What is Pilot Valve? Working Principle & Types – A pilot valve is a tiny valve that regulates the flow of a restricted-flow control feed to another piloted valve. This separate valve is usually used to regulate a high-pressure or high-flow supply. Pilot valves are valuable because they allow a tiny and easily controlled feed to control a much greater pressure or flow feed that would otherwise take a considerably bigger force to operate; moreover, when a solenoid is used to drive the valve, this is even more beneficial.
Human-operated pilot valves are frequently employed in critical applications (e.g., emergency and SIS controls). They can be set up as a dead man’s switch or a push-to-activate switch.
⇒ View a List of Valves for Sale and Their Suppliers ⇐
What is A Pilot Valve and How Does it Work?
Pilot valves are high-flow control valves for a system. The pressurized fluids mostly move the pilot-operated valves. When the set pressure is achieved, the valve opens and the pressure is released. The flow directing element of the valve changes when pressured fluid meets the valve piston. The main benefit of a pilot operation is that it may provide substantial shifting forces without the impact or wear that a manually operated valve would experience. Pilot controlled valves can be installed at any distant site where pressure fluids need to be piped. Because there will be no spark or rise in heat in this valve, it may be utilized in combustible situations.
You are encouraged to visit the Linquip platform, in which you can find numerous air release valve Companies and Manufacturers, along with Service Providers.
Applications of a Pilot Valve
The pressure in a system can be reduced by using a pilot valve. A pilot valve can be used to regulate the flow. Pilot valves can be used to regulate directional control valves, pumps, cylinders, and motors from a distance. A pressure decreasing valve can be thought of as a pilot valve. A remote pilot source can be utilized with some pilot valves. As a result of this characteristic, other valves in the logic circuit can shift a valve from a remote pressure source.
Advantages of a Pilot Valve
Pilot valves have the following features and advantages:
- This valve will be tight until it reaches the setpoint since pilot valves have a high seat tightness.
- When the pressure in the chamber exceeds the setpoint, it is immediately relieved by fully opening the door.
- In a pilot valve, precise shutting is possible.
- Its structure is quite tough, therefore it will not be destroyed easily.
- If there is ice in the valve as a result of specific applications, the icing will be broken during the rapid lifting procedure and the valve will not be interrupted.
- This valve may be used as a pressure and vacuum safety valve at the same time.
What Is a Pilot Operated Directional Control Valve (DCV) and How Is the DCV Shifted?
Because the system would require a huge force to shift the spool, pilot controlled DCV is employed to regulate the system with high flows. As a result, the pilot valves are mounted on top of the main valve. As a result, the pilot valve would move the main valve hydraulically. The valve piston is operated indirectly in this valve. The pilot valve is supplied with oil in order to do this. As a result, when the pilot valve is turned on, the oil will be directed to one side of the main spool, causing the spool to shift. As a result, the pressure port will be connected to the work port, and the fluid will flow back to the tank. External piloting has a few advantages, including a constant pressure supply and the ability to filter the source separately to prevent the pilot valve from silting. Pilot-operated DCV valves can be drained either internally or externally, depending on the situation.
What Is a Pilot Check Valve, and How Does a Pilot Check Valve Work?
This valve features an entrance and output port on the valve body, as well as a poppet that is biased against a spring. Only one direction of flow will pass via this valve. Pilot pressure is provided to the pilot pressure port of the valve to allow flow in the blocked direction. If the poppet’s spring force is less than the system pressure in the flow port, the poppet will be pushed or moved, and the flow will occur. Because the fluid pressure closes the poppet, there will be no backward flow. Pilot pressure must be applied to the pilot port in order to allow reverse flow.
What Is The Best Way to Maintain and Install a Pilot Valve?
Before installing the pilot valve, we must inspect it to see if there is any damage. The valve must be put on a soft clean gasket material before installation to avoid damage to the bottom flange surface. Before installation, the valve must be stored in a clean environment. Vertical installation of the valve is required. Using the lift eyes, the valve should be effortlessly raised into place during installation. The gasket should be inspected, and the nuts and studs should be greased. On the nozzle and flanges, the valve must be appropriately adjusted. This valve is easy to maintain because it does not create any problems. The seat must be inspected on a regular basis. The valve must be removed from the tank in order to examine the diaphragm, gaskets, and seals on a regular basis.
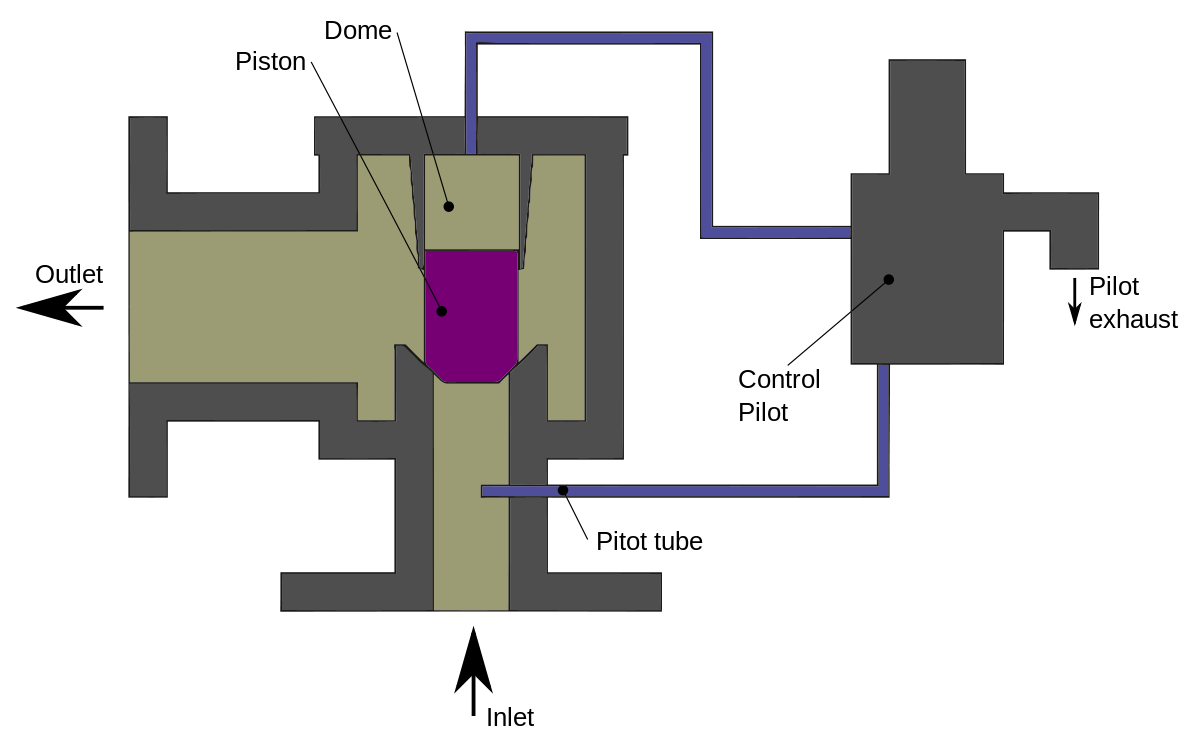
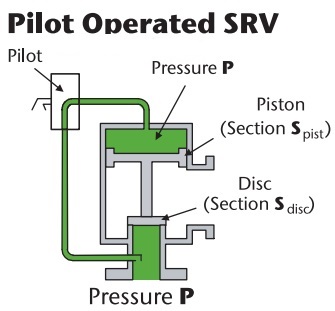
When Do We Utilize a Pilot-Operated Relief Valve and How Does It Work?
Pilot-operated relief valves are used for overpressure relief and other emergency tasks. A pilot-operated relief valve works differently than a pressure relief valve in that it seals the valve using system pressure. A pilot valve, main valve, pilot tube piston or disc, and seat are the basic components of this valve. A pilot controlled safety relief valve is another name for this valve. This valve is quite sensitive, and it can significantly minimize pressure override. These valves are employed in situations where a large flow must be relieved at low pressure. The pilot valve has two phases of action, the first of which is the pilot stage. The main valve would be controlled by a tiny spring-biased relief valve in the pilot stage.
The balanced piston stage is the next stage, when the hydraulic connections are created and a balanced piston is utilized to divert the whole flow volume. With the assistance of a light spring, the inlet pressure will keep the piston on its own seat. When the pressure in the valve reaches the appropriate value, the pilot stage poppet will be raised. The lower pressure in the upper chamber of the second stage piston will induce an imbalance in hydraulic force. If the hydraulic force is higher than the spring’s mechanical force, the poppet will be elevated. When the pressure differential between the upper and lower chambers is sufficient, the balance piston will be elevated, allowing complete flow to occur. This procedure will continue until the pressure in the system is lowered.
Techniques of Control
Directional Control valve control techniques may be divided into two categories.
- Unit with direct control
- Unit with indirect control
Unit with Direct Control
Direct control implies that the actuation is carried out by the oil pressure on a single large-spool valve.
Unit with Indirect Control
There are two elements to the indirectly controlled mechanism.
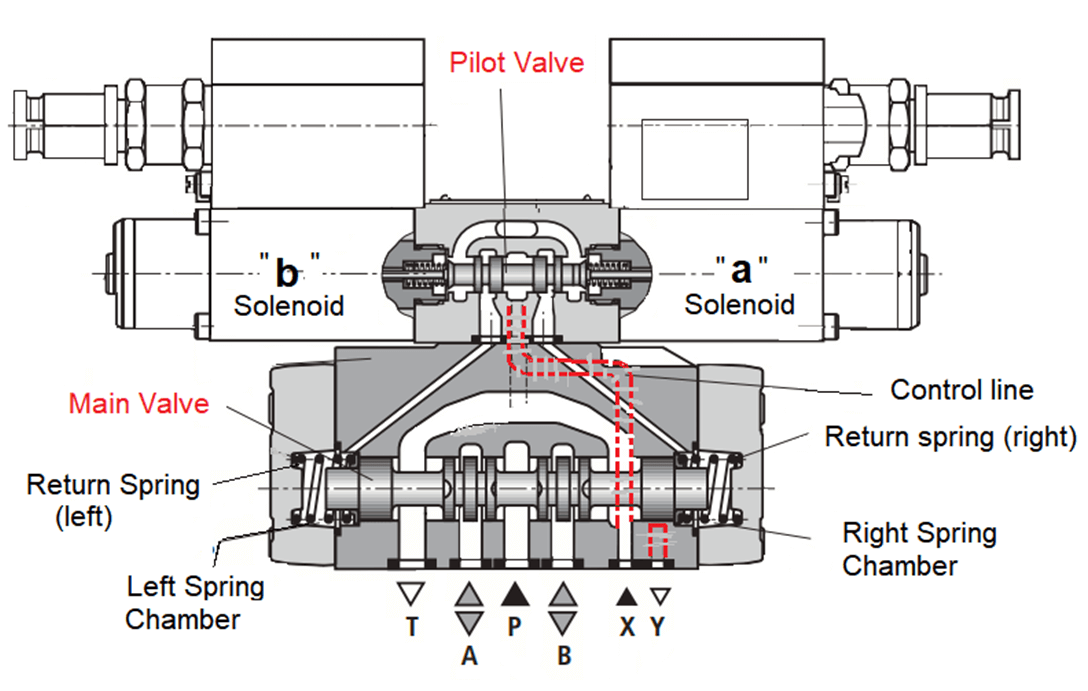
- Directional control valve with one pressure oil control.
- As indicated in the diagram below, one direct-controlled directional control valve, also known as a pilot valve, uses a solenoid as an actuation element.
Solenoids operate the primary valves, which in turn control the 3/2 and 4/2 directional control valves. As a result, these valves are known as pilot valves, whereas the regulated valve is known as the main valve.
Because hydraulic machines operate at moderate to high pressures, larger direct acting control valves may necessitate a greater actuating power.
The main valve spool is operated with oil pressure supplied to the spool by the pilot valve in pilot-controlled directional control valves like this.
FAQs about Pilot Valves
1. What is the purpose of the pilot valve?
A pilot valve is a tiny valve that regulates the flow of a restricted-flow control feed to another piloted valve. This separate valve is usually used to regulate a high-pressure or high-flow supply.
2. How does a pilot-operated pressure-reducing valve work?
A pilot-operated pressure-lowering valve balances the downstream pressure against a pressure adjustment control spring through a pressure sensor pipe. This modulates a control pressure by moving a pilot valve.
3. What is the purpose of the 4-way pilot-operated valves?
The 4-way pilot valves are used to regulate linear and rotary actuators in two directions while also emptying their working lines from a distance. Pilot-operated valves use one or two pilots and a return spring to move their spools.
4. What is the function of a pilot valve in a hydraulic system?
A hydraulic pilot valve is a piece of machinery that manages the operation of the other valves by controlling the high pressure of the hydraulic fluid as it goes through the machine. Pilot-operated valves are extensively utilized in hydraulic machinery.
5. What is the difference between pilot-operated and direct operated?
The major distinction between direct acting and pilot solenoid valves is that direct-acting solenoid valves directly connect to the opening and closing armature. In contrast, pilot-operated valves use the process fluid to help guide the valve’s functioning.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- What is Air Valve? Working Principles & Types (Clear Guide)
- What is Solenoid Valve and How Does It Work? 2022 Guideline
- What is Automatic Expansion Valve: A Basic Guide
- Strainer Valve: a basic guide to know it better
- What Is Actuated Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What Is Linear Valve? With Example, Working Principles & Types
- Valve Manifolds: Working Principles, Function & Diagram
- What is Balancing Valve? Working Principles,Types & Function
- What is Poppet Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What is Manifold Valve? With Function & Types
- What is Drain Valve? Working Principle, Types & Applications
- What are Coaxial Valves? Working Principles and Type
- What is Isolation Valve? Working Principle & Types
- What is Block Valve? Working Principle & Types



