
Fuel Pump: Working Principles, Function & Diagram
Carbureted engines frequently have low-pressure mechanical pumps located outside the fuel tank. Electric fuel pumps are commonly found within the tank of fuel-injected engines (and some even have two: one low-pressure/high-volume supply pump in the tank and one high-pressure/low-volume pump on or near the engine). The fuel pressure must be kept below certain limits in order for the engine to work properly. If the fuel pressure is too high, the engine will run rough and rich because it won't use all of the gasoline pumped, making it inefficient and polluting. The engine might misfire, lean, or stall if the pressure is too low.
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteTop Companies in Fuel Pump
Top Devices in Fuel Pump

What is a Fuel Pump?
Carbureted engines typically have low-pressure mechanical pumps mounted outside the fuel tank. In contrast, fuel-injected engines typically have electric fuel pumps (which is a type of industrial pump) mounted inside the tank (and some fuel-injected engines have two fuel pumps: one low-pressure/high-volume supply pump in the tank and one high-pressure/low-volume pump on or relatively close to the engine). The fuel pressure must be within particular limits for the engine to work properly. The engine will run rough and rich if the fuel pressure is too high since it will not consume all of the gasoline being pushed, making the engine inefficient and polluting. The engine may misfire, lean, or stall if the pressure is too low.
The engine does not always require the use of a gasoline pump. A carbureted engine's low-pressure gasoline can be provided simply by raising the tank above the carburetor and allowing gravity to supply the fuel. Carbureted motorbikes, where the tank is normally immediately above the engine, and high-wing airplanes with gasoline tanks in the wings both employ this technology.
Fuel Pump Types
There are two main types of fuel pumps, including Mechanical Fuel Pumps and Electrical Fuel Pumps.
Mechanical Fuel Pumps
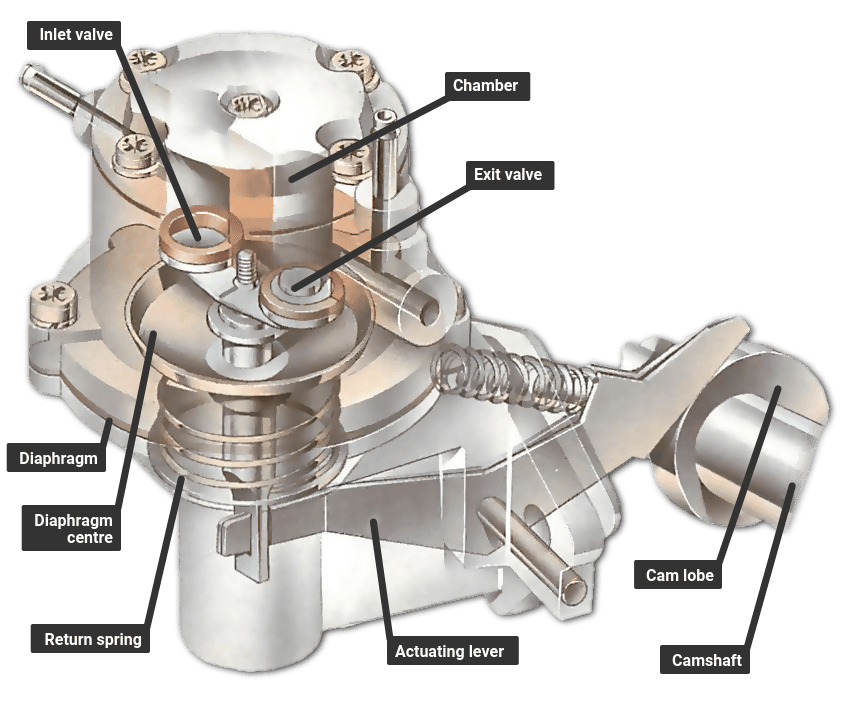
Prior to the widespread use of electronic fuel injection, most gasoline engines relied on mechanical fuel pumps to transport fuel from the fuel tank to the carburetor bowl. The eccentricity of the engine's camshaft drives the mechanical fuel pumps. It is located on the in-line cylinder block engine's side.
The most popular mechanical gasoline pumps are plunger-type and diaphragm pumps. A well-known positive displacement pump is the diaphragm pump. Similar to a piston pump, this pump has a pump chamber whose volume raises or lowers depending on the deflection of the flexible membrane.
Electric Fuel Pump
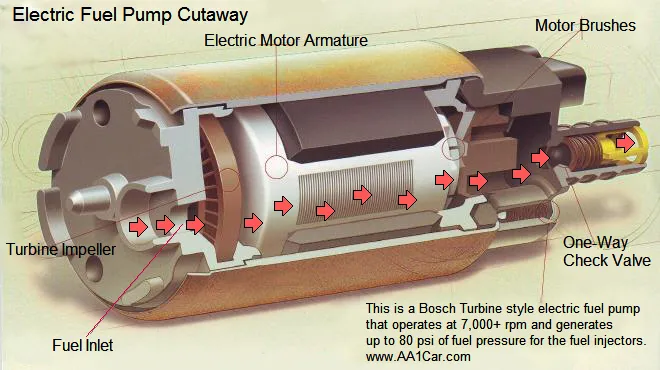
Electric fuel pumps are often used in modern cars' fuel tanks. This pump pumps gasoline/petrol into the engine by creating high pressure in the fuel lines. The boiling point of gasoline increases as pressure rises.
The components that take up the gasoline vapors from the engine (the pump itself) and submerge it in cold liquids are minimized by placing this pump within the fuel chamber.
Another benefit of putting the electric fuel transfer pumps within the fuel chamber is that it reduces the risk of fire. Sparks are generated and fuel vapors are ignited by electric equipment (such as fuel pumps), but liquid fuel does not explode. As a result, one of the most critical locations is to submerge the pump in a fuel chamber.
By replacing the mechanical fuel pump with an electric fuel pump, you may lessen the stress on the engine's components while also lowering the engine's fuel consumption. Similarly, an ECU can track gasoline supply more carefully (electronic control unit). If the pump continues to operate continuously, you can conserve gasoline by turning off the engine with a signal. However, the essential fuel pressure for a quick start is still available.
Fuel Pump Working Principle
A fuel pump is found in almost every contemporary car with an internal combustion engine. Electric pumps are either located within the gasoline tank, or inline pumps are located closer to the engine. You'll have a better knowledge of what occurs when a fuel pump fails if you understand the fundamental operation of the fuel pump. You'll also know how to spot when this happens.
- Your tank's fuel is pulled up via a line that leads to the engine. If you have an electric fuel pump, it is powered by a tiny motor that sucks the fuel from your gas tank up through a line. The pump moves when your camshaft spins in earlier vehicles with mechanical fuel pumps, and fuel is pulled via a line utilizing suction.
- The fuel line transports the gasoline to the carburetor or the cylinder. Depending on your engine, your fuel line will either travel straight to the cylinder or make a pit stop somewhere else.
- Fuel is injected with air in carbureted engines, forming a mixture in the carburetor. The mixture then makes its way to the cylinder.
- Fuel and air do not combine until they reach the cylinder in a fuel-injected engine.
To make a mixture, air is pumped into the fuel. Once the combination is in the cylinder, your automobile engages a variety of different components to make it operate. A spark is provided to the gasoline while it is still in the cylinder.
Another spark is created by your fuel and air combination. The piston compresses the gasoline and air combination within your cylinder, making it more combustible. The piston ignites as it travels and the fuel mixture becomes increasingly compressed.
The crankshaft is now powered by the released energy. You've made your first move. After its useful life, that gasoline has successfully driven your automobile further down the road and is being ejected as exhaust.
There are lots of lesser stages in between those five steps, but it all starts at the gas station. If the gasoline you put in your tank can't get to the point where it can be combined with air, steps two through five won't happen, and you won't be able to go forward.
You can find various Pump Suppliers and Companies in Linquip that can completely cover your requirements. You are also encouraged to visit the List of Fuel Pump Distributors in Linquip.
FAQs about Fuel Pump
- What kills a fuel pump?
Rust, dirt, or debris in the gas tank may swiftly destroy a gasoline pump. Rust develops on older steel tanks, whereas plastic tanks begin to degrade after 8-10 years. The fuel filter nearly completely fails to keep debris out of the fuel pump.
- How many years does a fuel pump last?
Fuel pumps are not serviced on a regular basis and must be replaced only when they fail. The majority of fuel pumps should last for at least 100,000 kilometers.
- What happens if the fuel pump is bad?
Your vehicle's performance and drivability will be severely hampered by a defective fuel pump. If your fuel-to-air ratio is wrong and the cylinders aren't getting enough fuel, the pistons won't fire, and your engine will struggle to propel the car ahead. Your automobile will simply not start if your fuel pump is damaged sufficiently.
- Can you clean a fuel pump?
If your car has an electric fuel pump, you may clear any sediment buildup or obstruction with a fuel system cleaning. You can actually open the pump to remove debris out of its internal filter if you have a manual one (typically seen in earlier model cars), but it isn't an option in most newer vehicles.

