Sectionalizers
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteTop Companies in Sectionalizers
Top Devices in Sectionalizers
Related RFQs
SF6 gas insulated Sectionalizer
LNQ-22011141
Automatic Sectionalizer
LNQ-22011140
The Complete Guide to Sectionalizer
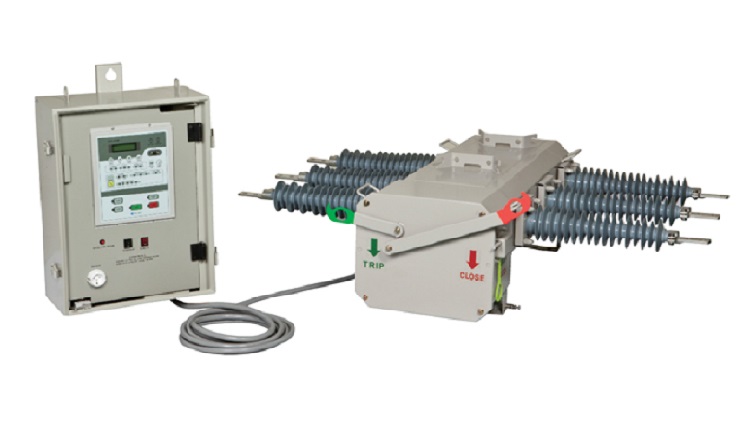

What is a Sectionalizer?
A sectionalizer is a protecting device that automatically isolates a faulted section of line from the rest of the distribution system. A sectionalizer should not be mixed with a recloser; it does not interrupt fault current. It only calculates the number of operations of an interrupting device that supports the circuit, namely a relay-controlled breaker or recloser or back at the substation. After a pre-selected number of current interrupting processes have been "seen", the sectionalizer opens, and the line or feeder on the load side of the sectionalizer is not re-energized.
Sectionalizers do the job of restoring service simpler after a fault has been eliminated since they do not need replaceable components, such as fuse-links, and they may be reclosed with a plain hook stick.
The length of the primary line that each sectionalizer can preserve depends on the value of the loads, lightning probabilities, tree conditions, etc. Normally, sectionalizers can efficiently control up to two or three miles of line. Additionally, reclosers may be used along with distribution feeders as well as the substation. Sectionalizers and line reclosers work together on distribution circuits to ensure higher reliability. Although they look almost the same, their functions are pretty different.
What is Sectionalizer Types and Working Principle?
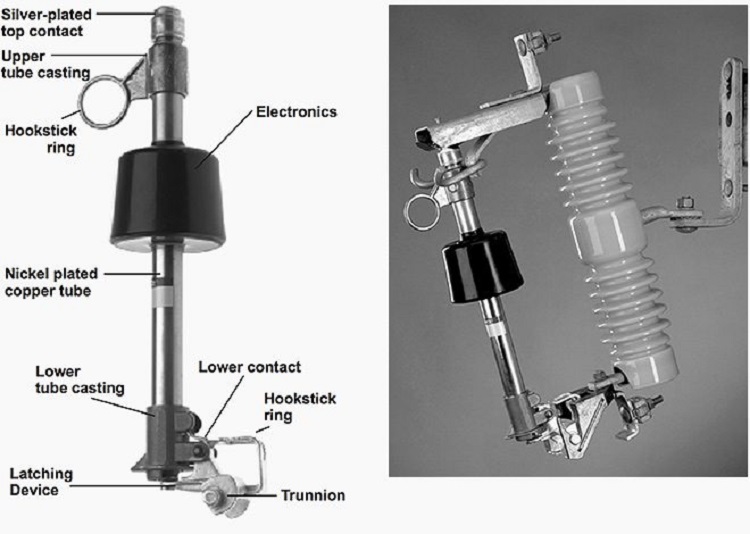
Several types of sectionalizing equipment and various sectionalizing schemes exist on distribution systems. Here, the purpose is to review two of these sectionalizing schemes and the coordination needed between the reclosing relay and the sectionalizing devices.
The pulse-counting sectionalizing scheme employs a downstream line sectionalizer that calculates the number of high current pulses that cross through it. After a predestined number of high current pulses (usually two), it will open on the next voltage loss when the feeder breaker opens.
The sectionalizer resets following a high current pulse if it recognizes no further high current oscillations within its reset time. Accordingly, if decent sectionalizing occurs for a permanent fault beyond the sectionalizer, the auto reclosing time of the reclosing relay associated with the feeder breaker requires to be less than the reset time of the sectionalizer.
The reclosing relay should have one auto reclose effort left after the sectionalizer opens to re-energize the unfaulted division of the circuit. In the scheme shown in the figure below, the auto reclosing sequence of the reclosing relay associated with the feeder breaker is 20 s, 20 s, and then lockout (R20 R20). The downstream sectionalizer is set to calculate two current pulses before opening and has a reset time of 25 s.
A three-phase loop sectionalizing scheme consists of two distribution circuits, each including a normally closed three-phase automatic line recloser and a normally open three-phase recloser as a tie switch placed between the two circuits.
The three-phase line recloser initiates after a 50 s delay for loss of any phase potential on its source side, and the tie switch terminates after a 55 s delay for loss of all three-phase potentials on each side of it. The feeder breaker auto reclosing sequence has to be less than the delayed opening of its connected line recloser for loss of potential.
This enables the feeder breaker to recover the circuit to normal in the event of a quick fault between it and the line recloser. For defects beyond the line recloser, unlike as outlined in the previous example of the current-pulse counting scheme, the overcurrent function of the tie recloser is organized with the three-phase reclosers. It will open the tie recloser, and the feeder breaker will remain closed.
The tie recloser has auto reclosing functions to lockout for overcurrent services; nevertheless, it will not auto reclose for a loss of potential operation and must be closed manually or via SCADA.
What is Sectionalizer Mechanisms?
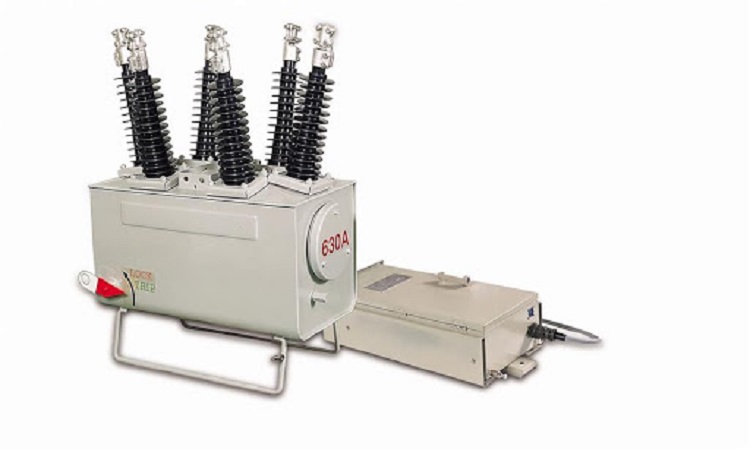

There are two major mechanisms of sectionalizers, namely hydraulic operating and electronic operating mechanisms.
Hydraulic operating mechanisms
Sectionalizers with hydraulic working mechanisms have an operating coil in series with the line. Each time an overcurrent happens, the coil drives a piston that initiates a counting mechanism when the circuit is opened. In this situation, the current is zero by the displacement of oil over the chambers of the sectionalizer.
Following a pre-arranged number of circuit openings, the sectionalizer connections are opened using pre-tensioned springs. This kind of sectionalizer can be blocked manually.
Electronic operating mechanisms
Sectionalizers with electronic working mechanisms are more adaptable in operation and more comfortable to set. The load current is measured utilizing CTs. The secondary current is supplied to a control circuit that calculates the number of operations of the recloser or the associated interrupter and then conveys a tripping signal to the opening mechanism. This sort of sectionalizer is built with manual or motor closing.
What is the Importance Factors to Consider When Selecting a Sectionalizer?
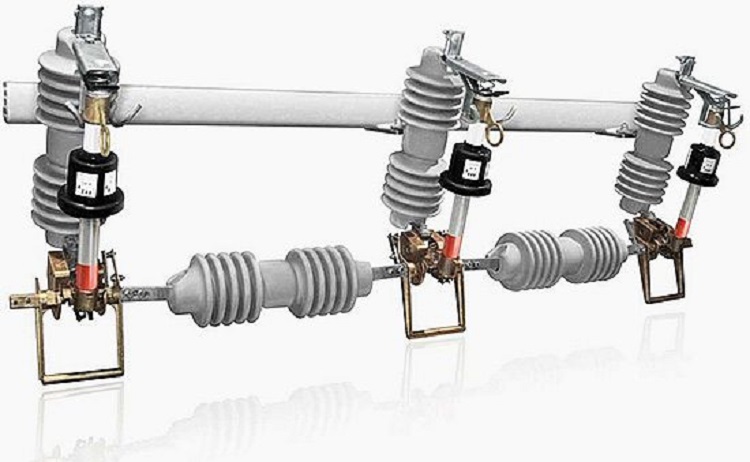

The following factors should be regarded when technically choosing a
- proper sectionalizer:
- The maximum load current.
- System voltage.
- Coordination with protection devices placed upstream and downstream.
- Maximum short-circuit level.
The nominal current and voltage of a sectionalizer should be equivalent to or higher than the maximum values of load or voltage at the point of installation.
The short-circuit capacity of a sectionalizer should be equivalent to or higher than the fault level at the point of connection. The maximum clearance time of the interrupter should not be allowed to pass the short-circuit rating of the sectionalizer.
Coordination factors that require to be taken into account incorporate the number of operations of the interrupter before opening and the starting current setting.