
What is an Air Release Valve? Working Principle & Function
Air Release Valves are frequently put at the highest point of a pipeline to continuously release undesired air in order to protect against unwanted surges and maintain system performance. Air release valves are used to vent trapped air in fluid pipes. Air release valves should ideally be placed at strategic high places in pipes where trapped air can accumulate. The use of air release valves protects and maintains the pipeline system's efficiency. They're ideal for fast releasing huge volumes of air during filling or startup. They also allow air to return into the pipeline while emptying. Negative pressure can cause pipelines to collapse, therefore this is crucial. A properly sized air release valve is essential for an effective, efficient, and safe air control system. The amount of air accumulated in the system is difficult to determine. Occasionally, 2% of the operational water flow rate is recommended based on the 2% solubility of air in water. Determine the maximum differential pressure that will be tolerated across the valve orifice by calculating the required flow.
Need industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteNeed industrial equipment, parts, or services? Submit an RFQ and get quick quotes.
Get a QuoteTop Companies in Air release valve
+6 Companies in Air release valve
Top Devices in Air release valve

VAG Group

VAG Group

VAG Group

VAG Group

VAG Group
Related RFQs
Air release valve category
LNQ-23081125
Vacuum Priming Air Valves
LNQ-23011375
air release valve
LNQ-22111122
air release valve
LNQ-22101548

What Is an Air Release Valve?
One of the most common types of air valves is the Air Release Valve. In addition to small cavities and heavy floats, this device has a leverage apparatus. The air release valve is capable of releasing trapped air with maximum force when all these features work together.
Basics of an Air Release Valve?
Pipes carry water from the source to the target of every irrigation system. It is common for pockets of trapped air to form within these pipelines during this process due to the irregular level of water supply. Water pipelines can become clogged with trapped air, which affects their performance and overall system lifespan.
For this reason, air valves are used. The air release valves help to get rid of trapped air, which allows the water to flow smoothly through the pipelines and the irrigation system to function properly. As the internal pressure builds up inside the water pipe, the air release valve opens up, releasing the air.
Air Release Valves, or Air Relief Valves, are used to release air pockets that accumulate at every high-pressure point in a pipeline. The internal lever mechanism of an air release valve makes the float force greater than the internal pressure, allowing it to open against internal pressure. Any time air pockets gather in the valve; this greater force opens the orifice. Air release valves are necessary to maintain the pipeline efficiency and protect it against water hammer.
There are many air release valve Companies and Manufacturers in Linquip, along with Service Providers.
Working Principle of an Air Release Valve
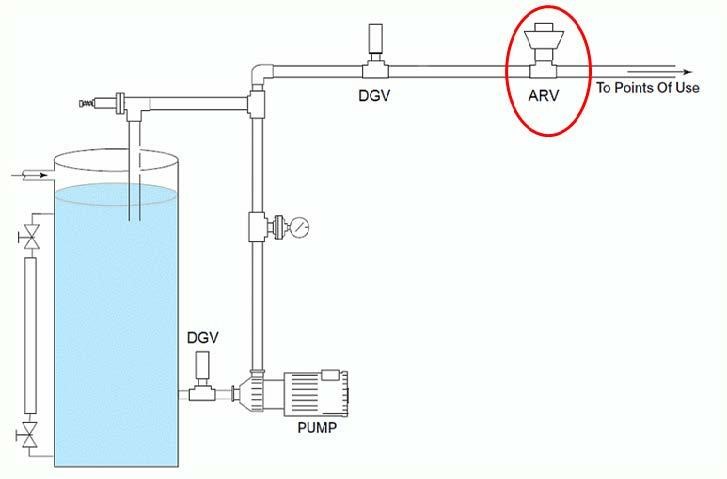
Often, the presence of air in pipelines is not the result of improper installation or supplemental equipment, but rather a failure to properly deaerate the lines.
There are three primary sources of air in pipelines:
● Pipelines aren't technically empty before they may be started; they're filled with air. The air must be evacuated from the pipeline until it is filled with fluid.
● When water is pumped, it contains 2% air by volume. Other fluids, such as adhesives, can trap air in their pockets. During fluid flow, air separates from the fluid and accumulates at high points of the system.
● Through mechanical equipment such as pumps, packings, valves, and pipe joints, air can be drawn into the system.
A pipeline's highest points, where air naturally collects, are equipped with automatic air release valves. When air bubbles enter a valve, they displace liquid inside and lower its level. The float drops when the level drops to a point where it no longer buoys. As a result of this movement, the valve seat is pulled away from the orifice, causing the valve to open and release the accumulated air.
Components of an Air Release Valve
The air release valve consists of the following parts:
Valve Body
It contains the inner floats and upper mechanism inside a compact ductile iron body. The body is designed so that the inlet is completely free of float guides, making it possible to use butterfly valves directly under the air valve without sacrificing performance. A lower 316SS grade tamper-proof drain valve is built into each valve body, making it possible to drain and test the valve safely and quickly.
Inner Float Assemblies
Inner floats are made of bar stock polypropylene, which ensures they never change shape or mass over time. The four guide ribs on the valve body ensure that the floats are all guided squarely to the body, ensuring they do not become offset to the side.
Function of an Air Release Valve
A water or irrigation system is usually equipped with an air release valve to ensure that any entrained air is automatically released in order to maximize the system's efficiency. When air is not properly released from entrapped pockets in pipes, excessive head loss and flow reduction may result.
During pipe drainage, an air release valve is used to maximize the amount of water that exits the pipe while ensuring the pipe is not subjected to vacuum conditions.
During water transfer, it also automatically releases any entrained air that accumulates at the high spots, maximizing the efficiency of the pipeline.
Under column separation conditions or if the pipe is filled at excessive rates, air valves can generate water hammer. By fitting the valves with Rapid Filling Prevention (RFP) designs, the pipe cannot be filled at an uncontrolled rate, preventing the water hammer phenomenon.
Linquip provides a wide selection of air release valves Distributors, Experts, and Equipment for Sale.
Usage of Air Release Valves
A pipe filled with trapped air can lead to pump failure, corrosion, and flow obstruction. It can also result in an increase in energy consumption. Air release valves allow the flow of air within a pipe to be controlled, excess air to be released, and the system to operate efficiently. The valves are installed through pipelines where air naturally accumulates.
Common Applications of Air Release Valves
Air release valves are commonly found in water pipelines and sewer force mains. They are visible at the high points and peaks of the system if they're installed correctly. They might be located slightly downstream or be paired with a vacuum/air combination valve. Any closed-loop system or pressurized pipe that can entrap air is a good candidate for air release valves. Comparatively to other types of air valves, air release valves have small orifices. Therefore, they are best suited for applications with smaller volumes of exhaust air.
Advantages of Air Release Valves

The pipeline system is protected by air release valves, which maintain its efficiency. Venting large volumes of air is easy with these valves during filling or startup. During emptying, they can also let air back in. The importance of this is that some materials may collapse under negative pressure. Air release valves automatically operate when installed.
Disadvantages of Air Release Valves
A pipeline's air release valve cannot always handle the air flow demands if filled or emptied too fast. The valve must be sized appropriately for the application.
FAQ about Air Release Valve
- How Do Air Release Valves Work?
When the system is under pressure, the automatic air release valve enables accumulated air to be let out. When air is present in a water system, it can reduce the effective cross-sectional flow area, which can result in decreased flow and increased head loss.
- What Are Air Release Valves Used for?
A line restriction occurs when air accumulates at high points of the system. Line restrictions increase head loss and increase pumping cycles, which increases energy consumption. Fluid velocity increases as it is forced through a restricted pipe. There is a possibility that the air pocket could break away and be carried downstream as the velocity increases. The result is a water hammer or high-pressure surge.
Pumps, valves, and pipelines can be seriously damaged by pressure surges and water hammer. If air is allowed to accumulate at the high point of the system, this is the most significant effect. The air pocket will continue to grow if not carried away by the velocity of the fluid, resulting in a complete blockage of the flow. By constantly releasing excess air from the system, air release valves ensure smooth and efficient operation.











