
Submersible Pump: Working Principles, Function & Diagram
A submersible pump (also known as a sub-pump or ESP) is a pump with a hermetically sealed motor that is tightly linked to the pump body. The injected fluid submerges the entire device thoroughly. This type of pump eliminates pump cavitation, which is caused by a significant elevation difference between the pump and the fluid surface. Unlike jet pumps, which utilize air pressure to produce a vacuum, Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface. Submersibles are utilized in heavy oil applications where the motive fluid is hot water, and instead of an electric motor, a hydraulic engine is driven downhole by pressured fluid from the surface. Submersible pumps are preferred for high-demand water systems. On the other hand, Jet pumps are better at draining unwanted ponds and bodies of water. Submersible pumps use less energy than jet pumps since they do not require much electricity to function. Jet pumps demand more maintenance than submersible pumps.
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteTop Companies in Submersible pumps
+44 Companies in Submersible pumps
Top Devices in Submersible pumps
Related RFQs
Drainage Pumps
LNQ-23081098
Vertical pump
LNQ-23011402
submersible pump
LNQ-23011201
Submersible pumps category
LNQ-23011164
HYDRAULIC SUBMERSIBLE SEWAGE/WASTEWATER PUMP
LNQ-23011029
Drainage Pumps
LNQ-22121115
submersible pump
LNQ-22111423
Submersible Pump
LNQ-22111040
Top Submersible pumps Experts

What are Submersible Pumps?
A submersible pump is a type of industrial pump. A submersible pump (also known as a sub pump or an ESP) is a device with a hermetically sealed motor that is tightly linked to the pump body. The whole system is immersed in the pumped fluid. The major benefit of this type of pump is that it eliminates pump cavitation, which is a problem caused by a large elevation difference between the pump and the fluid surface. Submersible pumps, as opposed to jet pumps, which produce a vacuum and rely on air pressure, push fluid to the surface. Submersibles are utilized in heavy oil applications using hot water as the motive fluid, and they utilize pressured fluid from the surface to drive a hydraulic engine downhole rather than an electric motor.
Submersible Pump Working Principle
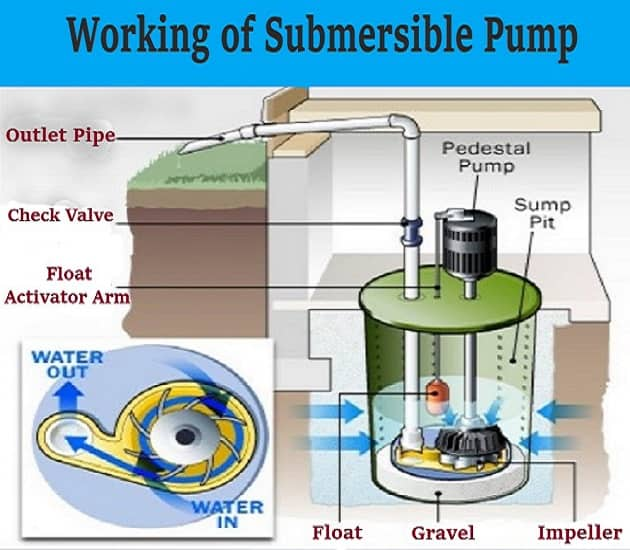
Electric submersible pumps are vertically functioning multistage centrifugal pumps. Liquids that have been driven by the impeller lose kinetic energy in the diffuser, where it is converted to pressure energy. Radial and mixed flow pumps use this as their primary operating mechanism. The motor in the HSP is a hydraulic motor rather than an electrical motor, and it can be a closed cycle (letting the power fluid separate from the generated fluid) or open cycle (maintaining the power fluid separate from the produced fluid) (mingling the power fluid with the produced fluid downhole, with surface separation).
A mechanical coupling at the bottom of the pump connects the pump shaft to the gas separator or protector. Fluids are drawn into the pump via an intake screen and elevated by the pump stages. The radial bearings (bushings) that run the length of the shaft and provide radial support to the pump shaft are among the other components. Although an optional thrust bearing absorbs some of the axial forces generated by the pump, the thrust bearing of the protector absorbs the majority of those forces.
There are also screw-type submersible pumps, which have a steel screw as its operating part. The screw allows the pump to operate in sand-filled water and other mechanical contaminants.
Submersible Pump Applications
Submersible pumps are utilized in a variety of situations. Drainage, sewage pumping, ordinary industrial pumping, and slurry pumping are all applications for single stage pumps. Pond filters are very popular with them. Multiple stage submersible pumps are often dropped down a borehole and are used for water extraction (abstraction) in residential, commercial, municipal, and industrial settings, as well as in water wells and oil wells.
Sewage treatment plants, seawater handling, firefighting (due to the flame retardant cable), water well and deep well drilling, offshore drilling rigs, artificial lifts, mine dewatering, and irrigation systems are among the other applications for submersible pumps.
Pumps used for flammable liquids or water that may be contaminated with combustible liquids in electrically hazardous places must be built to avoid igniting the liquid or fumes.
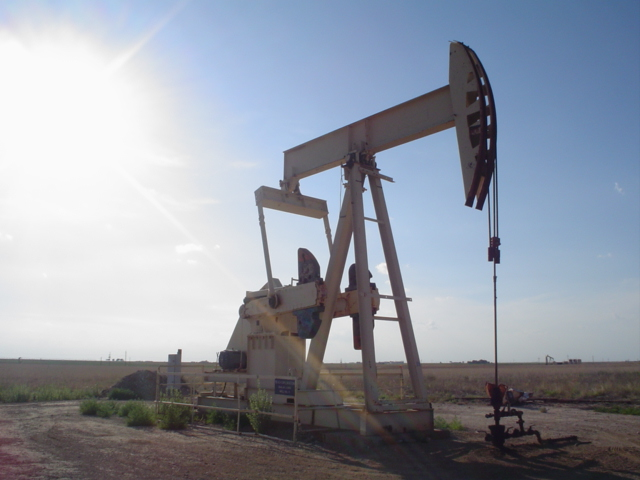

Submersible pumps are employed in oil production to provide a cost-effective kind of "artificial lift" that can handle a wide variety of flow rates and depths. When compared to natural production, much more oil may be obtained by lowering the pressure at the bottom of the well (by decreasing bottom-hole flowing pressure or raising drawdown). Electrical Submersible Pumps (ESP) or Hydraulic Submersible Pumps (HSP) are the two most common types of submersible pumps (HSP).
Surface components (housed in the production facility, such as an oil platform) and sub-surface components make up ESP systems (found in the well hole). The motor controller (typically a variable speed controller), surface wires, and transformers are all surface components. The subsurface components are installed by connecting them to the downhole end of a tubing string at the surface and then lowering them into the well bore with the tubing.
Types of Submersible Pump
Submersible pumps come in a variety of sizes and are used in a variety of tanks and wells. The following are the most well-known varieties of submersible well pumps:
- Deep Well Pump: A submersible well pump transports water from a well to your home or another location.
- Stainless Steel Pump: This type of pump is known as a stainless steel pump because it is fully clad with stainless steel.
- Bottom Suction Pump: Rivers, dewatering, mining, swimming pools, and lakes are all places where these pumps are used. Underneath the pump, they have a guide sleeve.
- Oil Filled Pump: An electric motor submerged in oil drives the oil pump. These pumps are commonly used to provide water to mountain areas, drainage systems, service water, water raising in wells, irrigation of agriculture, hills, and domestic water supply, among other applications.
- Water Cooler Pump: Industrial water cooler pumps, home water cooler pumps, agricultural land irrigation pumps, and other industries all use submersible water cooler pumps.
- Submersible Utility Pump: Drainage, sewage drainage, water solidification pumping stations, sewage treatment, river drainage, and overflow control are all applications for this pump. Its non-clog and large flow qualities make it easier to use.
- Mixed and Axial Flow Pump: A multifunctional and multi-purpose pump is a submersible utility pump. They're known for removing aquarium drainage and troublesome stagnant water from homes and outdoor spaces.
- Crompton Submersible Pump: Cast iron makes up the Crompton submersible pump. It just has one impeller. This pump can handle solids up to 30mm in diameter. It has a stainless steel cable hood.

You can find various Pump Suppliers and Companies in Linquip that can completely cover your requirements.
Parts of a Submersible Pump
The following are the parts of a submersible pump:
- Safety Rope
- Clamps
- Submersible Pump
- Check Valve
- Safety Rope
- Pump cable
- Tank Tees
- Pressure Gauges
- Sediment Filter
- Pressure Switch
- Torque Arrestor
- Drain Valves
- Flow Control Valves
- Impeller
- Ball Valves
- Inlet and Outlet Valve
- Relief Valves
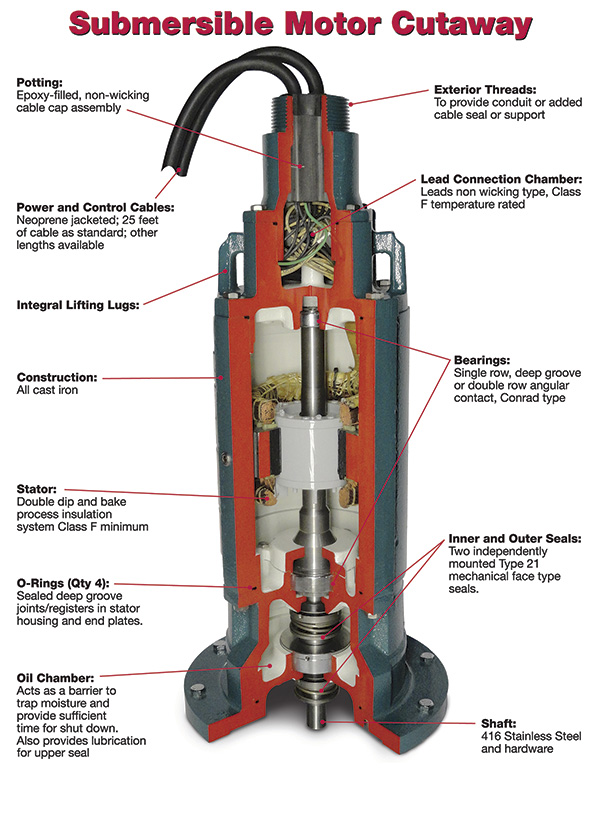
You are also encouraged to visit the List of Submersible Pump Distributors in Linquip.
FAQs about Submersible Pump
- What is the Difference Between Submersible Pump and Water Pump?
The water pump shaft and the motor shaft are the same shafts, the pump and the motor are merged into the water, and the transport medium is water.
- Which is Better Submersible or Jet Pump?
For high-demand water systems, submersible pumps are preferable. Jet pumps, on the other hand, are more effective at draining undesired ponds or bodies of water. Submersible pumps save energy since they do not require as much electricity to operate as jet pumps. Submersible pumps require less maintenance than jet pumps.
- Can Submersible Pump Run Dry?
Some submersible pumps, such as submersible well pumps with plastic impellers, are intended to run dry indefinitely, while others, such as submersible well pumps with plastic impellers, can melt and seize up in less than 15 seconds.
- Is Submersible Pump Better Than Normal Pump?
Submersible pumps are entirely immersed in a clean water supply, as their name implies. They have a variety of benefits over their unprotected counterparts as a result of this. One of the most important features is their efficiency; rather than using energy, water pressure will naturally drive water into a submerged pump.

























