be fitted within the shell if the TV’s power supply utilizes a metal oxide film capacitor as a filter and if the capacitance and voltage withstand are necessary to meet the filter.
As a result, only a polarized capacitor may be used in the filter, and polarity capacitance is irreversible. The electrolytic capacitor, which contributes to coupling, decoupling, power supply filtering, and other functions, is usually above 1 MF. Non-polarized capacitors are used in resonance, coupling, frequency selection, current limiting, and other applications. Non-polarized capacitors with big capacity and high voltage are also available and are commonly employed in reactive power compensation, motor phase shifting, frequency conversion power phase shifting, and other applications. Non-polarized capacitors come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
The Difference in Capacity and Structure
As previously stated, capacitors of the same volume have various capacitances when the dielectric is varied.
Furthermore, in principle, any capacitor of any shape can be used in the environment without regard for point discharge. Circular electrolytic capacitors are the most common, and square electrolytic capacitors are uncommon. Capacitors come in a variety of shapes, including tubular, deformed rectangle, sheet, square, circular, combination square or circular, and so on, depending on the use. Of course, in high-frequency and intermediate-frequency devices, invisible ones called dispersed capacitors must not be overlooked.
The Difference in Usage in Various Environments
The capacity of polarity capacitors can be relatively large due to the internal material and construction. However, because their high-frequency properties are poor, they are best used for power filters and other applications. There are also tantalum electrolysis polarized capacitors with good high-frequency properties, although they are relatively expensive.
These non-polarized capacitors, which include ceramic capacitors, monolithic capacitors, polyethylene (CBB) capacitors, and others, are compact in size, low in price, and have strong high-frequency characteristics, but they are not appropriate for large capacity. High-frequency filtering and oscillation circuits commonly use ceramic capacitors.

The meson in magnetic dielectric capacitors is ceramic, and the electrode is a silver layer on the surface. Magnetic dielectric capacitors are ideal for high-frequency and high-voltage circuits because of their consistent performance and low leakage.
Big dielectric permittivity materials (such as ferroelectric ceramics and electrolytes) are ideal for capacitors with large capacity and compact volume but high loss. Ceramics and other materials with low dielectric permittivity have a minimal loss and are appropriate for high-frequency applications.
What is the Best Way to Charge a Non-Polarized Capacitor?
When a non-polarized capacitor is charged with a DC source, it does not matter which lead is positive or negative. A closer look at the capacitor will reveal that it is marked differently from a polarized capacitor because it does not have any polarity markings.
FAQs about Non-Polarized Capacitor
What Is the Difference Between Polarized and Non-Polarized Capacitors?
A non-polarized (“non-polar”) capacitor is one that has no implicit polarity and can be used in either direction in a circuit. A polarized (“polar”) capacitor has an inherent polarity, meaning it may only be connected in one direction in a circuit.
What are The Types of Non-Polarized Capacitors?
Types of Non-Polarized Capacitors are:
- Ceramic Capacitors
- Silver Mica Capacitors
- Polystyrene Capacitors
- Polypropylene Capacitors
- Polyester Capacitors
- Teflon Capacitors
- Polycarbonate Capacitors
- Glass Capacitors
What Is the Difference Between Fixed and Polarized Capacitors?
Electrostatic capacitors are non-polar, which means they can be connected in any polarity direction and have no effect. By their very nature, electrolytic capacitors are polar. They can only be linked with terminal polarities that are fixed. The positive and negative terminals have been identified.
What Is the Function of a Polarized Capacitor?
They give enormous capacitance values in tiny, cost-effective packaging. Their primary function is to filter power supplies (storage). They’re also utilized to prevent DC in amplifier stages when they’re coupled together. A film or ceramic capacitor is an alternative although they are physically larger and do not come in high capacitance values.
How Can You Tell If a Capacitor Is Non-Polarized?
The negative lead on electrolytes is frequently indicated with arrows and “-” marks. The positive lead is noted on tantalums. The cap will not be polarized if it is ceramic, monolithic, film, polyester, or silver mica.
Why are Non-Polarized Capacitors Preferred?
Although electrolytic capacitors offer a larger capacitance, non-polarized capacitors are recommended for most applications. They’re less expensive, may be put in any direction, and have a longer lifespan.
Can I Replace a Polarized Capacitor with a Non-Polarized One?
Non-polarized capacitors are polarized capacitors’ supersets. In general, a polarized capacitor can be replaced by a polarized or non-polarized capacitor with the same capacitance and a voltage rating equal to or higher than the original.
What Is the Difference Between Fixed and Polarized Capacitors?
Electrostatic capacitors are non-polar, which means they can be connected in any polarity direction and have no effect. By their very nature, electrolytic capacitors are polar. They can only be linked with terminal polarities that are fixed. The positive and negative terminals have been identified.
Download Non-Polarized Capacitor PDF
You can download this article as a PDF so that you can access it whenever you like.
Watch Videos about Non-Polarized Capacitor
For more information about non-polarized capacitors, watch this video about Non-Polarized Capcicator.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More In Linquip
- What is a Paper Capacitor?
- What is a Polarized Capacitor
- Types of Capacitors: All You Need to Know
- Difference Between Condenser and Capacitor in a nutshell
- What is Mica Capacitor Used for?
- What is an Electrolytic Capacitor? Usage & Application
- What is Film Capacitor & What is it used for?
- What is Capacitor and How Does it Work?
- 7 Types of Capacitors and Their Uses
- What is Ceramic Capacitor Used for?
- What are Mica Capacitors? Comprehensive Overview
- What is an Electrolytic Capacitor?
- What is a Polarized Capacitor? Function and Applications
- What is Capacitive Circuit? Formula & Function
- What is Film Capacitor? Different Types & Working
- What is Ceramic Capacitor? A-Basics Description
- Types of Capacitors: All You Need to Know
- Difference between Capacitor and Inductor- Capacitor vs. Inductor



