Motors
A motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works by using the interaction between a magnetic field and an electric current. Motors are used in a wide range of applications, from powering small devices such as electric razors and toys to driving large industrial machinery.
There are several types of motors, including:
- DC motors: They operate on direct current (DC) and are classified into two types; brushed and brushless.
- AC motors: They operate on alternating current (AC) and are classified into three types; induction, synchronous, and stepper.
- Servo motors: These are a type of DC or AC motor that is used in applications that require precise control of speed and position.
- Linear motors: These motors convert electrical energy into linear motion, rather than rotary motion.
- Hybrid motors: These motors combine two or more of the above types of motors.
Each type of motor has its own unique characteristics and is suited to different types of applications. For example, DC motors are often used in small, portable devices because they are inexpensive and easy to control. AC motors are commonly used in industrial applications because they can handle large loads and operate at high speeds. Servo motors are used in applications that require precise control of position and speed, such as robotics and automation. At Linquip you can find the verified list of motor manufacturers, suppliers, and service providers which helps you to find the best solution for your needs.
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteMotors Subcategories
Top Companies in Motors
+779 Companies in Motors
Top Devices in Motors
Related RFQs
AC Motor
LNQ-23081181
AC Motors category
LNQ-23081134
Large Induction Motors
LNQ-23021040
Electric Motors category
LNQ-23011340
Worm Geared Motors
LNQ-22121256
FQD COMPACT ASYNCHRONOUS MOTORS
LNQ-22121165
SIMOTICS SD Severe Duty motors
LNQ-22121102
Large AC Synchronous Motors
LNQ-22111137

What is Industrial Motor?
An industrial motor is an electric motor to modify electricity into mechanical energy. Motors produce forces, including linear or rotary. They are typically powered by alternating current (AC) resources such as power grids or generators; however, some of them may be supplied by direct current (DC) resources like batteries. How vital are industrial motors? Beyond imagination. All new industries utilize one of them.
They are used in various applications such as blowers, industrial fans, machine tools, pumps, power tools, compressors, turbines, rolling mills, alternators, ships, movers, paper mills, and other particular ones. Their special types can also be used in highly corrosive environments like nuclear power plants and highly aggressive applications, including corrosive materials and gases.
Types of Industrial Motors
Motors and especially Industrial Motors have different types based on various characteristics and definitions. There are several classifications for them: DC motors, AC motors, universal motors, and Induction motors. Modern industries must set up some kinds of motor to drive force across their production line. New technologies provide a wide variety of industrial motors for different usages.
- DC, AC & Universal Motors
DC motors cannot operate if they are powered with AC force and vise versa. However, Universal motors can run when powered with either AC or DC. The properties of motors change with the type of application they are anticipated to supply and the nature of their goal. For instance, procedures such as steep/sudden starts, constant torque, and frequent start/stops should be meet some requirements in the selection of the right motor.
- Induction Motors
The most popular of all types of industrial motors that are employed in modern industries is the Induction Motor. It has a particular power derived from the stator. When voltage is applied in the rotor with no need for brushes, this can create an electromagnetic field generating rotation through the armature. Nevertheless, the rotor requires to move slower than the magnetic field to exist the induced voltage practically. As a result, the induction motor is much slower than a universal motor. The windings placed in the stator can determine the motor’s speed.
An induction motor utilizes some magnets to generate mechanical energy from electricity. This energy can move the axle of the motor. Induction motors are employed typically in different industries, and the most common types are the single-phase and the 3-phase.
Parts of Motor
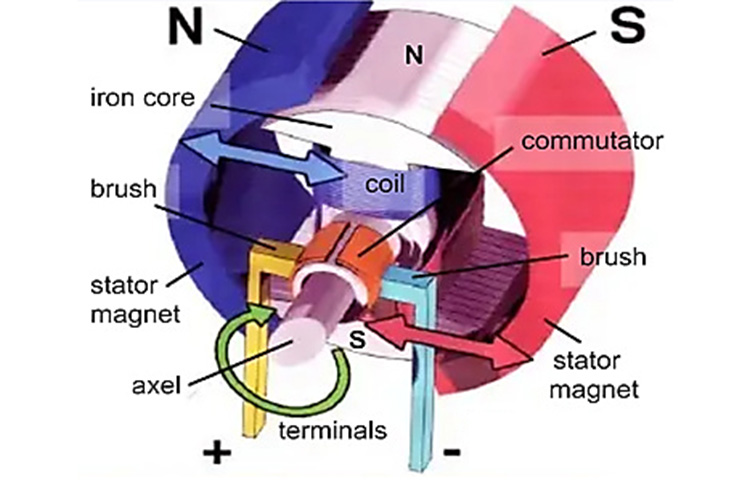
The essential parts of the motor are described below:
- Armature
The armature or rotor is the moving part of the industrial motor, which rotates the shaft to produce mechanical power. It normally has some conductors to move currents through the stator's magnetic field to produce a force rotating the shaft. It is typically in the center of the engine and moves when the poles are induced.
- Stator
The torque or ability of the motor is specified by the features of the electromagnet's wire in the stator. It is the middle section of the electromagnetic circuit and has a core with a few metal sheets to decrease energy usage.
- Air Gap
The air gap between the rotor and stator is one important part of an industrial motor because it can increase the produced current and is too crucial to improve the performance. Nonetheless, this gap must be as little as possible.
- Winding or "Coil"
Windings are particular wires that are circulated around a soft iron core with magnetic properties to produce electromagnetic energy. This wire should be insulated and is commonly copper due to its conductive characteristics. Aluminum may be employed but should be thicker.
- Commutator
A commutator is the switching process which makes the reversal of electrical power and applies it to the rotor. The motor stops without this current reversal. The commutator usually is constructed from slip ring segments that are separated from the shaft of the motor.
How a Motor works
The particular conductor is located in a magnetic field and produces a mechanical power according to Flemings’ left-hand principle. The force influences the coil, which rotates it non-stop when a rectangular coil is in the magnetic field, and a current flows through it. The two sections of the wire in the core are attached to the commutator. These two conductors are insulated by some strips.
In addition, two brushes are employed to attach the commutator to terminals. When the electrical terminals are combined with an appropriate battery, the electricity will pass within the coil. The top section of the rotor is alternated by the north pole and induced to the south part of the stator. Likewise, the bottom of the rotor is induced by the south pole and attracted to the north section, and these magnetic fields all joined together to rotate the rotor clockwise.
The electricity passes through the system in the opposite line and the poles are reversed when the brushes have direct contact with the other section of the commutator. So, the poles are induced by the opposite parts of the stator, and the rotor will rotate clockwise continuously.
Industrial Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers
Industrial Motor Manufacturers and Suppliers are presented below based on the "Electric Motors Global Market Report 2020". The worth of the global market was $106.9 billion in 2019. It is anticipated to improve at a CAGR of 7.57% and become $143.2 billion by 2023.
This report includes market shares, global features, segmentation, size and growth, regional and country drawbacks, trends, competitive landscape, and strategies for this market. It also covers the market's historic and forecast growth by geographical matters. For example, this report explains that North America was the greatest location in the motor production market in 2019. This market is anticipated to gain the largest CAGR during 2019-2023 in Asia-Pacific.
The development of the motor production market is anticipated according to the increasing applications of using them, such as rising disposable income, improvement the electrification, and rapid urbanization. For example, the total appliances manufacturing market is anticipated to increase from $283.8 billion in 2019 to about $396.2 billion in 2022. This will become the main reason for the growth of the industrial motors market in the next years.
- Great Suppliers of Industrial Motors
Here, we present some major players in this market. For example, ARC Systems, ABB Ltd., Brook Crompton UK Ltd. Asmo Co., Regal Beloit Corporation, Emerson Electric Co., Rockwell Automation Inc., Siemens AG, Ametek Co., and Baldor Electric Co. are some of the main industries providing new technologies for motors’ manufacturing.
Autotrol's motors are popular for stability, design, and service. Their productions contain AC and DC motors, electric gear motors, stepper motors, permanent magnet motors, synchronous motors, and custom motors. They are also ISO 9001:2015 certified.
Mamco Corp. is a designer of industrial motors, including DC motors, AC motors, gear motors, and permanent magnet motors. They provide design assistance, quality, and on-time services. They also supply variable speed in motors for particular applications.
Electro-Craft presents appropriate services and modern products. This responsible company has beneficial partnerships and the best relationship between their workers and their customers. They provide the highest standards and quality in 2020 according to the "Electric Motors Global Market Report 2020".
AMETEK is a high-class company providing key methods for the most complex problems due to its unique technological products. Their Advanced Motion Solutions (AMS) part supplies various controllers, drivers, pumps, fans, and custom-designed systems.
Regal Beloit is a global and famous company for its energy efficiency, effective motors, and particular power transmission devices. Their popular productions can be found in generally all household air-conditioning systems in the United States.