The hype around renewable power generation and going green grows every day, and with wind energy being one of the important renewable energy sources, a question might come to light: What is a wind turbine? Well, wind turbines come in different designs and different sizes, and each is suitable for its specific application. What we intend to do in this post is to provide e simple answer to the question of “what is wind turbine”.
Additionally, here at Linquip, we have also provided our customers with a convenient platform for finding the right wind turbine, purchasing it, and receive technical consultation.
What is wind turbine?
The law of conservation of energy states that no energy is generated or destroyed and it only converts from one form to another. So, when we talk about wind turbines, we are talking about converting the wind (kinetic) energy into electrical energy. Now, what is a wind turbine? A wind turbine is a device that generates electrical energy from rotation of its shaft, which itself is induced by rotation of some compartment that moves as air stream passes over it. This compartment is the rotor of the wind turbine.
Depending on the application, wind turbines come in various sizes. The small-sized wind turbines can be used for domestic power sources, the bigger ones for back-up electrical power sources of industrial facilities, and the biggest ones are used for large scale power generation in wind farms.
Why using wind turbines?
The demand for energy rises every day, and with all the environmental issues the world is facing today including global warming and air pollution, it is not wise to still be solely reliant on the conventional hydrocarbon power sources. Therefore, the need for green and renewable sources of energy is growing at a fast speed.

One of the most important sources of green and renewable energy is the wind. Wind blows everywhere in the world, and there are so many spots where it can be actually utilized to generate power from small scales used for homes to industrial ones as well as feeding the power grids of towns and cities.
In many places the government actually supports citizens if they could and decided to switch to renewable sources of energy. Moreover, without the need to pay for the electric bills is an interesting motivation to consider wind turbines for many applications.
What Is Wind Turbine? – Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
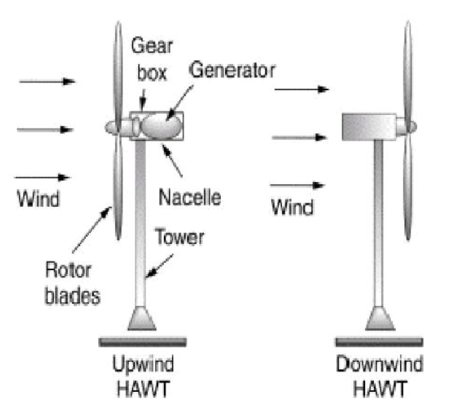
To answer the question of “what is wind turbine” more completely, apart from what has already been mentioned, one must say that wind turbines come in two different designs, one of which is called the Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine (HAWT).

In this configuration, there are rotors installed on a shaft also called collectively as the turbine. There is an electrical power generator coupled with the turbine via the shaft. This way, as the rotors rotate, the kinetic energy of the wind is converted to electrical energy at the generator.
The reason this design is called horizontal axis is that the rotating shaft axis is placed horizontally. The most conventional design of HAWT is one for which the turbine/generator set is taken to a height at the top of the turbine tower, and the rotors are configured in a way that looks like a giant airplane propeller installed at the top of a tower instead of an aircraft wing.
There is also a wind sensor on the large-sized versions of these wind turbines that adjusts the facing direction of the rotors along to the path of the wind using a servomotor. The smaller wind turbines might use other configurations such as wind vanes to redirect the air.
The mechanical coupling of the turbine shaft and the generator is usually done via a gearbox, which bears the responsibility of converting the slower rotation of the turbine rotor to a higher rotating speed at the generator. There are also direct-drive designs that do not have any gearboxes. These gearless turbines make use of permanent magnets instead of gearboxes for generator speed adjustment. They are more expensive than their geared counterparts, but require a lot less maintenance costs structural fatigue and reliability issues of geared wind turbines.
The most common and standard design of HAWT is the three-blade design. However, single-bladed and two-blade design are also available as well as rotors with as many as twelve blades. The three-blade design is more stable and is less prone to torque ripple. Torque ripple is a phenomenon in many electric motor designs referring to periodic ups and downs of their output torque as the turbine rotates.
The rotors are mostly installed upwind, which means before the air blows past the tower and its flow field is affected by the structure. The are also downwind designs which have their own advantages such as their lack of need for alignment with the wind. They are, however, prone to turbine damage due to load changes on the turbine blades.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the advantages of horizontal axis wind turbines is their ability to handle higher wind speeds than the other wind turbine design. Their downwind configuration does not require a yaw mechanism to place the turbine inline with the wind direction and could weigh less due to having variable-pitch blades.
The disadvantages however include the requirement for a yawing mechanism for the common upwind designs and structural fatigue for the downwind configuration due to flow field passed the mast. They also require tall masts and are inefficient near the ground. Another disadvantage of this design is the necessity for large spaces between each turbine due to having normally aligned wind streamlines for each unit of the wind turbine.
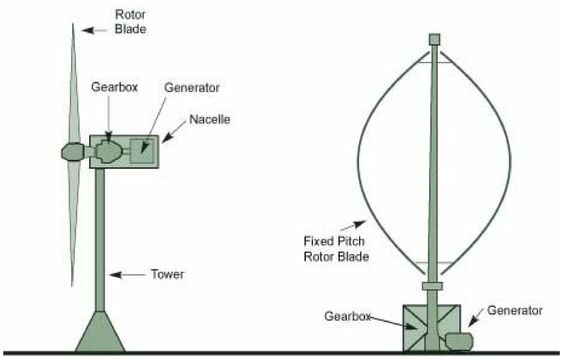
What Is Wind Turbine? – Vertical Axis Wind Turbine
The complementary answer to the question of “what is wind turbine” is the other of the two designs of wind turbines called the Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT).
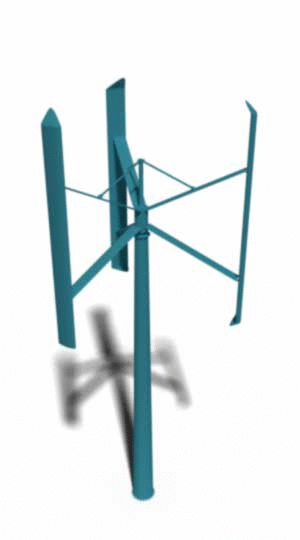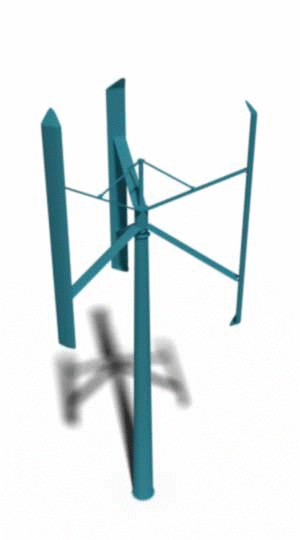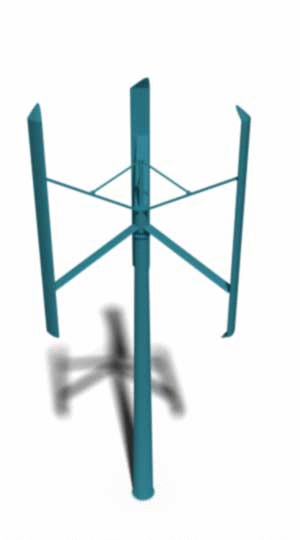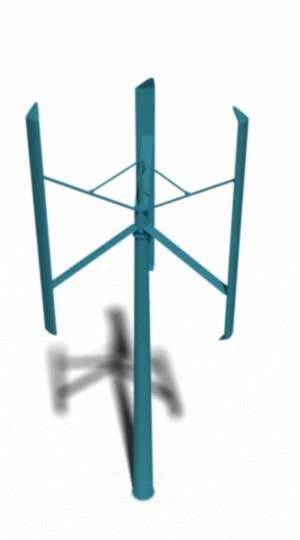
In these designs, the rotating shaft is vertically installed which means it is perpendicular to the direction of the wind and the ground. There are also some other designs that .
In any ways, due to the nature of this design, there is no need for any wind sensors or yawing mechanism to align the rotors with the wind directions. The design also allows for less structure heights, which makes them suitable options for being installed on the rooftops for small scale power generation. The design also allows for an easier service and repair dues to the fact that the gearbox and generator are placed near the ground.
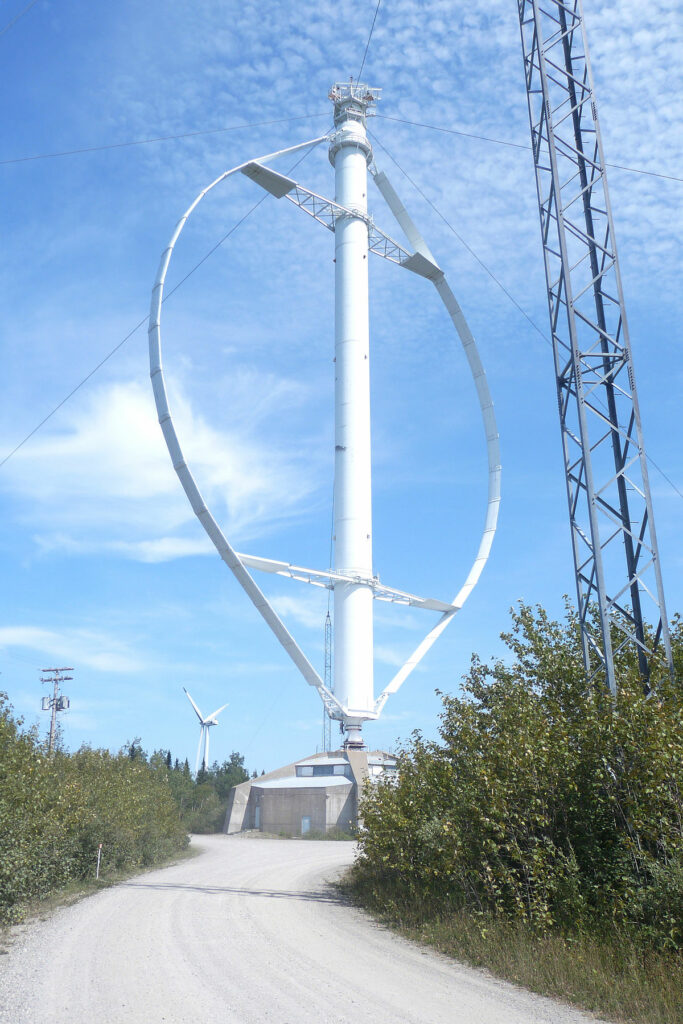

Despite all the advantages, due to having less power outputs and the resilience this design against high wind speeds, horizontal axis wind turbines are more commonly used for power generation that vertical axis wind turbines.
Advantages and disadvantages
One of the advantages of VAWT over HAWT, as already mentioned, is that they do not require any yawing and wind direction sensing or even pitch varying mechanism, and they work with the wind coming from all directions, so are the best choice for places where the wind direction changes frequently and significantly. Their design also allows for a better performance in turbulent winds.
As already mentioned, their gearbox and generator maintenance and repair are also easier and a lot less costly since they are closer to the ground. Moreover, their design allows for less space required between each two VAWT, which means possibly a more power generation level per unit of area. In some creative installations, VAWTs are installed below the existing HAWTs as supplementary power generation units.
The most important disadvantage of vertical axis wind turbines is their significant torque ripple for many of the designs due to dynamic stall of blades following the quick alteration of their angle of attack. Due this situation, the blades are also more prone to structural fatigue for more conventional designs.
“What is wind turbine”-related Q&A
-
- What is the required wind speed for a wind turbine to work?
Those wind turbines that are connected to the power grid require an annular wind speed of roughly 26 mph (12 m/s) to 30 mph (13 m/s) to operate at their rated capacity, but wind speeds as low as 11 mph (5 m/s) start the power generation process as well. Lower wind speeds of as low as 7 mph (3 m/s) might be enough for smaller applications.
- What is the typical size of a wind turbine?
The rotors length (excluding the hub radius) usually range between 70 ft to 260 ft (20 m to 80 m) for HAWT, which are the most common wind turbines. However, the longest rotor designs belong to GE Haliade-X (351 ft or 107 m) and Siemens Gamesa 14-222 DD (354 ft or 108 m).
The turbine masts would usually range between 213 ft (65 m) to 394 ft (120 m) with the tallest mast belonging again to Haliade-X and SG 14-222 DD being approximately 492 ft (150 m).
- What is the power output of wind turbines?
The power output usually range from as low as 100 KW to 8MW offshore wind turbines. Éole is currently the largest VAWT with the output of 10 MW and the output of SG 14-222 DD is 14 MW which could be raised to 15 MW with Power Boost.
- What is the RPM on a wind turbine?
HAWTs rotate at a speed of 10 to 22 revolutions per minute (rpm) because of their large rotors. VAWTs however have higher RPMs such as 100 and higher.
- What is the typical lifespan of wind turbines?
Wind turbines are usually designed to operate around 120,000 hours (20 – 25 years), but the gear box lifespan is about 1.5 years and need to be replaced.
- What is the typical cost of a wind turbine?
Home applications require wind turbine units that usually cost around $10K to $15K. However, for a wind turbine every feet of the tower costs around $500 and every kilowatt electrical power installed costs around $1000.
To see a short video answering “what is wind turbine?” and “how does wind turbine work?” click here.
Buy Equipment or Ask for a Service
By using Linquip RFQ Service, you can expect to receive quotations from various suppliers across multiple industries and regions.
Click Here to Request a Quotation From Suppliers and Service Providers
Read More on Linquip
- Wind Energy Advantages and Disadvantages Fully Explained
- The 8 Best Home Wind Turbines
- Types of Wind Turbines: The Quick and Easy Intro
- Efficiency of Wind Turbines
- How Fast Does a Wind Turbine Spin? The Surprising Answer
- What Is Solar Farms? All You Need to Know About Solar Parks
- What is Propeller Turbine? Types and Working Principles
- What are Floating Wind Turbines?
- Top Wind Turbine Manufacturers In India (Comprehensive Guide)
- What is Distributed Generation? (Clear Guide) + PDF
- Why Is Wind Energy Considered A Renewable Resource?