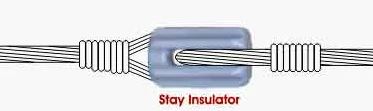
A Stay insulator is a form of low voltage insulators made to counterweight and fasten the dead-end pole by combining stay wire or guy grip. It is also introduced as an egg insulator or stay part. One should choose the suitable forms of stay insulators and pole line fittings to prevent the dead-end pole or terminal pole from falling down. Professional stay insulators have the structure to prevent the electric conduction on the main wire by accident.
What is an Insulator?
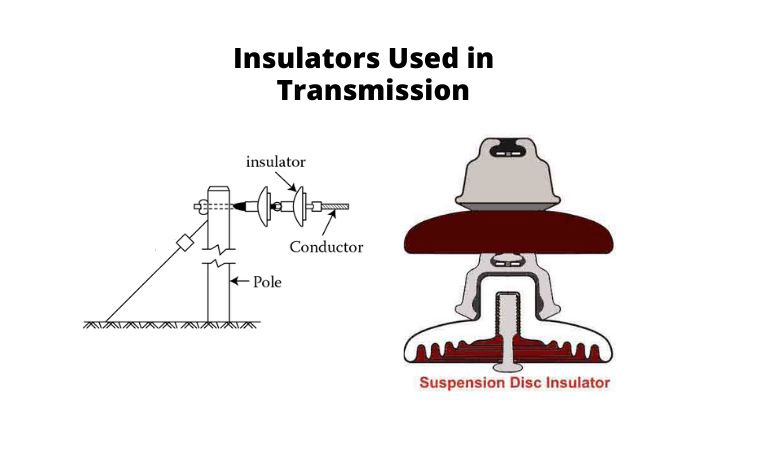
There are various forms of insulators for overhead power lines. All of them are employed for different but related operations. As you know, the main performance of an insulator is to avoid the flow of electric current regions to regions that it is not supposed to go. Shortly, insulators avoid the unwanted moving of electric current.

In a common transmission path, the overhead conductors are supplied by towers and poles. Insulators are placed between the poles to control the current from moving toward the earth.
The main kinds of insulators employed on overhead power lines are:
- Stay insulator
- Strain insulator
- Pin insulator
- Suspension insulator
- Shackle insulator
Different forms of insulators play different roles in an overhead power line configuration. In this post, our focus will be on the stay insulators for a transmission system. Do you want to use them? This guide will be beneficial for you. You can click here to know them fundamentally before we want to explain them completely below.
What is a Stay Insulator?
Stay insulators are a form of insulators that are utilized on the stay path. They are modeled to supply insulation in case the wire cuts and falls on the ground. The stay insulator will guarantee that the wires don’t contact the ground.
Knowing the performance of a stay insulator is important. There are some holes in the body of the stay insulator. The two pieces guy grips go through from the body in the opposite path. The guy grip will wrap the main wire to create the connection. The connection path isn’t confirmed. For different types, there are various ways to connect, and any manufacturer can make the insulator fittings according to the customers’ requirements and application.
The importance of the stay insulator is commonly witnessed once the poles fall on the ground or when the main wires accidentally cut because of the excess mechanical load. It is among the most suitable insulators for overhead transmission lines that you should install. The stay type insulator is normally installed in the middle of the stay path. In the case the pole fails, the insulator will ensure that the lower part of the system will have no voltage.
How Does a Stay Insulator Work?
A usual stay insulator has two holes that are placed on opposite sides of each other. Pieces of stay wires enter within one hole and exit through the other. Guy wires are employed to support the grip and ensure that there is a complete connection between the stay insulator and stay wire.
So, what happens when the wires find themselves on the ground? Let’s say the tower or pole fails and everything breaks. The wires will be completely insulated and No voltage will go to the earth.
A dead-end or anchor tower or pole is employed where a straight sector of line ends or angles off in another direction. These poles should tolerate the lateral (horizontal) tension of the long straight sector of wire. In order to withstand this lateral load, some strain insulators are used. Shackle insulators are also employed as strain insulators for low voltage lines (less than 11 kV). Although for high voltage transmission systems, strings of cap-and-pin or disc insulators are employed, joined with the cross-arm horizontally. Once the tension load in lines is extremely high, two or more strings are employed in a parallel configuration (such as a long river span).
The stays are to be insulated from the ground at a certain height for low voltage lines. The insulator applied in the stay wire is known as the stay insulator and is commonly made of porcelain and is so modeled that in case of cut-off of the insulator, the main wire will not fall to the ground.
Stay Insulator Material
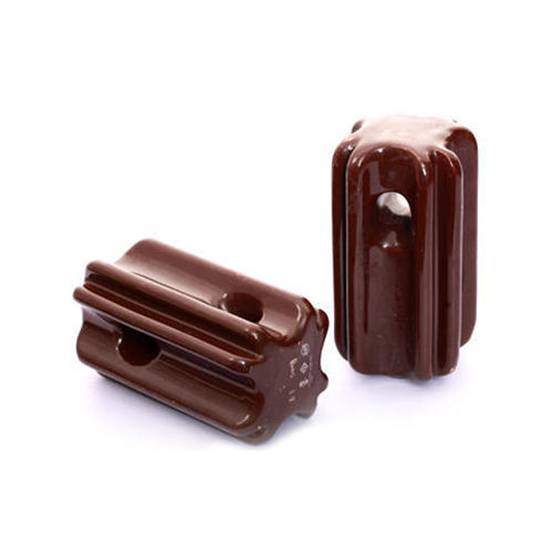

What is a Stay Insulator Made of?
Porcelain is the basic material that is employed to construct stay insulators for overhead transmission systems. Porcelain is chosen since it has appropriate physical and chemical features.
Why is Porcelain Used for Stay Insulator?
Obviously, there are other substances that can be used to produce stay insulators. Here are the top reasons which make most insulator manufacturers employ porcelain.
- Porcelain has mechanical and physical strength. Fundamentally, porcelain material is physically strong to control the weight and tension of the conductors. Its heavy mechanical strength also means that it can tolerate different vagaries of nature.
- A good insulator should supply adequate resistance to electricity and Porcelain material has high insulation resistance. This feature means that there will be no leakage of the electricity to the ground.
- Porcelain has great dielectric strength. As a result, with a large dielectric strength, a porcelain insulator can withstand high voltage load and voltage stress.
- Porcelain is impervious. It should be noted that a stay insulator is installed outside. So, it is probably to be exposed to water and other unwanted liquids. Porcelain is not penetrable hence no liquid can get inside it to face the flow of current. Generally, it can be said that fluids and gases cannot find a simple way into the porcelain.
- Porcelain is resistant to a great temperature change. The electrical and physical characteristics of porcelain material are not influenced by the extreme temperature change. This is because high temperatures can influence the electrical conductivity of a substance. With this feature, it means that a porcelain stay insulator can perform anywhere regardless of the climatic and environmental variations.
- Porcelain is non-reactive to chemical variation. The physical features of a porcelain stay insulator prevent it from simply reacting with chemical changes and other impurities. This is essential since some impurities can influence the conductivity of a wire leading to the leakage of electricity.
In addition to the above features, the stay insulators are appropriately glazed to avoid any traces of water from creating on the surface of the insulator.
So, how can we tell about the property and type of the material applied to stay insulators?
In most applications, stay insulator constructors commonly determine the specifications of the material. They can also determine the dielectric and comprehensive strength of the instrument. The constructor will also specify the tensile strength of the insulating substance.
Stay Insulator Working Principle
An electrical insulator is an instrument in which the electron does not move freely or the atom of the insulator has extremely bound electrons whose internal electricity does not transform easily; very little electric current will move across it under the effect of an electric field.
This contrasts with other substances, conductors, and semiconductors, which conduct an electric current more simply. The feature that highlights an insulator is its strong resistivity; insulators have greater resistivity than conductors or semiconductors. The most usual examples are non-metals.
A complete insulator does not exist since even insulators include small numbers of mobile charges (also known as charge carriers) which can carry electricity. Besides, all insulators become electrically conductive once a sufficiently great voltage is performed that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms.
This is introduced as the breakdown operation of an insulator. Some substances such as paper, glass, and Teflon, which have great resistivity, are very suitable electrical insulators. A much larger class of substances, even though they may have smaller bulk resistivity, are still appropriate enough to control significant current from flowing at normally employed voltages, and thus are used as insulation for electrical cables and wiring. Examples contain rubber-like polymers and most plastics that can be thermoplastic or thermoset naturally.
Insulators are utilized in electrical systems to control and separate electrical conductors without allowing current within themselves. An insulating substance used in bulk to handle electrical cables or other equipment is introduced as an insulation process. The name insulator is also employed more specifically to refer to certain supports used to combine electric energy distribution or transmission systems to utility poles and in-line towers. They tolerate the weight of the suspended wires without permitting the current to flow through the tower to the earth.
Stay Insulator Coating
A very adaptable coating of an insulator is usually applied to the electric cable and wire, this is introduced as the insulated wire. Wires occasionally don’t utilize an insulating coating, just air, because a solid (e.g. plastic) covering may be infeasible. However, wires that contact each other generate short circuits, cross-connections, and fire hazards.
The center conductor should be supported precisely in the middle of the hollow shield in a coaxial cable to handle wave reflections. Eventually, cables that expose voltages greater than 60 V can cause human shocking and electrical hazards. Insulating coatings help to control all of these issues.
Some cables have a mechanical covering with no voltage level (e.g. welding, service-drop, doorbell, and thermostat wire). An insulated cable or wire has a voltage level and a maximum temperature range of the conductor. It may not have an ampacity range (that means current-carrying potential), because this is based on the surrounding conditions (e.g. ambient temperature).
In electronic applications, printed circuit boards are constructed from fiberglass and epoxy plastic. The nonconductive boards provide covers of copper foil conductors. The tiny and delicate active components are embedded in electronic devices through non-conductive phenolic or epoxy plastics, or across the ceramic coatings or baked glass.
The silicon material is typically a conductor because of doping in microelectronic cases such as ICs and transistors. But it can simply be selectively transmitted into a good insulator by the application of oxygen and heat. A typical example of oxidized silicon is the quartz, i.e. silicon dioxide, the basic part of the glass.
In high voltage devices including capacitors and transformers, liquid insulator oil is the common solution employed for preventing arcs. The oil replaces air in the gaps that should support a considerable voltage without electrical cut-off. Other high voltage types of stay insulator materials contain glass or ceramic wire holders, vacuum, gas, and easily placing cables far enough apart to employ air as insulation part.
Purpose of a Stay Insulator
The purpose of a stay insulator is various from other overhead line types since it is employed in guy strain wire of stay arrangement. Some of the main applications include:
- Employed with stay wire to pull them and revise the stay wire and stay configuration together onto the earth.
- Mainly utilized on the guy wire configuration to balance the tensile
- Supporting the insulating between the transmission poles and stay clamps to be insulated from the ground at a particular height.
- Used to handle stay wires from becoming powered from accidentally broken live cables.
- Used in utility pole guy wires to control any voltage on the guy resulted by an electrical failure on the pole from reaching the lower parts accessible to the public.
So, as a type of low voltage insulator, a stay insulator plays an essential role in power systems, and the purpose of stay insulator is too obvious and irreplaceable by other kinds of insulators.
Stay Insulator Price

Just like shackle insulators and other forms of insulators, we need to know the cost of stay insulators. The price of stay insulators is based on various properties and among them are the mechanical, physical, and electrical features of an insulator. The tensile, compressive, and dielectric strength values will identify how much we will pay for a stay insulator.
Stay insulators are also determined according to their voltage. We can use an 11 kV, 15 kV, or even 36 kV stay insulator. Obviously, the capacity of the stay insulator will identify the total price that you will pay. To understand the exact cost of the stay insulator, we should take a step to contact a reliable stay insulator constructor.
Reliable Stay Insulator Constructor

So, where can we buy a high-quality stay insulator? The surest solution is from a reliable stay insulator constructor. The supplier and manufacturer must have adequate resources and potential to provide the most appropriate stay insulators for overhead systems.
We must also check to see what other consumers are saying about the stay insulators from a certain constructor. This is feasible by reading the reviews about stay insulators.
But what if we want the main characteristics of the stay insulators to suit our stay wires? In this case, we simply require to tell the constructors and they will design custom type of stay insulator fittings according to our applications and designs.