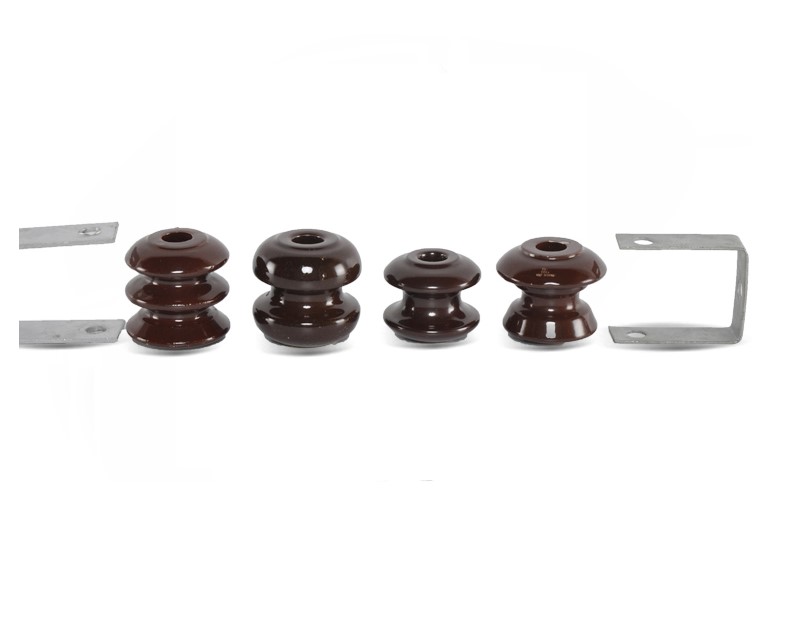
Different types of insulators are used in transmission lines. There are several types available: shackle insulator, pin, strain, guy strain, busing, suspension, solid core line, post, and stay insulators. In the medium to high voltage lines, suspension and strain insulators are used, while stay and shackle insulators are used in low voltage systems. Insulators have vital roles in electrical systems to evade surplus electrical current flow between the earth and the conductors. They are essential pieces of equipment in the power system because of their high resistance.
Types of Insulators
We can name shackle insulator, strain insulator, post insulator, suspension insulator, bushing, line post insulator, pin insulator, station post insulator, and cut-out as the different types of insulators.
Pin Insulator
As the name implies, the pin type insulator is located on a pin on the pole’s cross-arm, and there is a groove on the top end of the insulators. The conductor is arranged in this groove and is fastened to the insulator with tempered wire with the same material as the conductor. Pin type insulators are employed to transmit and distribute communications and electric power with voltages up to 33 kV. Insulators designed to operate at voltages within 33 kV and 69 kV are regularly very big, and using them has become uneconomical in the past years.
Post Type Insulator
This type of insulator is more compact than conventional pin-type insulators and, in the late 1930s, have rapidly replaced many pin-type insulators on systems with voltages up to 69 kV. We can use them to perform at up to 115 kV in some configurations.
Suspension Insulator
If the voltages are higher than 33 kV, it is common to use suspension type insulators. A suspension insulator includes many porcelain or glass discs connected by metal links in a series and a string. There is the suspended conductor at the bottom head of the string, while the top end is connected to the cross-arm of the tower. Based on the voltage, the number of disc assemblies can vary.
Strain Insulator
There are towers, dead-ends or anchor poles while a straight section of line ends or angles off in another direction. These poles must maintain the horizontal (lateral) force of the long straight part of the wire. For withstanding this lateral force, strain insulators are employed. Shackle insulators can be utilized in low voltage lines for less than 11 kV as strain insulators. But, in high voltage transmission lines, suspension insulators (strings of cap-and-pin) are employed and in a horizontal direction connected to the cross-arm. In some cases, such as long river spans, the tension in lines is very high, and we should manage two or more strings in parallel.
Shackle Insulator
Engineers used shackle insulators rather than strain insulators in the earlier days. But in current years, they are commonly used for low voltage distribution systems. We can utilize these insulators in both vertical or horizontal position. They can be attached to the pole with a bolt or to the cross arm directly.

What is Shackle Insulator?
The type of insulators used in low voltage distribution networks is known as a shackle insulator. People know shackle insulator as spool insulator too. We can use these types of insulators to operate in both two positions of horizontal or vertical. Today, they are less used in the transmission lines because of using the underground cables for distribution purposes.
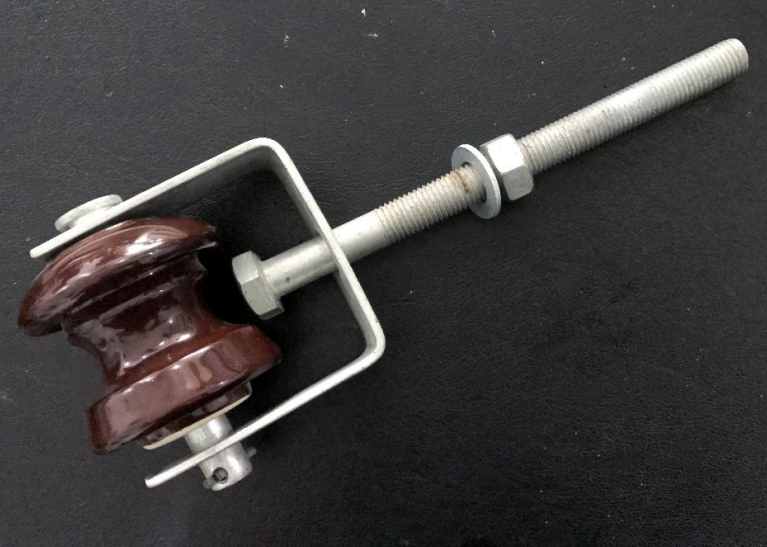
The shackle insulator’s tapered hole distributes the load force more consistently and also decreases the chance of fracture once loaded heavily. The shackle insulator holds a conductor within the groove while it is fixed using a soft binding wire.
Parts of Shackle Insulator
The shackle insulator is round-shaped and includes a hole in the middle for bolting. A wide galvanized plate is prepared at both sides of the shackle insulator. The conductor is fastened within the channel and is adjusted by utilizing soft binding wires. These insulators are efficient compared to the strain insulators when we have a changing direction, and the distribution line alters its angle.
Usually, we have shackle insulators in three various sizes such as 100 mm x 115 mm, 75 mm x 90 mm, and 50 mm x 65 mm. Commonly, the 100 mm x 115 mm and 75 mm x 90 mm sizes of shackle insulators are appropriate for main lines. In contrast, the 50 mm x 65 mm size insulator is employed in houses to provide low voltage power.
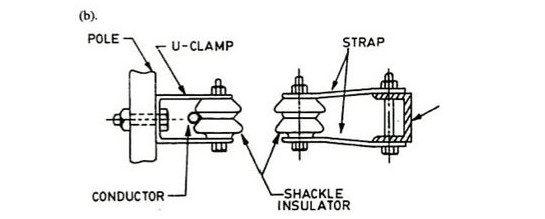
Shackle Insulator Working
A cover should be prepared on the surface of this insulator to prevent flowing water through it. The common raw material using in this insulator is porcelain or aluminum silicate (Al2SiO5). This material is mixed with plastic kaolin, feldspar and quartz to get the last porcelain shackle insulator material.
As mentioned before, the tapered hole in the insulator helps to distribute the load more uniformly to reduce the chance of breakage once intensely is loaded. The conductor inside the groove can be set by using the soft binding wire.
Applications of Shackle Insulators
We can use shackle insulators in the following applications:
- They can be used in a distribution system by designing based on the towers and conductors to insulate and support.
- They can be used in overhead lines with medium and low voltages.
- This insulator is employed with a bolt by installing on the pole otherwise telegraph to evade outflow current from conductors.
- We can use them in both positions of horizontal and vertical.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Shackle Insulator
Advantages and disadvantages of shackle insulators are:
- These are highly dependable to conductors.
- These can easily be designed to satisfy the requirements of electricity.
- These can be employed in vertical applications as well as horizontal settings.
- Porcelain shackles Insulators can bear high current and temperature.
- The most satisfactory solution for securing protection in different electrical apparatuses is this type.
- These are appropriate only for low voltage distribution networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) What is an Insulator?
The material with the property of not flowing current through is called an insulator.
2) What is a Shackle Insulator?
The type of insulator for low voltage distribution lines, in which the conductor is placed inside its groove, is called a shackle insulator.
3) What are the Common Conductors and Insulators?
We can name gold, copper, silver, and aluminum as conductors, while air, plastic, glass, wood, and rubber are examples of insulators.
4) Does the Shackle Insulator Have Another Name?
The other name of the shackle insulator is the spool insulator.
5) Why do We Use an Insulator?
It protects devices by opposing the flow of current.
6) What is the Most Robust Insulator?
Aerogel is known as the strongest insulator.



